Google, Bing, and other alternative search engines are doing their best to reduce spam, provide the most relevant answers, and personalize user experience. That is why semantic search is such a large part of search engines' endeavors to deliver high-quality content that matches a searcher's intent.
To improve these attributes means creating continually evolving algorithms. These more complex algorithms are getting increasingly better at understanding each search query's intent and contextual meaning by using several factors such as a user's location, previous searches, natural language elements, and more.
On the one hand, semantic search helps to return better and more relevant search results. It adds a new layer of complexity to SEO, making it necessary to approach tasks like keyword research and content optimization in new ways.
But if you want to optimize your site for semantic search, you need to understand just what it is and how it works. In this guide, we will specifically look at:
What Is Semantic Search and How Does It Work? Why Is Semantic Search So Important? The History of Semantic Search What Does Semantic Search Mean for SEO? How to Optimize Your Content for Semantic Search Building a Semantic Search StrategyWhat Is Semantic Search and How Does It Work?
It is 2020, and by now, you have probably noticed that Google has gotten pretty good at understanding and answering the questions you ask. It wasn't always that way, but in recent years the search engine has rolled out numerous updates to improve the understanding behind the intent of a query that is typed into the search engine.
In simple terms, semantic search was created to better understand search intent through a search query's contextual meaning.
Semantic search drives an enhanced level of understanding behind the meaning of search queries (let's not forget that 15% of searches have never been made before), returning results that are both more relevant but also personalized.
In short, the main thing to understand that semantic search uses the intent, query context, and the relationships between words to produce the most accurate search results.
Semantic Search: An Example
Let's run a search for "boy who lives in a cupboard under the stairs."
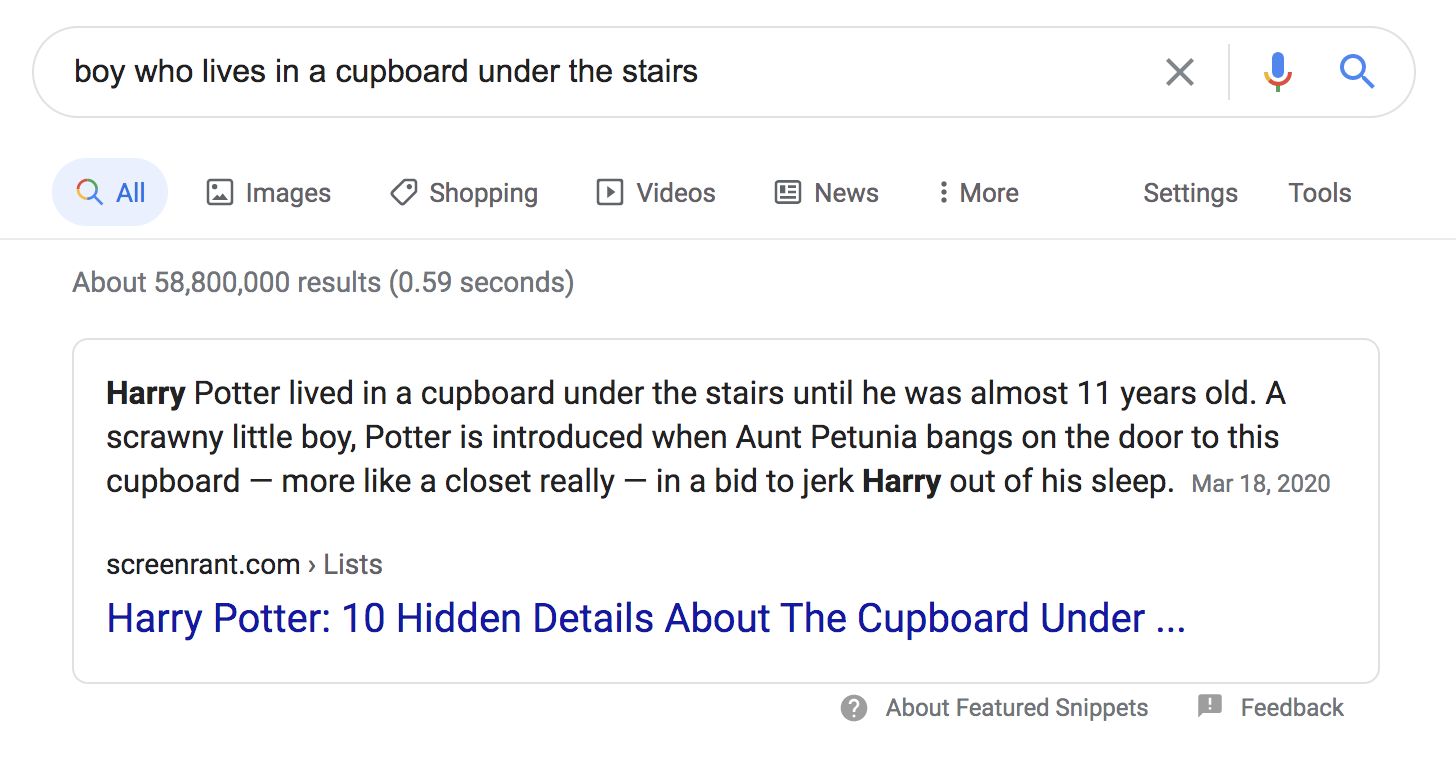
Google, of course, knows that you mean Harry Potter.
But how? Let's break down what is happening when you run this search.
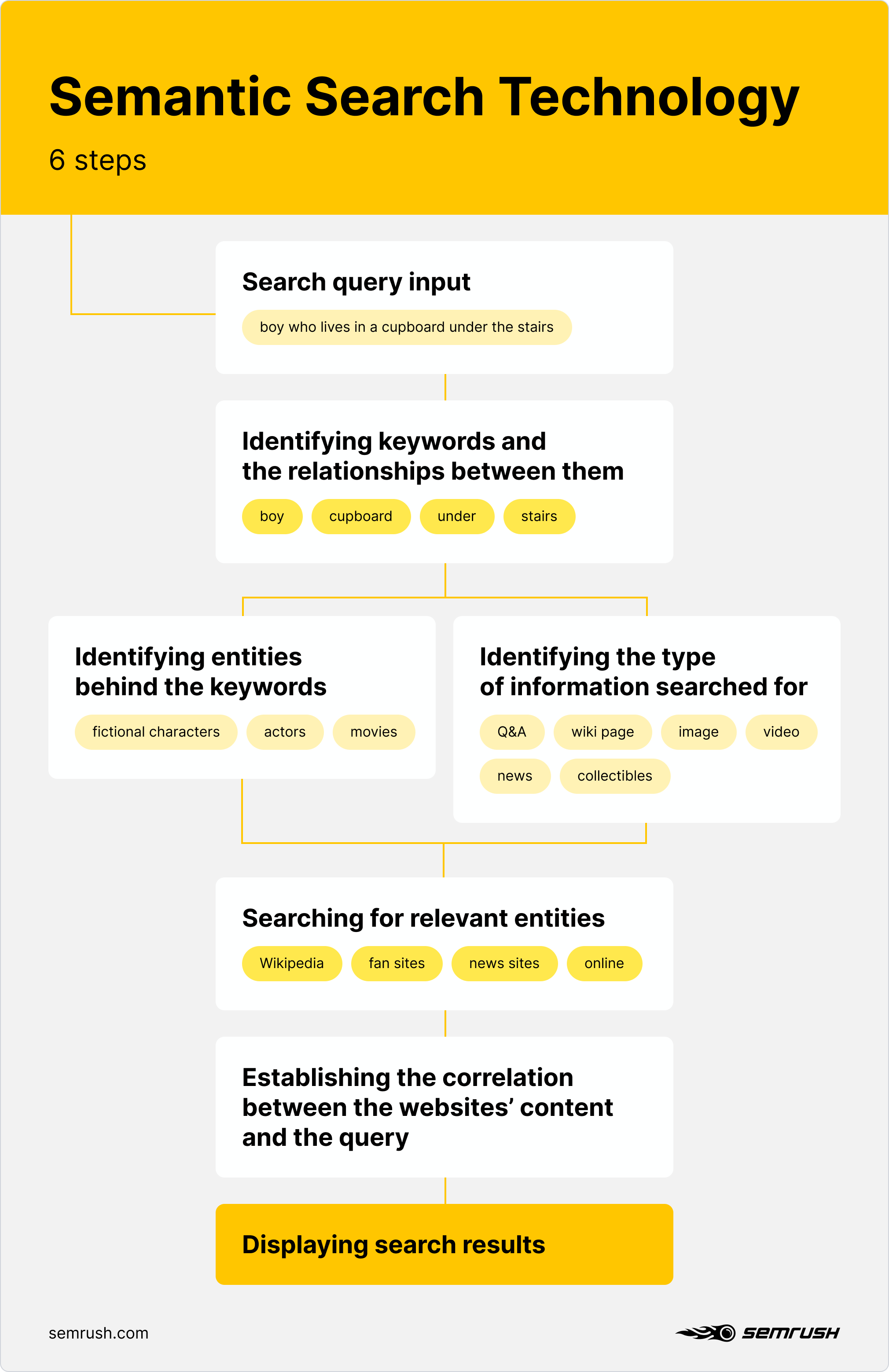
Google has taken a search query and returned the result by understanding the intent and the context behind how these words are connected.
But semantic search works to drive much more than the answers to the questions that we ask.
Search for a plumber? Google knows your location and returns local results.Search for "restaurants near me"? Google knows your location and returns local results. Search for "corona"? Google understands the context. If it were a search made 12 months ago, you would have seen results about beer; now it is the virus. Search for "Amazn"? Google knows that you misspelled Amazon and returns results accordingly.
Why Is Semantic Search So Important?
But let's look at why semantic search is vital for SEOs to understand and consider when planning strategies.
You see, users do not always search by using the same words and in the same way as the content that best answers their query. Search in 2020 is far more conversational than it ever has been before. And Google has to return relevant results, meaning the need to evolve and adapt to this way of searching.
The History of Semantic Search
Semantic search is nothing new.
In 2012, Google introduced the Knowledge Graph to offer a quick answer to the queries right on the SERPs.
However, to understand the complexity and development of semantic search in today's world, you must be familiar with its evolution over the past eight years.
Knowledge Graph (2012)
The Google Knowledge Graph (rolled out in 2012) is a collection of entities and the relationship between them. Over 500 billion of them.
And to see how Google describe this, let's take a look at a snippet from their reintroduction to the Knowledge Graph that states:
Sometimes Google Search will show special boxes with information about people, places, and things. We call these knowledge panels. They’re designed to help you quickly understand more about a particular subject by surfacing key facts and to make it easier to explore a topic in more depth. Information within knowledge panels comes from our Knowledge Graph, which is like a giant virtual encyclopedia of facts.
— Danny Sullivan
You are likely already familiar with the knowledge panel, even if you are not aware of what it is called. These are what appear to the right of the search results for entities such as people or businesses. For example, here is Apple's knowledge panel :
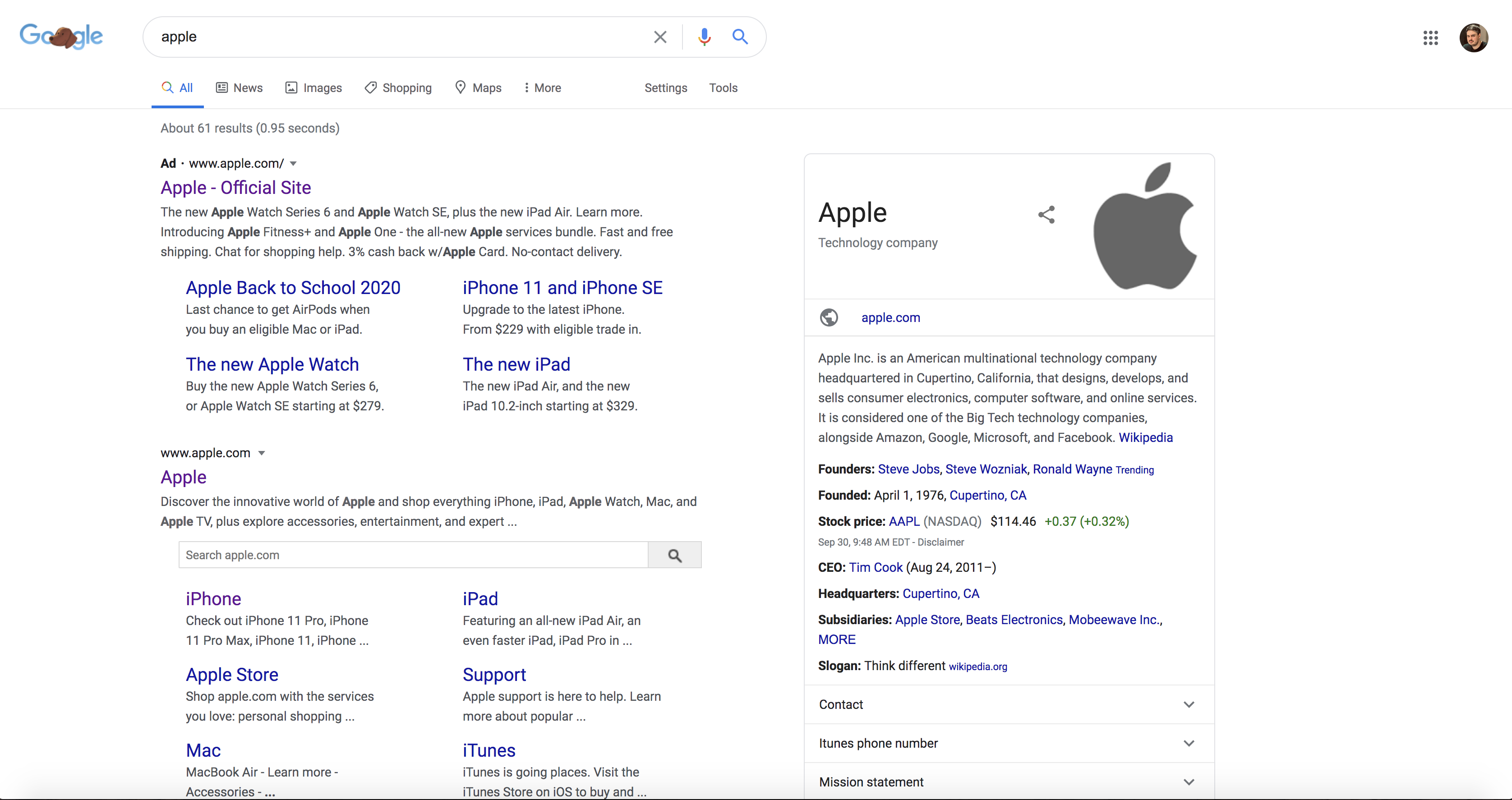
Google's knowledge graph powers these knowledge panels, and we can think of this as a collection of facts, information, people, places, businesses, and how they are connected.
The knowledge graph helps Google to return facts and information about these billions of connected entities.
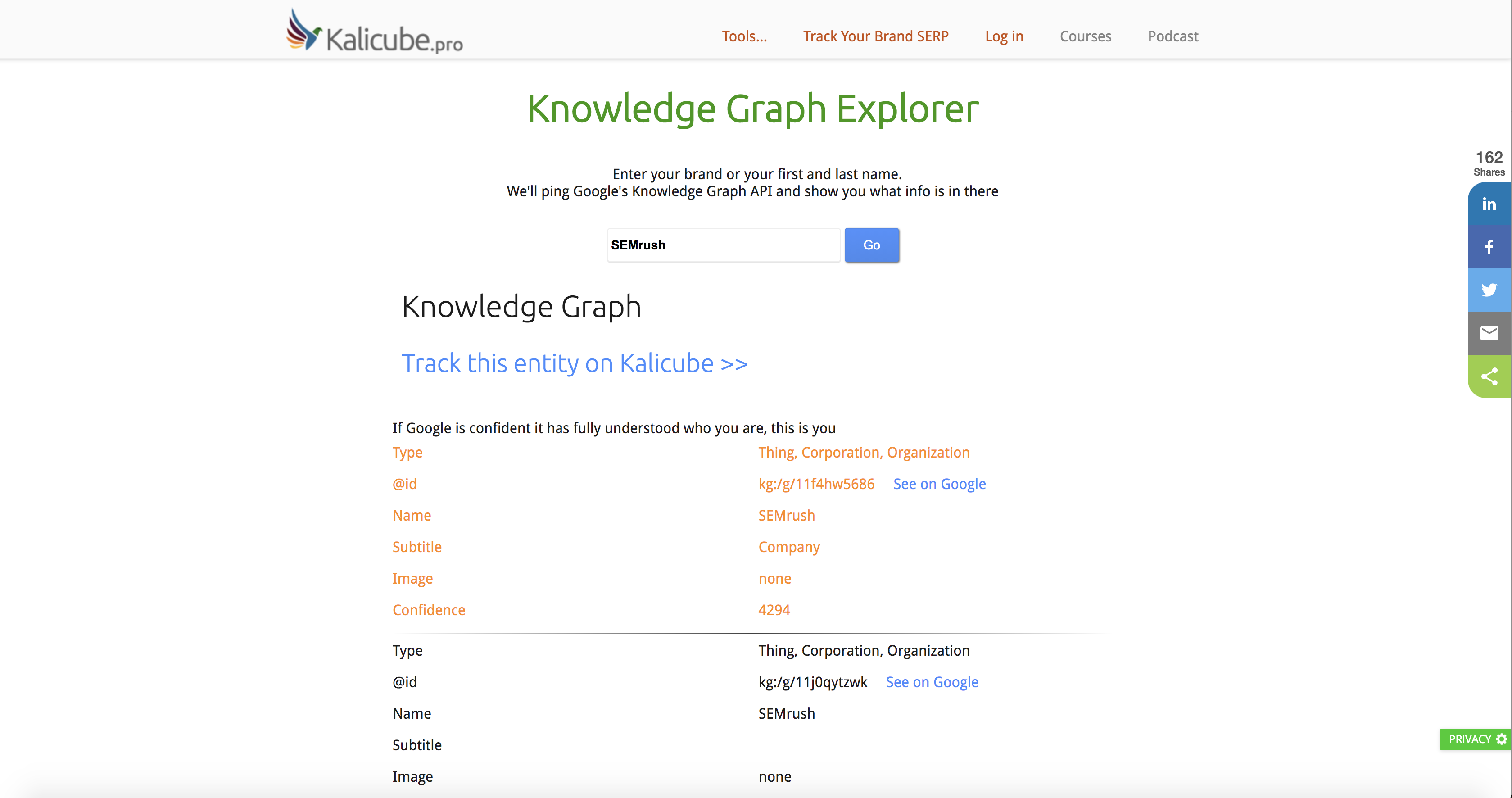
But we recommend going and exploring the knowledge graph for yourself (either your brand or you as an individual) using Kalicube's Knowledge Graph Explorer. You can then see how Google understands you:
Hummingbird (2013)
Google announced its Hummingbird algorithm back in 2013 in a bid to return better search results.
At the time, we reported that Danny Sullivan described this new iteration of the algorithm as:
Think of a car built in the 1950s. It might have a great engine, but it might also be an engine that lacks things like fuel injection or be unable to use unleaded fuel. When Google switched to Hummingbird, it’s as if it dropped the old engine out of a car and put in a new one. It also did this so quickly that no one really noticed the switch.
— Danny Sullivan
However, the most significant change with Hummingbird was Google's ability to understand conversational search better.
The search engine got better at returning results for questions such as, "What is the difference between A and B?"
Hummingbird was the start of search engines getting smarter. This change was driven partly by the shift to mobile, and that the algorithm needed to recognize different types of searches better and provide better results based on a difference in the way a user was searching.
And Scott Huffman, a Google engineering director, told Forbes Magazine that "they want to get into a more 'natural conversation' between people and Google."
Seven years on, it is hard to imagine that Google struggled to answer questions in the not-too-distant past, but Hummingbird changed things up in a big way and marked the start of what we see today.
RankBrain (2016)
RankBrain is one of Google's top 3 ranking factors.
But what is it, and why is it so important?
In short, it is a machine learning technology that Google uses to deliver search results and was designed to help the search engine to understand the meaning of the words that are entered by users.
And back when this was launched in 2016, we wrote that:
RankBrain harnesses artificial intelligence to implant words into numerical entities in order to make them more understandable to computers. Any words or phrases unfamiliar to RankBrain will be converted into words and phrases with similar meanings for filtered results. This increases Google's accuracy and efficiency when tackling new search queries.
— Courtney Capellan
Again, this was all about Google getting more intelligent and better, answering a searcher's queries. It was the start of the need for SEOs to dive deep into understanding search intent.
BERT (2019)
The latest update you need to know about concerning semantic search is BERT, otherwise known as Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers.
But what is BERT?
BERT, our new way for Google Search to better understand language, is now rolling out to over 70 languages worldwide. It initially launched in Oct. for US English. You can read more about BERT below & a full list of languages is in this thread.... https://t.co/NuKVdg6HYM
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) December 9, 2019As with the other updates we have defined above, BERT is all about Google better understanding search queries. The technology that sits behind it allows anyone to train their own state-of-the-art question answering system.
Danny Sullivan confirmed that "it impacts about 10% of queries where BERT is live in. The other 90% do not use BERT for understanding queries and content."
BERT considers the full context of a word by looking at the words that come before and after it, making it particularly useful for understanding search queries' intent.
Again, notice the importance of intent?
Hold on to this thought, as we will be discussing it in more depth shortly.
What Does Semantic Search Mean for SEO?
So then, just what does semantic search mean for SEO?
At the top level, it means a search engine that better understands a user's search query and the ability to serve more relevant, personalized SERPs.
But in terms of the ways SEOs need to approach optimizing for semantic search, this means:
Thinking about topics, not just keywords.
Understanding that high-volume keywords matter less than they once did, and that long-tail, related keywords and quality content matter more than ever.
There is a distinct need to analyze and understand search intent before creating content. There is also a need to format your content to fit the query type and the SERP features you may want to win.
That structured data is a must.
You should be thinking about how you can create a Knowledge Graph entity.
In many ways, optimizing for semantic search is what we should now be thinking of as best-practice SEO, but what should inherently stand out is the need to create content and optimize for users, not search engines.
Think about how your customers are searching for your products, services, and their search intent. Then place this as your primary focus.
How to Optimize Your Content for Semantic Search
Wondering how to optimize your content for semantic search to increase your site's organic visibility? Here are seven things you need to make sure you are considering:
1. Think Topics, Not Keywords
It is time to stop optimizing for single keywords and start optimizing for topics.
Is keyword research as we know it dead? Of course not, it’s just become more complicated.
Google understands that searches like "home renovation loans," "home improvement loans," and "loans for home renovations," mean the same thing. The intent is the same, meaning that the content returned for each of the queries should be pretty much the same.
It will at least be the same page on a site that should rank for all of these queries.
You might have created separate pages to target singular, plural, and other variations of a keyword in the past. But it would help if you were not doing this in today's world. Ideally, it would help if you never had in the first place, but as Google has become better at understanding semantics, this has become even more important.
To give an example, ranking your page at the top of the SERPs for "home improvement loans" with its 27.1k search volume (taken from the SEMrush Keyword Overview Tool) is not your goal anymore.
At least not the only goal.
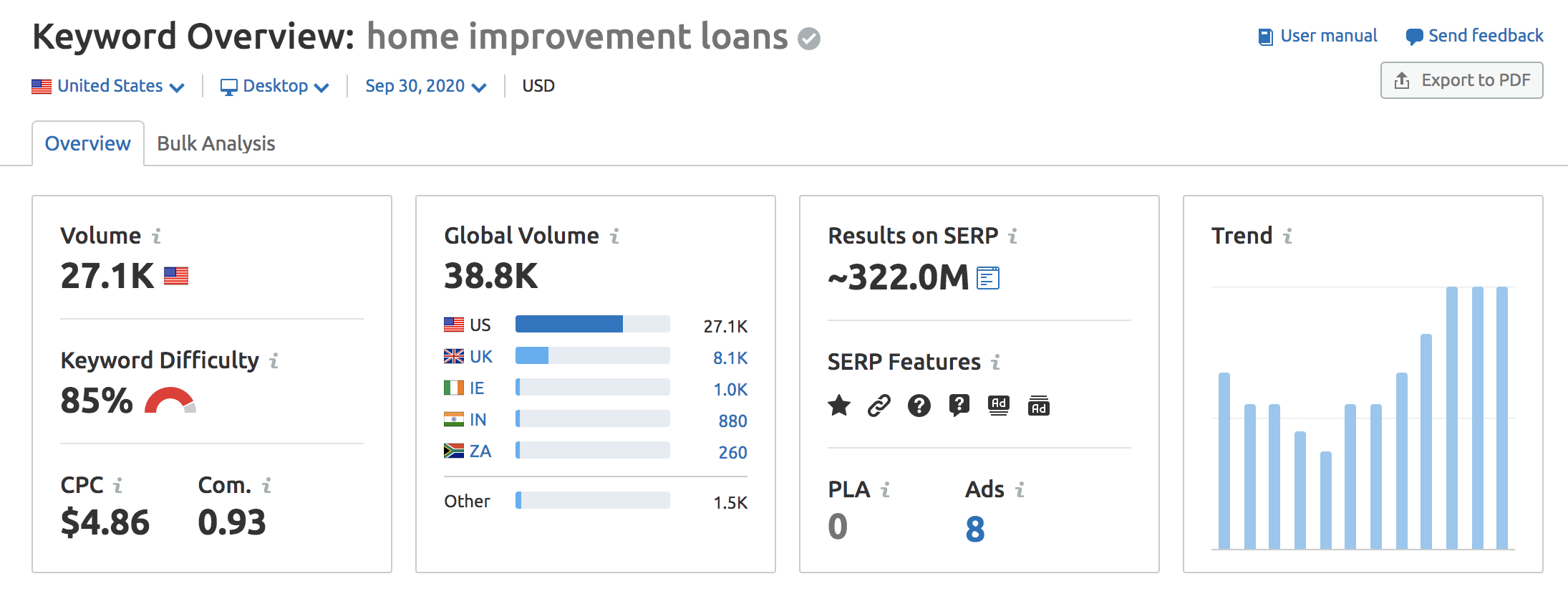
You can cover the whole topic and have your website displayed for many different long-tail queries. We can see here that those close variations amount to a much higher search volume that your page could benefit from - 65.5k searches—a big difference to the 27.1k from the single keyword.
And then there are another 3.8k searches that come from questions. We can find both of these by entering our main keyword into the tool.
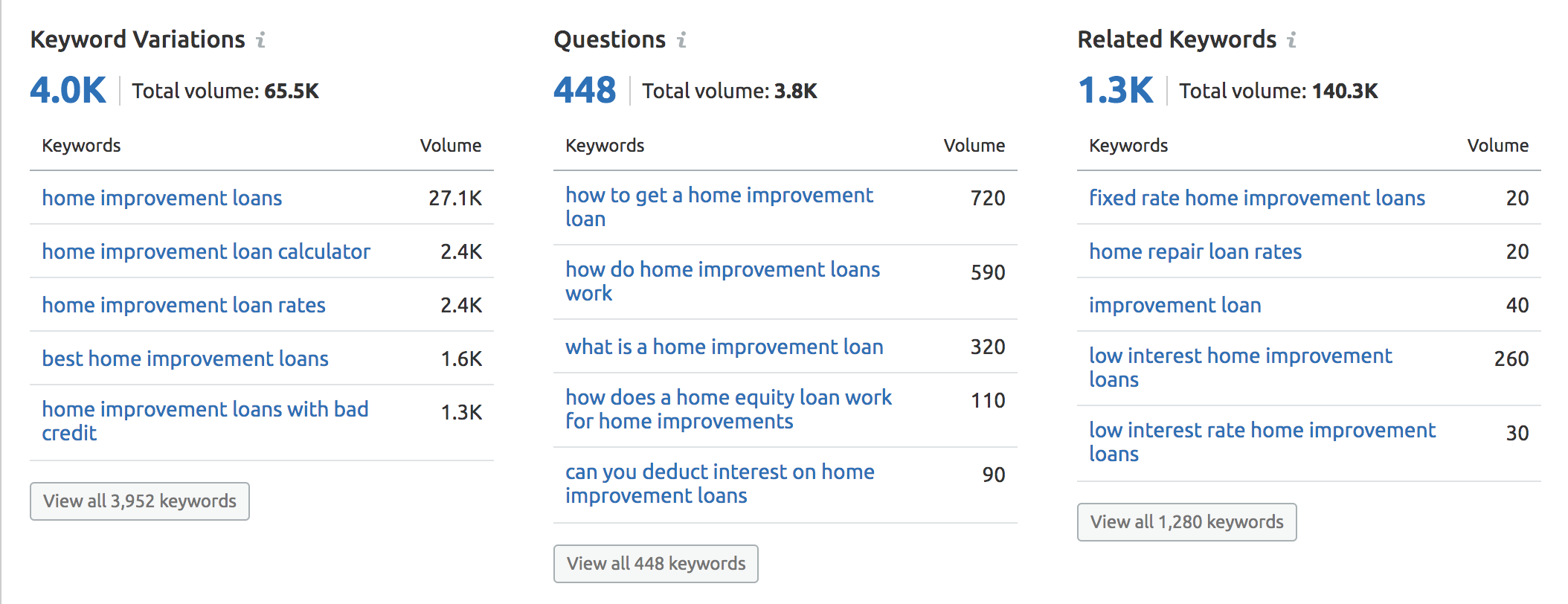
Take the time to understand how keywords fit together to form topics, optimize for these, and you'll win big as a result
2. Understand and Optimize for Search Intent
Every search query that a user types into Google is essentially a question that reflects your audience's intent.
Understanding it can be a daunting challenge as you are trying to get into your users’ heads. But if you can create content that satisfies this intent, you will find it far easier to rank at the top of the SERPs.
And we can look at this from the way that search intent usually falls into three main categories:
Learning something (informational)
Buying something (transactional)
Finding something (navigational)
These informational, transactional, and navigational intents correspond with informational, transactional, and navigational keywords accordingly.
For example, if I am looking to compare smartphones, the search engine will not offer me to buy some in the first place. It understands I am in an informational stage, not lower in the funnel looking to make a transaction.
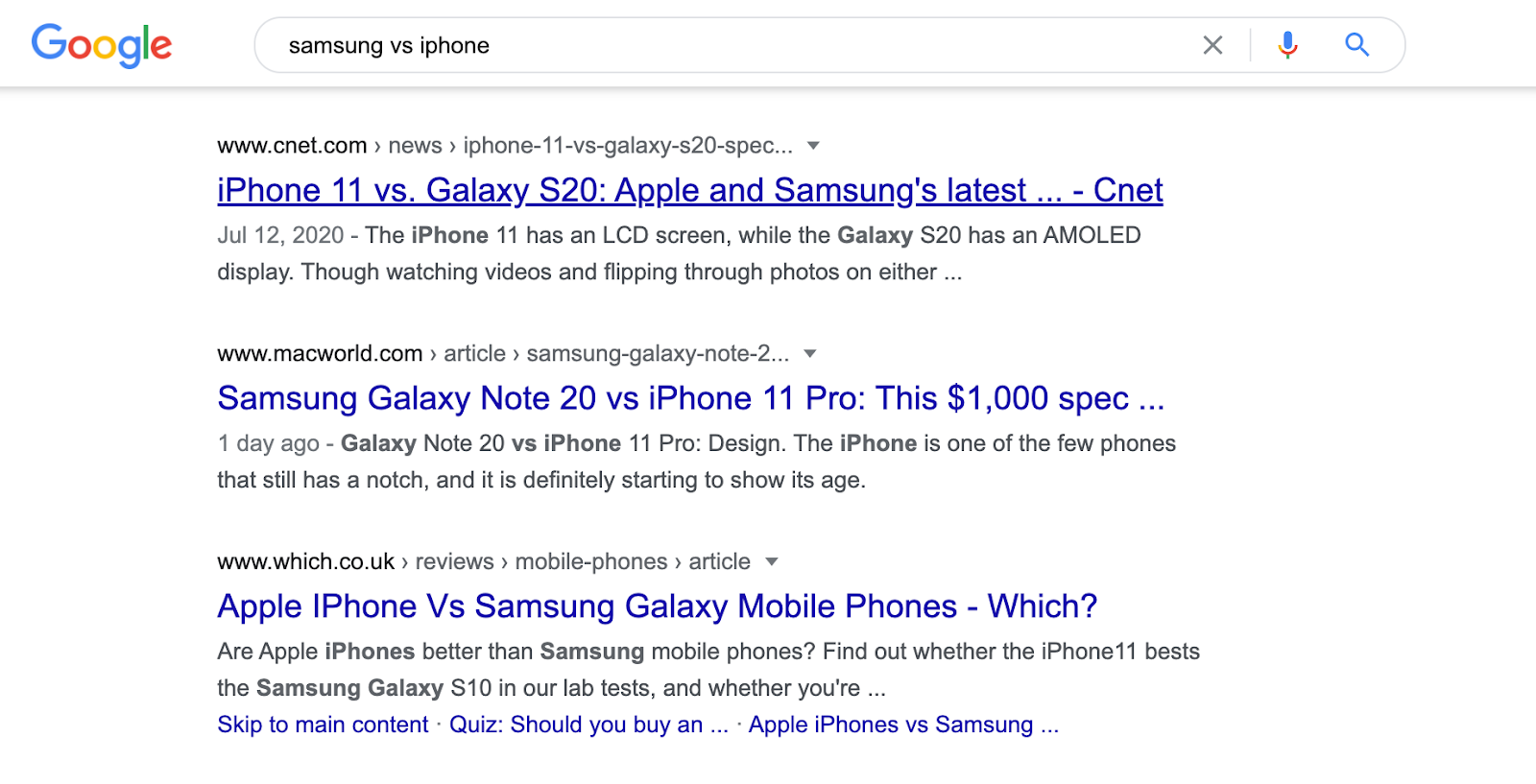
This means you need to be creating different content to satisfy different intents. While you may think that creating additional content for the same or similar keywords is duplicating your efforts, it may not be. Our guide to keyword cannibalization will help you understand that the issue here is when you are duplicating intent, not the keyword itself.
Take your time to analyze the SERPs to understand the different intents for the topics you are targeting.
3. Use Semantic HTML
A great starting point in optimizing for a semantic web is to use semantic HTML.
Not come across this before?
HTML.com describes this as:
Semantic markup is the use of a markup language such as HTML to convey information about the meaning of each element in a document through proper selection of markup elements, and to maintain complete separation between the markup and the visual presentation of the elements contained in the document.
To a certain extent, this means rethinking the way we write our code.
You are likely familiar with HTML elements like <span> and <div>. These are non-semantic. They do not indicate the contents.
However, look at a semantic tag such as <header>, <footer> or <article>.
These give a clear understanding of what is contained within these elements. You can learn more about semantic HTML in our guide so that you can start marking up your code in this way.
4. Optimizing Content for the Featured Snippet
The Featured Snippet, or position zero, is one of the most desired SERP features to grab and is based upon semantic search.
To land the coveted featured snippet, you need to show Google that the answer your web page provides to a searcher's question is the most direct and helpful on the web. It is a bold claim to make. But if you want to win the featured snippet, that's where you need to aim.
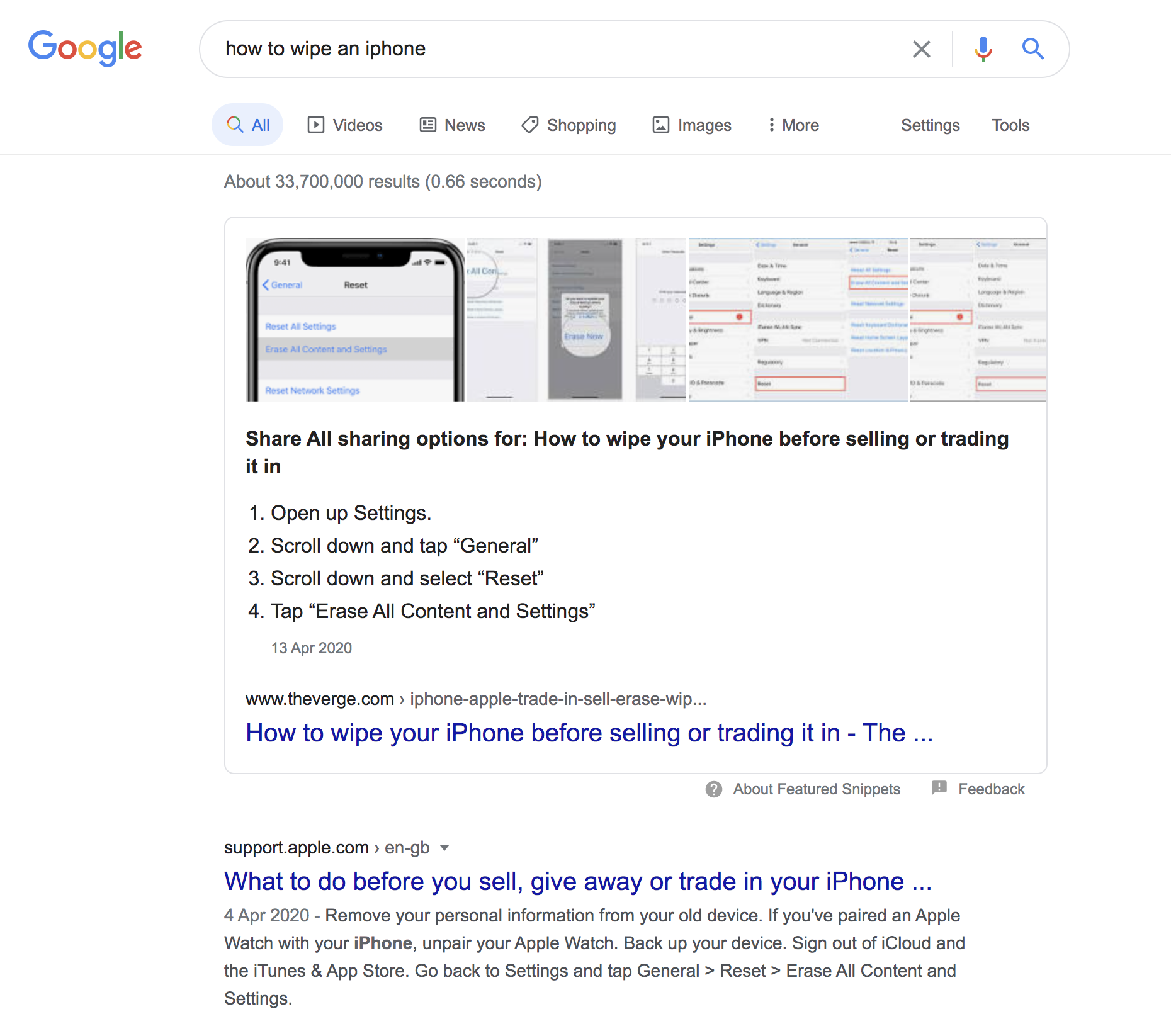
But what can you do to increase your chances of landing this spot?
Explore the most frequently asked questions in your niche and determine which of them trigger the Featured Snippet. You can see the SERP features that are triggered when analyzing a keyword with our Keyword Overview Tool.
Analyze the structure of the article currently ranked in the snippet. Look for bulleted lists, tables, visuals, headings depth, etc. and try to replicate this in your content.
Create text that answers the question directly and structures your sentences to read naturally.
5. Understand and Use Structured Data
When a search engine crawls your site, structured markup helps it to understand the context of your content and sort through individual entity attributes to provide the user with more targeted search results.
Besides that, structured markup increases your chances of triggering rich snippets.
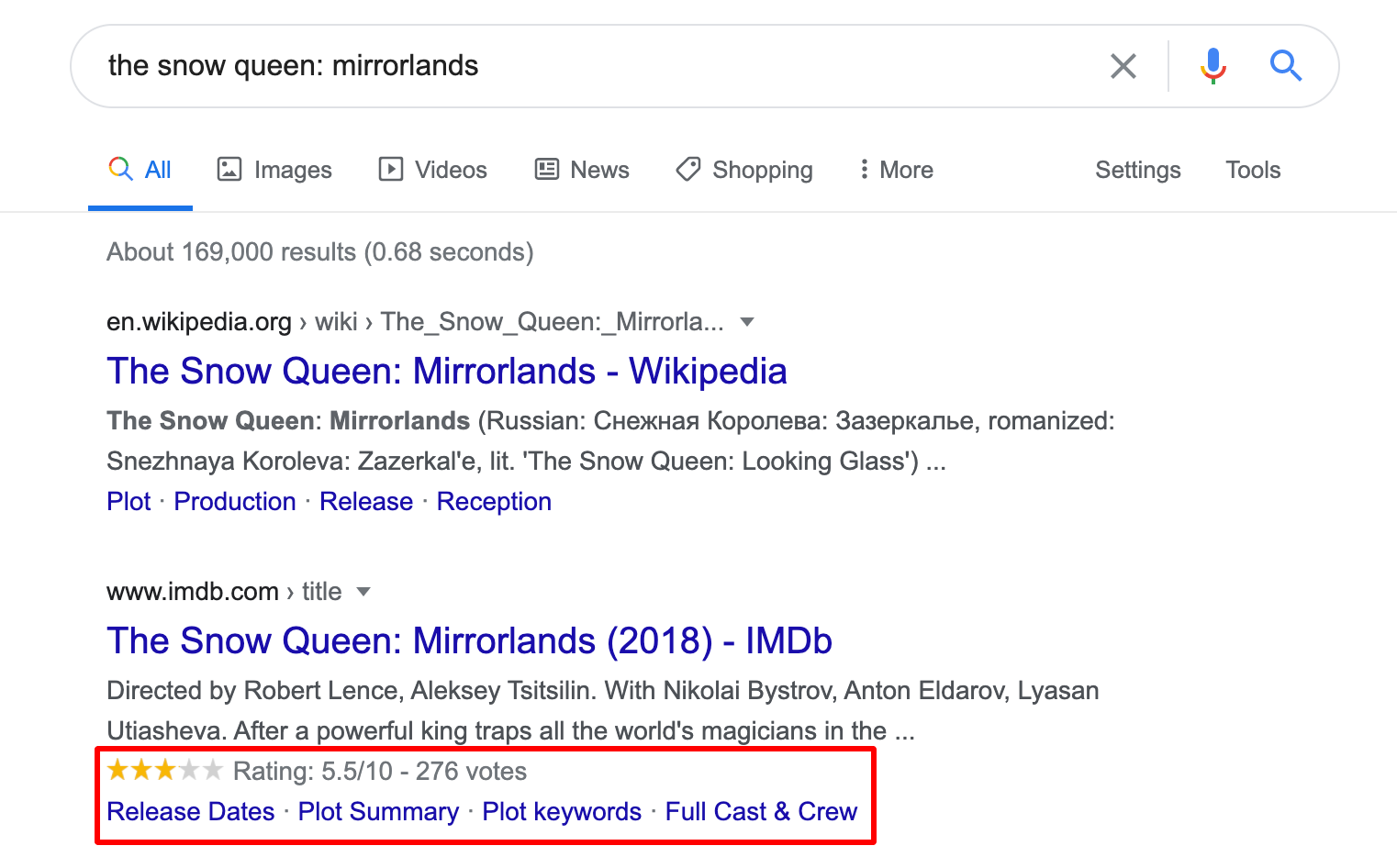
You can check out our guide to schema and structured data to use this markup to define entities, actions, and relationships and to help the search engines to understand your content better.
And as we claim in the guide:
As Google continues to build a more semantic web, these markups become increasingly valuable in effective Internet communication.
But what can you do to use structured data to mark up your content?
Check out schema.org and browse a wide range of vocabulary templates understood by Google, Microsoft, Yandex, and Yahoo! Find the most suitable type and implement it.
Use Google's Structured Data Markup Helper to assist in marking up your content. Merkle's Schema Markup Generator is another great option.
For the time being, use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to check that your markup was implemented correctly. However, be aware that this is soon to be replaced with the Rich Results Test.
6. Become a Knowledge Graph Entity
People think differently, which means that they search in a variety of ways. That is why semantic search relies on a constellation of entities scattered across the web (people, places, things, ideas, concepts, etc.) and their connections.
This is why it is beneficial to become a Knowledge Graph entity, something that you can learn how to do in Jason Barnard's " How to get Entities and Their Attributes in the Knowledge Graph" episode of #SEOisAEO.

Suppose you manage to turn your brand page or blog into a Knowledge Graph entity. In that case, you will buy yourself a place in SERP features like Knowledge Panels and Knowledge Cards with all the associated visibility, authority, and trust.
However, it may cost you some organic traffic, as there is a chance that searchers can learn all they need to know about your company right from the SERPs page.
But think beyond your business' organic traffic. Think about the visibility and authority you could benefit from by being at the top of a SERP!
7. Build Links That Demonstrate Relevance
Both internal links and backlinks can demonstrate topical relevance and help Google understand your content better.
And while it is easy to assume that the links you earn could come from anywhere, as long as they are authoritative and editorial, you will see a better impact when these topically align.
Why?
Because these links are helping Google to understand your content better. Think carefully and plan a solid link building strategy that targets links that position you as an expert in your field, and you will see benefits.
But do not underestimate the power of internal links. They are just as important as backlinks, especially when demonstrating the topical connection between two pages.
Building a Semantic Search Strategy
Search engines continue to add semantic features to fine-tune their ability to understand user intent.
And this is not going to change any time soon.
On the one hand, keeping pace with the evolving algorithms requires constant optimization efforts. On the other, it makes life easier for users. By ensuring that your content strategy includes developing content that covers different types of intent, you can better answer the questions users are searching for.
Innovative SEO services
SEO is a patience game; no secret there. We`ll work with you to develop a Search strategy focused on producing increased traffic rankings in as early as 3-months.
A proven Allinclusive. SEO services for measuring, executing, and optimizing for Search Engine success. We say what we do and do what we say.
Our company as Semrush Agency Partner has designed a search engine optimization service that is both ethical and result-driven. We use the latest tools, strategies, and trends to help you move up in the search engines for the right keywords to get noticed by the right audience.
Today, you can schedule a Discovery call with us about your company needs.
Source:





