If your website rankings crash, your site can lose a lot of its visibility. This is the number one horror story for online marketers around the globe.
It can be even more terrifying if you can't identify the cause or typical SEO strategies don't seem to be working. In this article Evgeni Sereda (who will cover analysis and tools) and Ralf Seybold (who will cover examples and defense) take on a complicated cause for ranking losses: content spam.
This article aims to explain the issue as simply as possible. The real-world examples below have been blurred or replaced.
What is Content Spam?
Content spam is the unwanted and unauthorized use of content from one's own website on third-party websites in connection with other content, negatively affecting your brand's and website's reputations. Content spam is one of the techniques referred to as negative SEO.
Which Sites are Affected by Content Spam?
The main targets of content spammers are strong websites in certain niches, including ecommerce websites.
Spammers often use keywords that usually get more than 500 searches per month. Content is stolen from targeted websites and published on other domains in order to rank on the SERPs.
The stolen content is often republished on hacked pages whose owners have no idea that their websites are being used for such trickery.
How Can You Identify Content Spam?
The first signal is alarming ranking losses; however, these losses can be caused by many other factors as well. You should rule these out through analysis before assuming that content spam is to blame.
1. Analyzing Ranking Losses
First, you can check with Semrush whether our competitors have also lost rankings or traffic. If they have, the cause may be another surprising Google update. These usually affect the entire industry.
To check for this, enter your and your competitors' domains in the Domain Overview tool. Switch to daily view to better spot outliers.
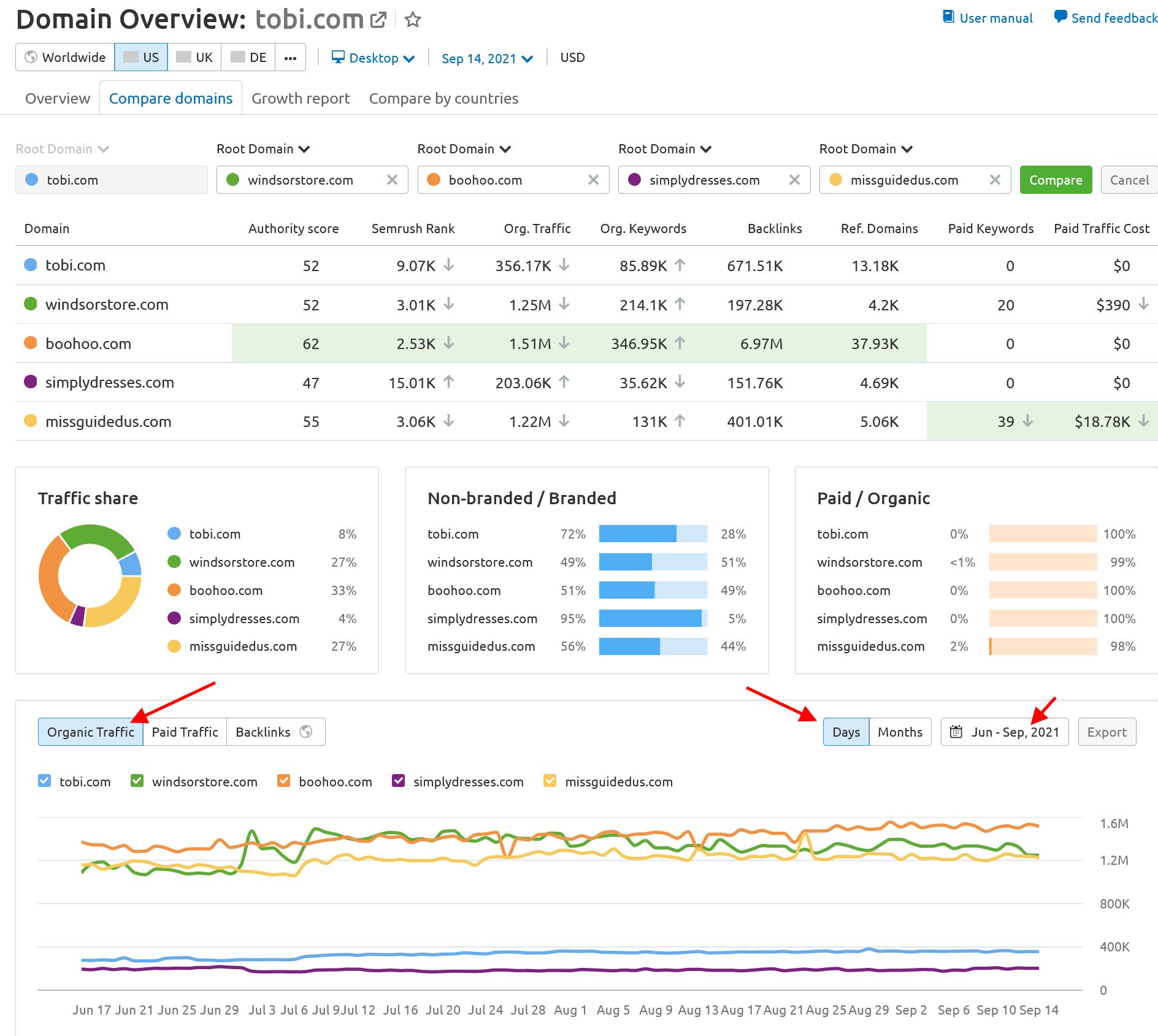
You can also use the Organic Research tool to check if your domain's traffic has been affected by a Google update.
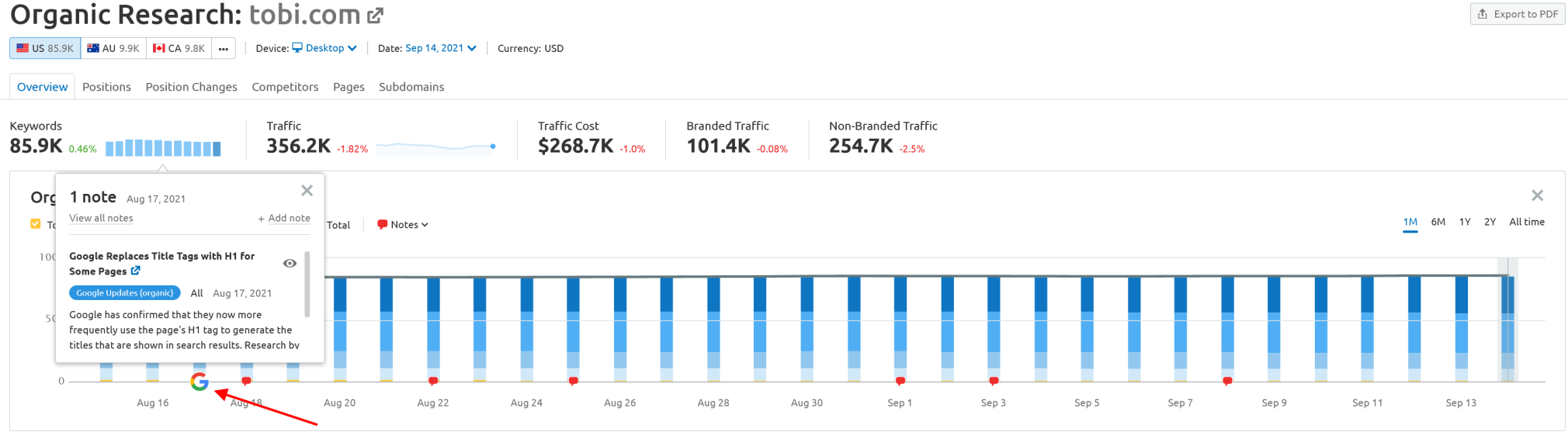
Unfortunately, ranking losses will have an impact on traffic — and likely sales — as well. So at this point, many SEOs react with frantic defensive measures. Technical SEO is optimized, content is added, new pages are uploaded, and backlinks are bought. But what if none of this seems to be working?
It is very likely that you will not detect anything unusual, neither on your own nor on your competitors' websites.
And this is where you have to dig deeper. To do this, open the Positions tab in Organic Research and click on either the brand keywords or the high-volume keywords you rank well with. You may find this general pattern:
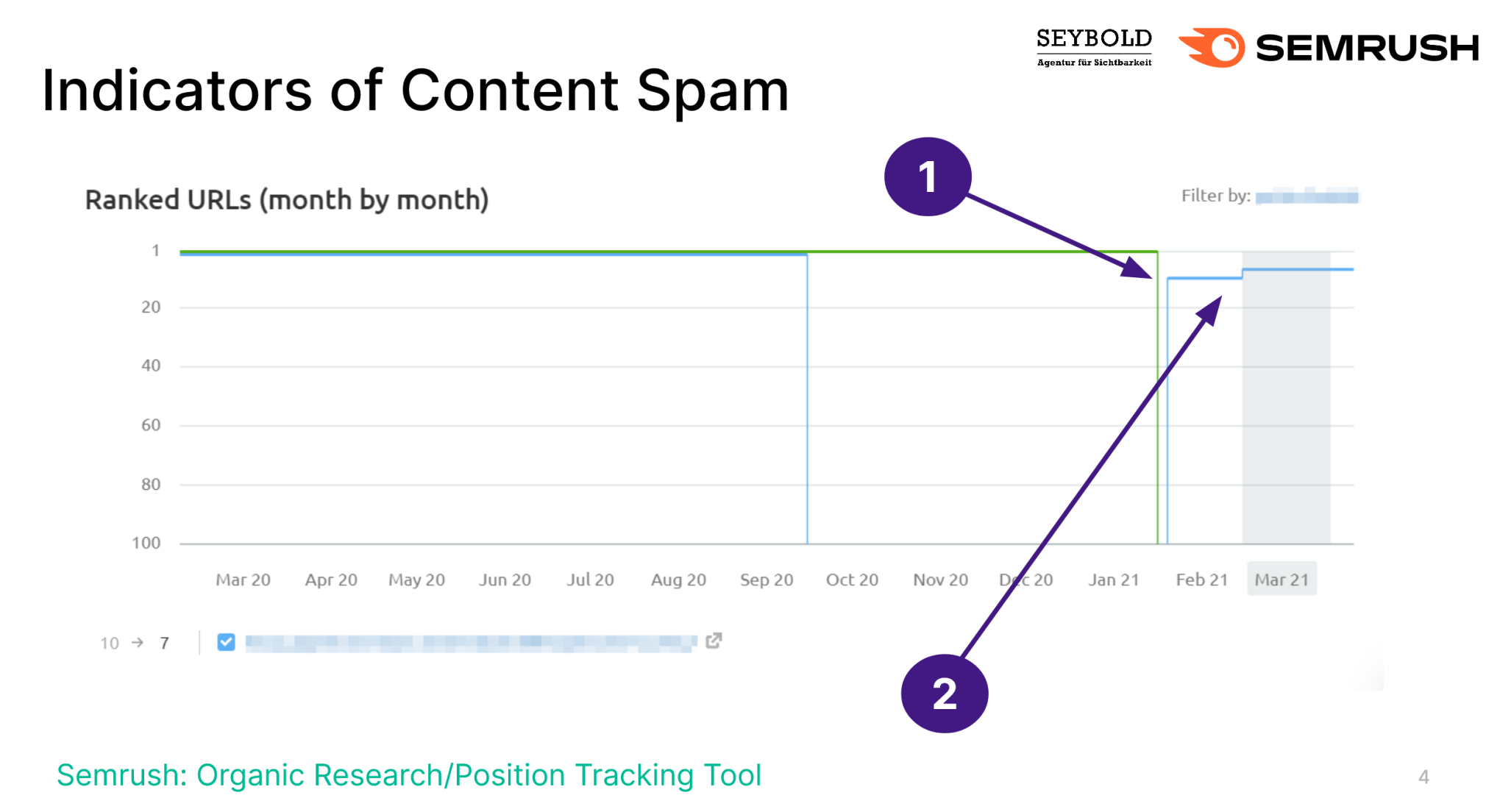
Top rankings drop off and are replaced by a different URL that ranks lower. Instead of a homepage for a brand, a product page now occupies the spot — for the same keyword.
2. Conducting an SEO Audit of the Website
If the cause of the issue is still unclear, it's time to carry out an SEO audit of your website if you haven't already done so.
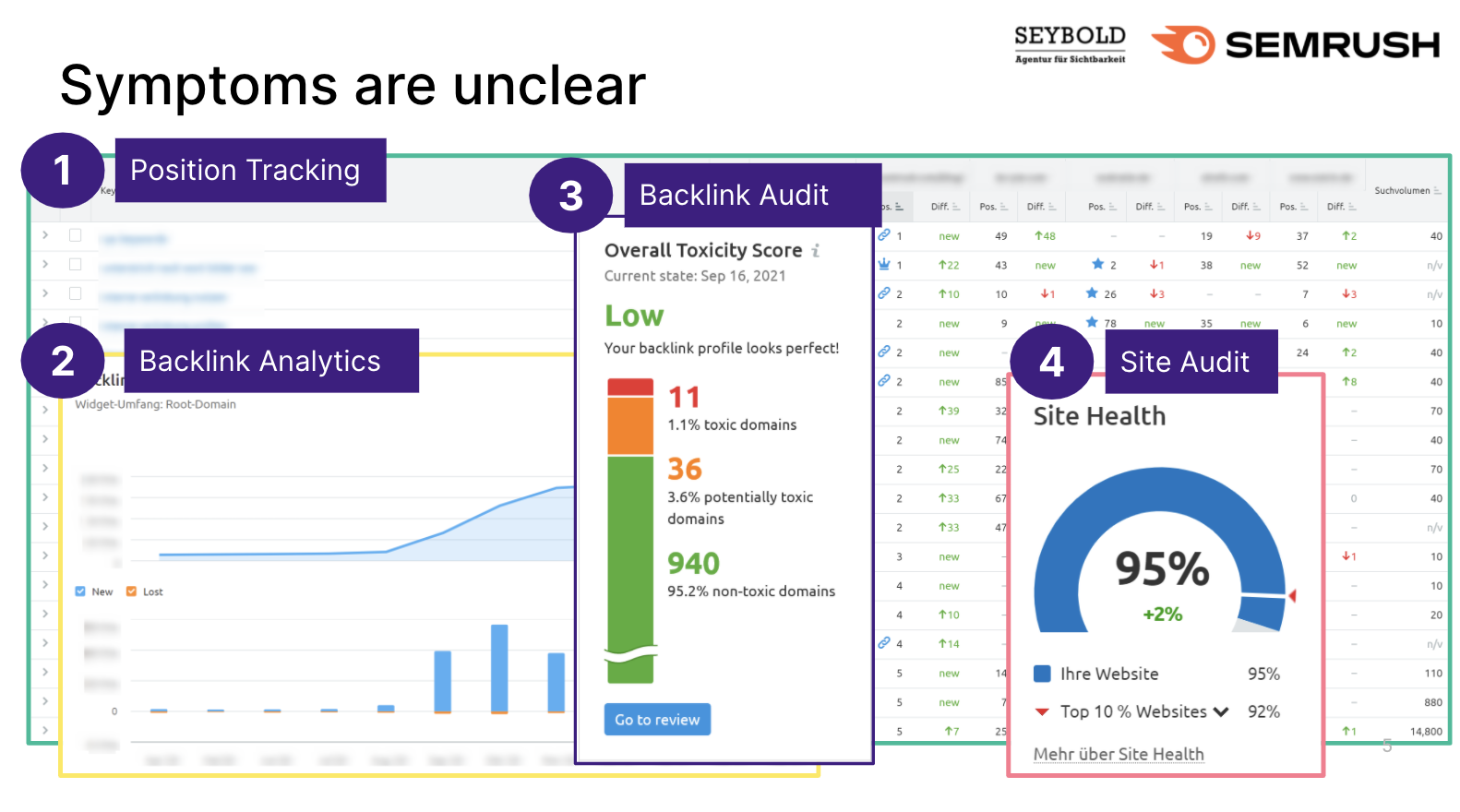
If you're using Position Tracking to monitor rankings, you won't see any abnormalities besides the ranking losses.
You won't see any major changes in your or your competitors' backlink profiles in Backlink Analytics either, even though Semrush has the most powerful and fastest crawler.
The Backlink Audit tool shows no significant increase in toxic domains and the Site Audit doesn't report any new technical errors.
So what can we do?
As time passes, more and more rankings are affected.
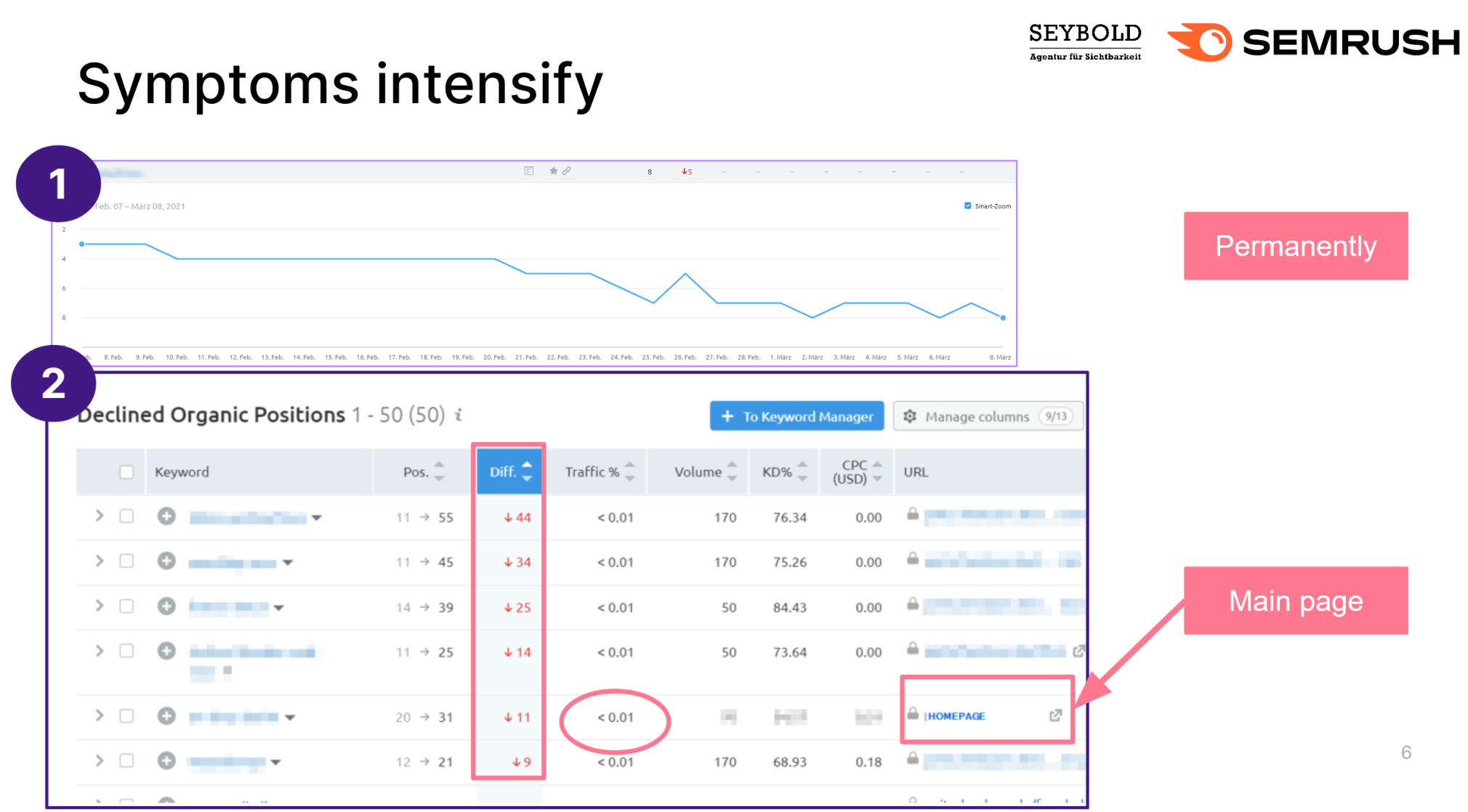 More ranking losses caused by content spam
More ranking losses caused by content spamOur checks indicate the website is in good technical condition. No toxic backlinks have been built and backlink growth looks fine. Our competitors neither have built a lot of strong, new backlinks nor have they optimized their content. Our website should be fine.
There also hasn't been a recent Google update that could have caused the ranking losses. Only now do many realize — often by chance — that their ranking problem could really be a content spam problem.
3. 3 Steps of SEO Analysis to Narrow Down the Problem
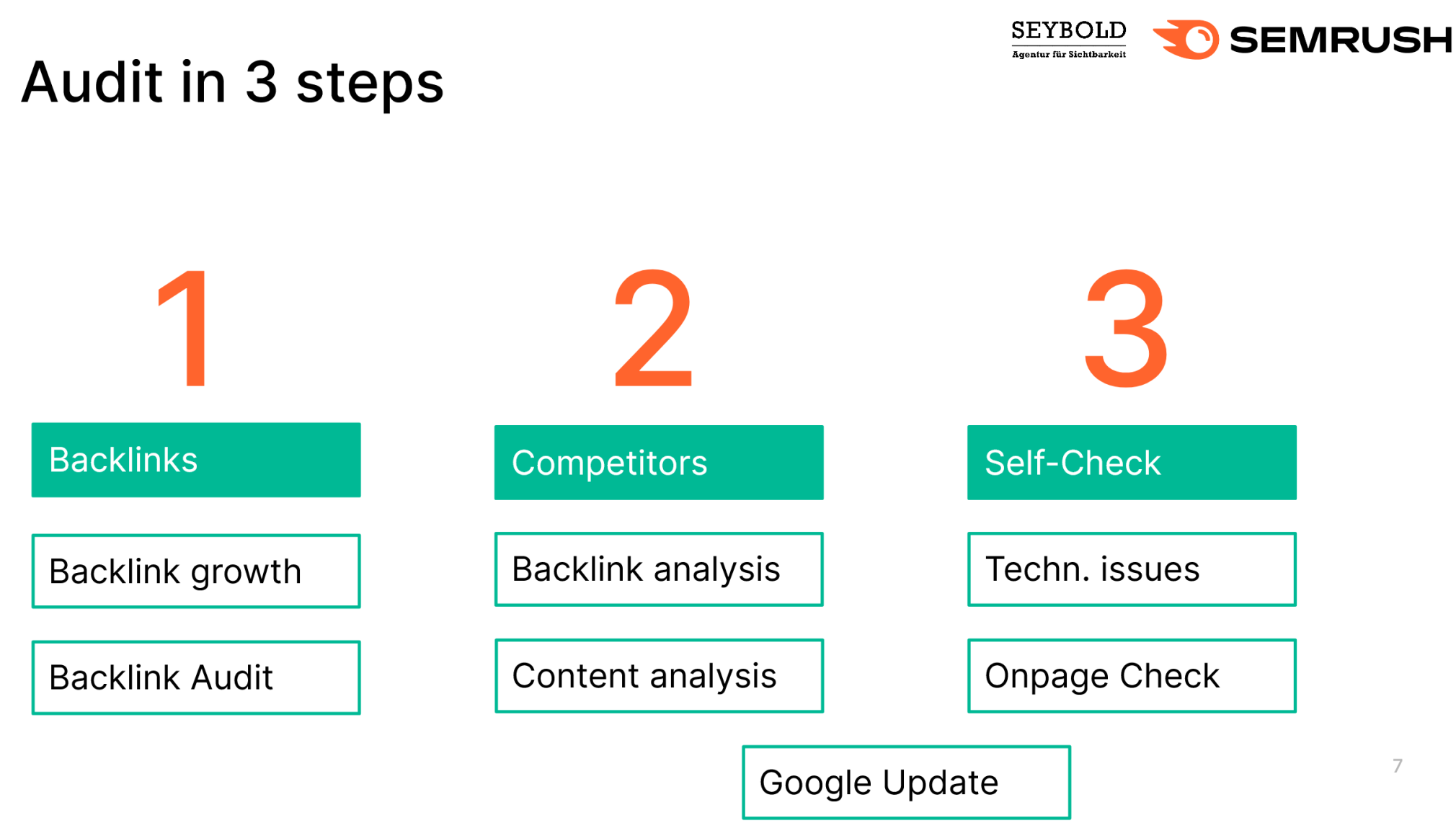
Rule of thumb: eliminate all other potential causes before considering content spam as the root of your problem. Also, don't resort to costly measures while the cause is still unclear.
The typical analysis includes the following steps:
Auditing your own domain Analysis of backlink gains or losses Backlink audit Auditing competitors Analysis of backlink gains or losses Analysis of competitors' content Checking your technical and on-page SEO Site Audit + technical issues On-page check (page titles, etc.) Special case: checking for Google updatesAre You Affected by Content Spam?
Content spam can come to haunt any website, from small affiliate sites to big players in the market. The example we discovered in September 2019 is a phishing scam that attempts to steal users' log-in data for a popular SEO tool.
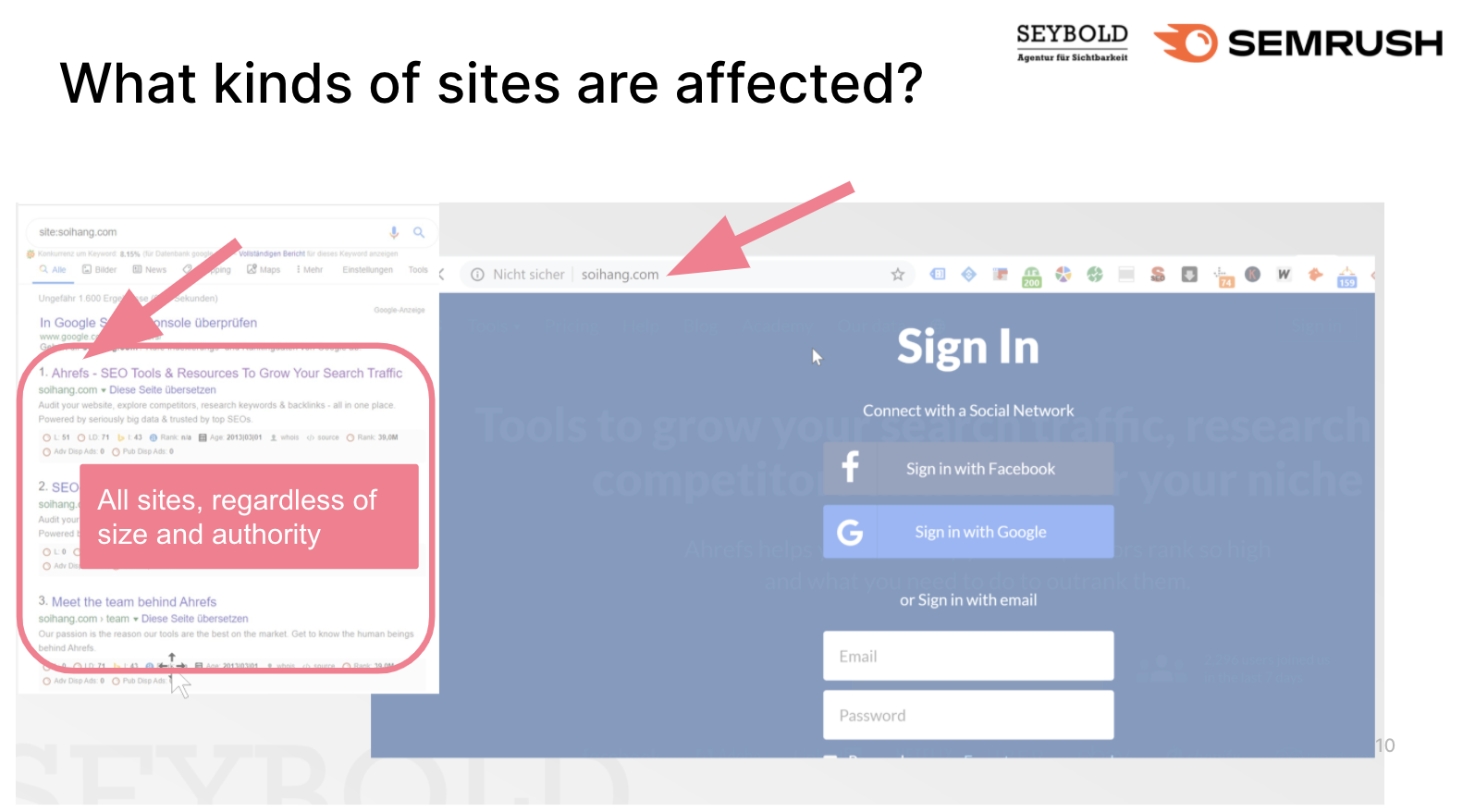
A copy of the original website's content was published under an unrelated domain, including the login option, of course. The aim here was to attain users' login details and thereby get hold of further information such as credit card or bank account data.
This raises the question: how do pages like this rank well on the SERPs?
How Google Detects Duplicate Content
Google is quite good at identifying duplicate content and detecting on which pages the content appeared first.
So why do so many spam sites rank? See what John Mueller of Google had to say:
But even if we know which one is the original and which one is the copy, sometimes it makes sense to show a copy in the search results...And one of the situations where I have seen this happen consistently is if a website is of lower quality overall, where when our systems look at it they’re like, well we can’t really trust this website.But if a higher-quality website were to take some of this content and publish it, we would say, well we know more about this website and actually maybe we should show this content in the search results.
— John Mueller, Google Webtrends Analyst, June 2021
Google believes that copied content should sometimes show up in search and may even work better on someone else's domain than on the original website. Mueller limits this case to pages that are of higher quality and known to Google.
Looking at many websites that we see in search results every day, we can't help feeling that Google favors more spam sites than originals — despite the spam updates rolled out in June and July of 2021.
A comparison using a search phrase with clear intent to purchase shows how search engines deal with spam.
For our comparison, we entered a search for an Apple iPhone in a local retail chain into Google and Bing.
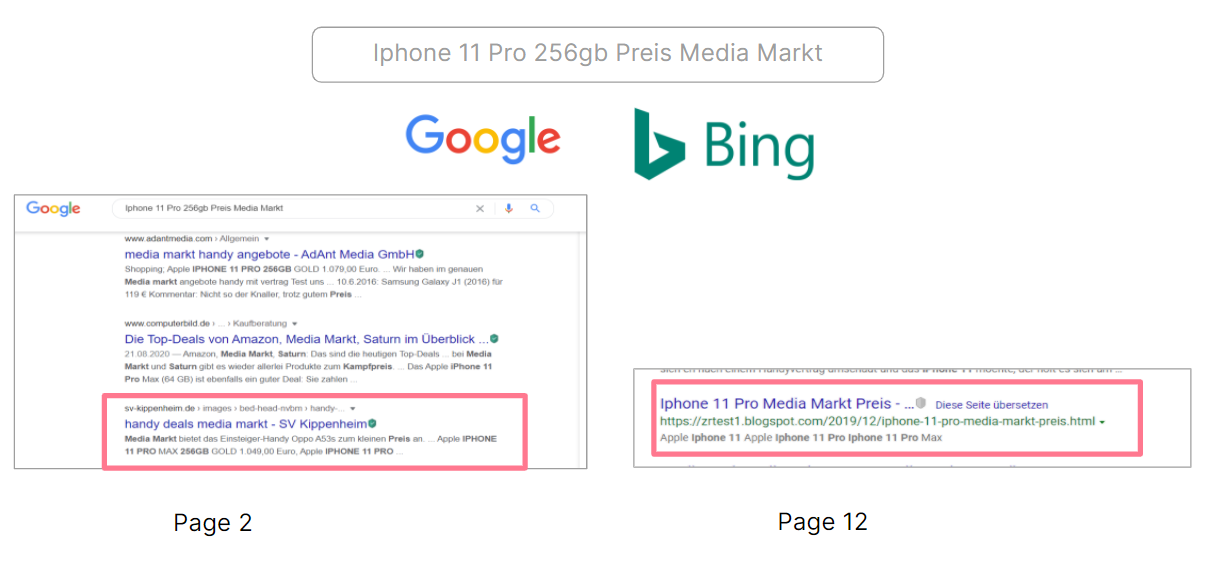 Content spam in search results
Content spam in search resultsOn Bing, the first spam page appeared far back in the search results on page 12, while Google ranked the first spam entry on position 13 (page 2 of search results).
Based on this example, spam seems to be much more prevalent in Google than in Bing.
We can also see that copied content may receive a better ranking on a third-party site than on the original in Google:
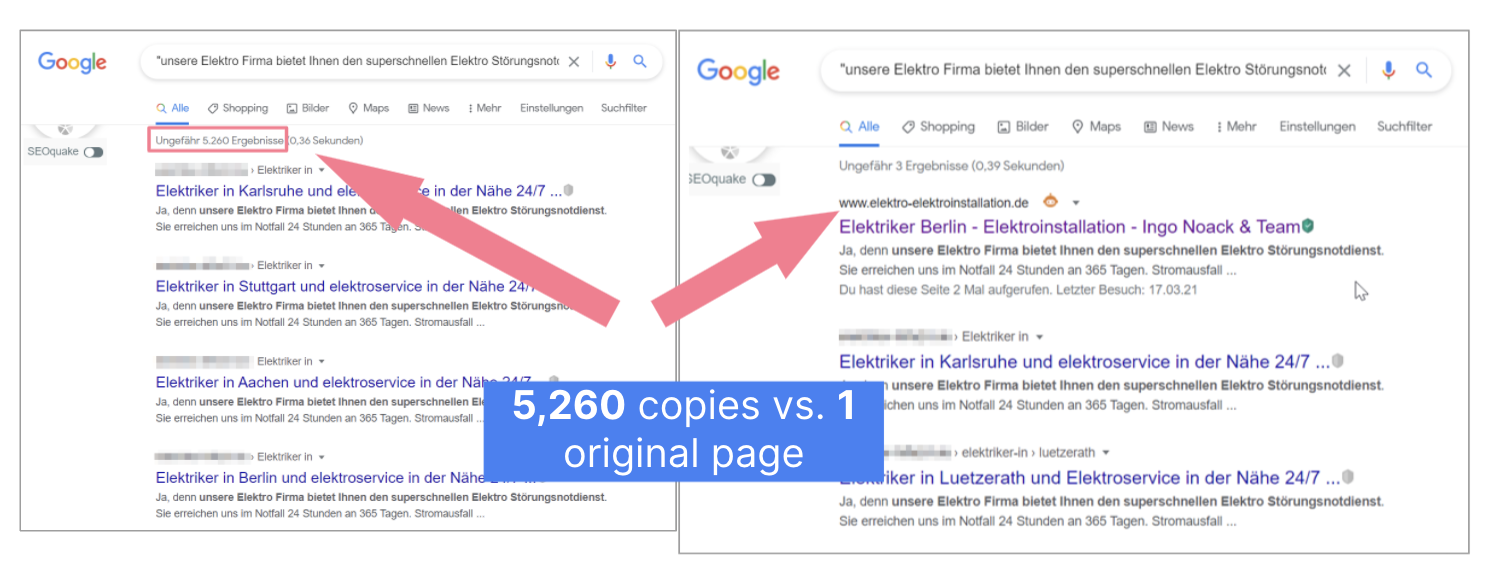
Here's an example: one website belongs to a local artisan. The other one belongs to a company that appears to offer the same services. But calls to the given phone number aren't answered and the physical address doesn't seem to exist either. You can only get in touch via email.
It's best to decide for yourself which is the more legitimate craftsman.
Content Spam: Original Content is Multiplied
Original content becomes duplicate content through copies — in this case, 5,260 of them. This destroys the original site's authority and the quality of the text as far as Google is concerned. So even the original page ranks worse.
This is because the original site has fewer backlinks and is significantly smaller. The size of its individual pages is smaller too, as the company offers a local service ("Electrician Berlin"), while the copied version aims at a national ranking, exactly as John Mueller explained.
But does that make sense?
Semrush clearly shows the growth in the number of keywords. The copy shows up in search results with both low and high-volume keywords.
For example, it ranks 6th nationwide for a keyword with 1,300 searches per month ("elektriker notdienst", meaning "electrician emergency service").
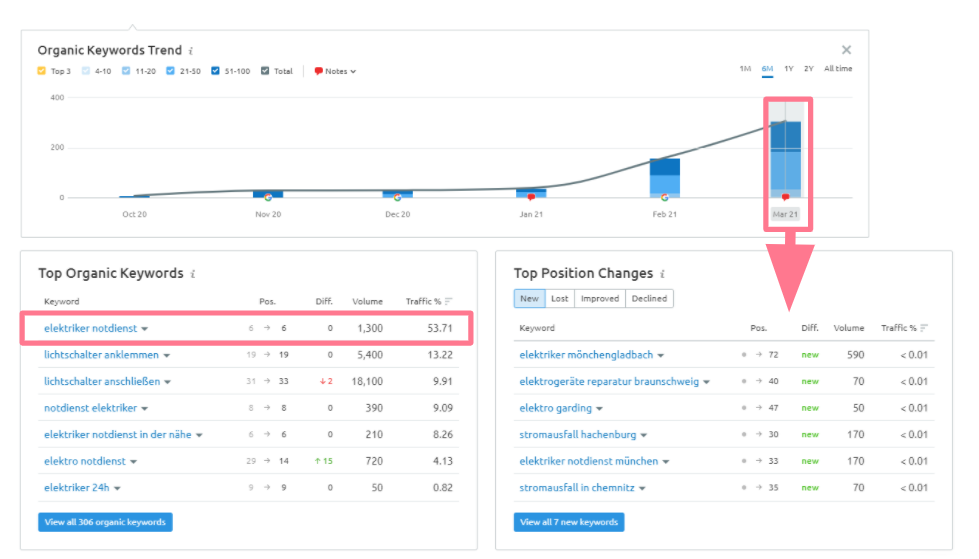
Rankings this high can be reached with plagiarism in Google. Mind you: stolen content performed better in Germany-wide rankings.
How is Stolen Content Used on Content Spam Sites?
Plagiarism is not only used to place spammers' websites or offers in search results. They also post snippets of stolen content on social media platforms for quick SEO wins. Backlinks alongside known, relevant text content in social media linking to completely different domains are employed as an easy way to boost these domains.
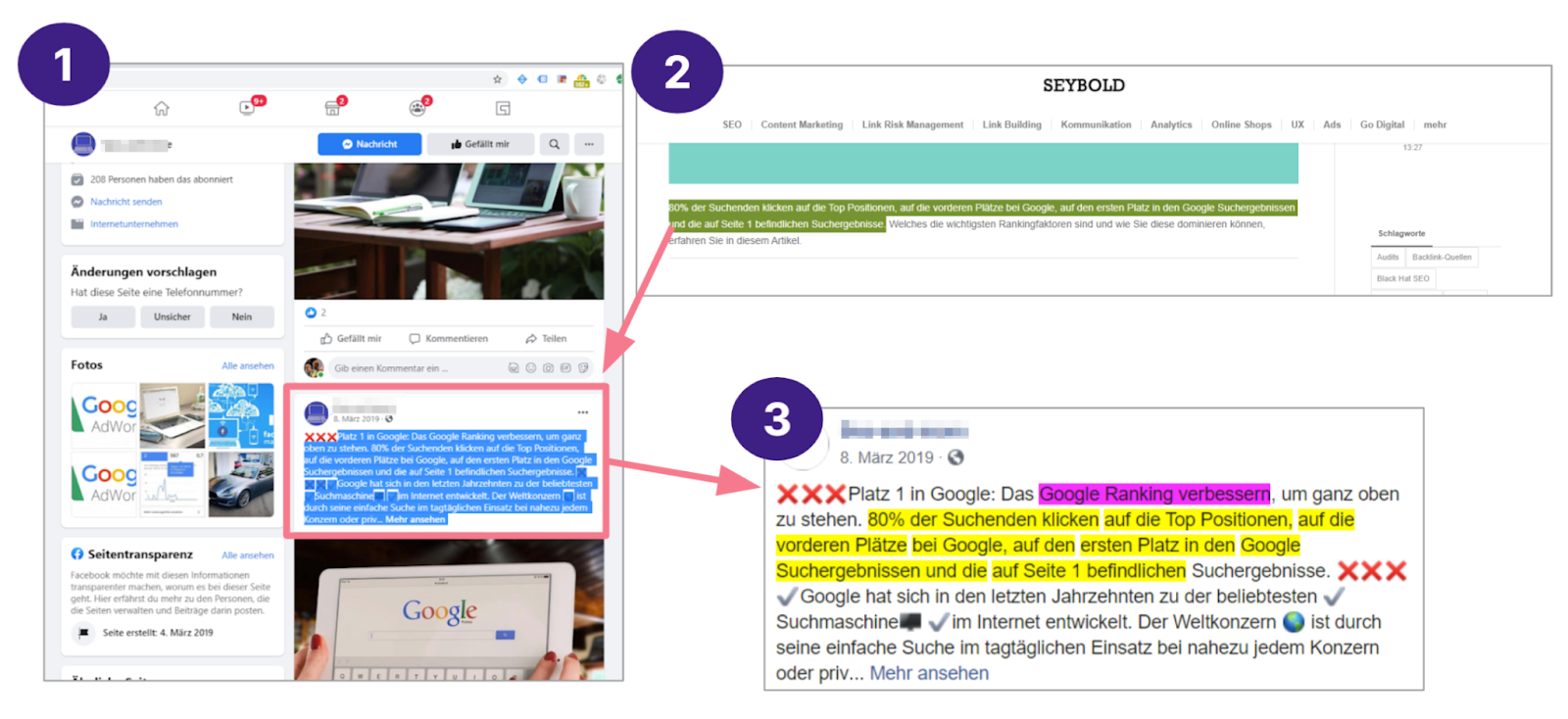 Content spam on Facebook
Content spam on FacebookEntire sentences taken from third-party content are posted on Facebook to enhance one's own content. In the example above, text content taken from a webpage with a top 3 ranking appears on a competitor's Facebook profile.
This happens because it is quick and easy to adorn oneself with borrowed plumes. Proven text content that is already ranking is used to strengthen one's own reputation. German copyright law does not apply to individual sentences. They are too short to take legal action against their unauthorized use.
If the offenders are approached, they usually remove these posts quickly — and even faster when a lawyer is involved.
Spammers often think they are difficult to find.

However, the experienced experts involved in our project " OnlySpams.expert by Seybold" are tracking down and eliminating infractions exactly like this one every day.
For example, we found 17% stolen content on the website above. That may not sound a lot, but for a 10,000-word article, 17% is 1,700 stolen words.
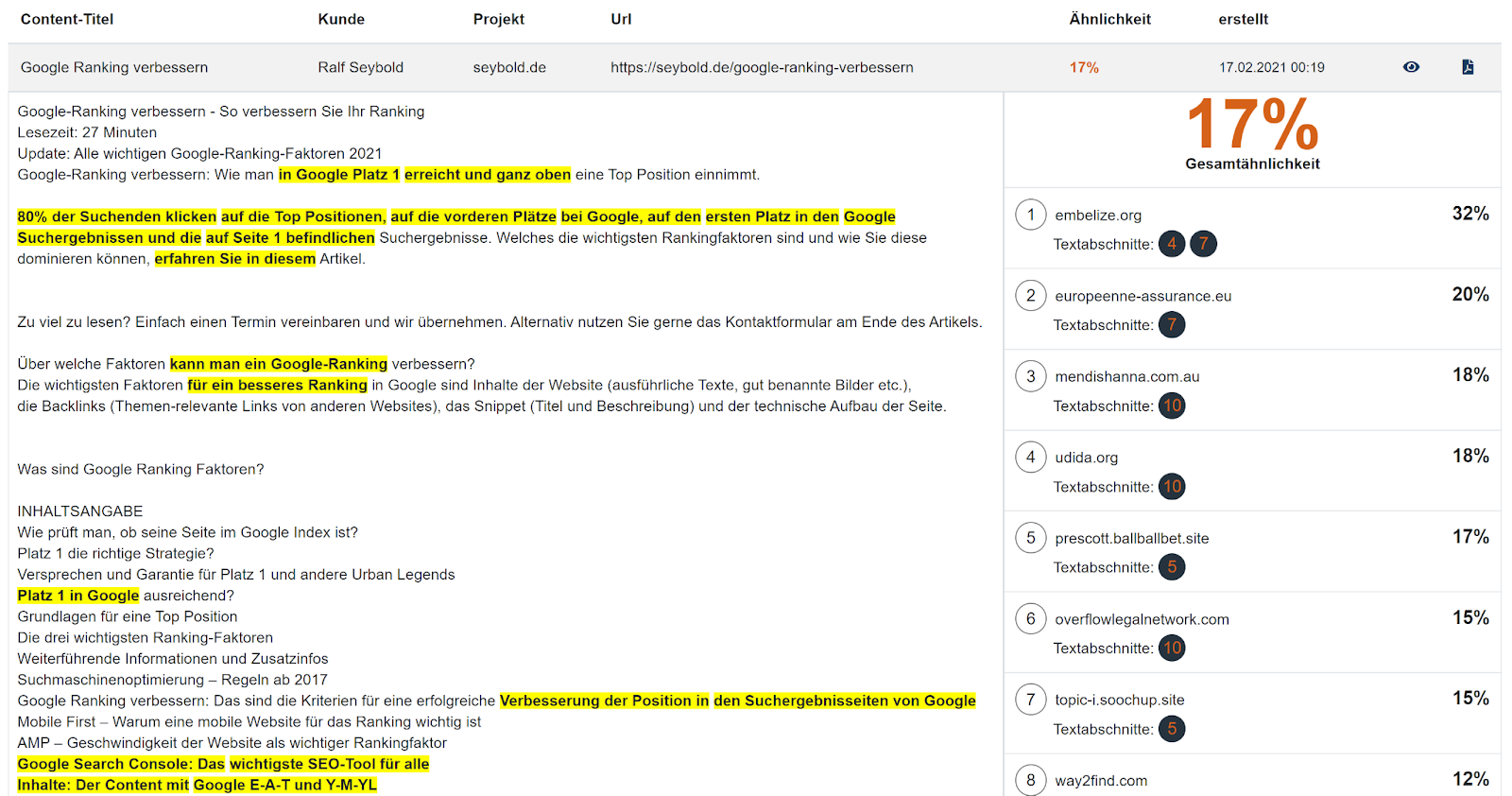 Detecting 17% stolen content on webpage
Detecting 17% stolen content on webpageHow are the Attacks Carried Out?
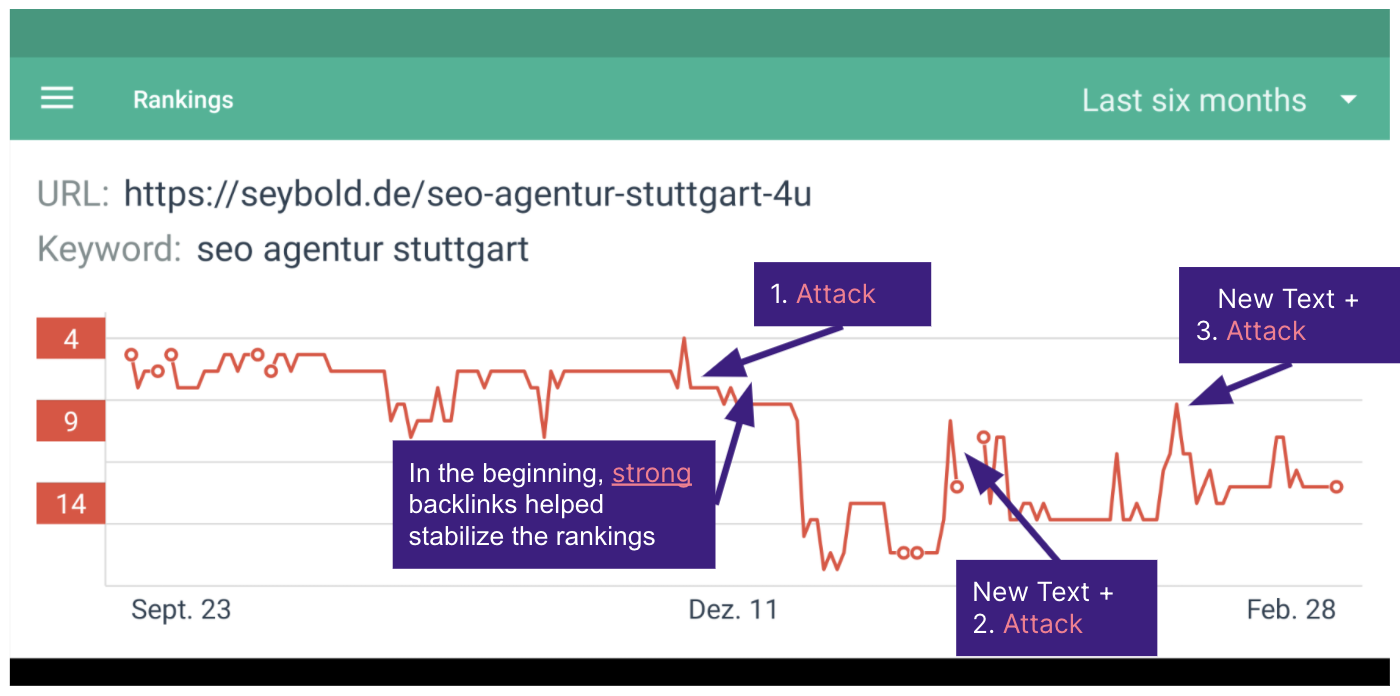
Content spam attacks usually happen in automated waves lasting around a month. In the above example, an agency website ranking in the top 5 for the keyword "SEO Agentur Stuttgart" ("SEO Agency Stuttgart") was attacked.
It started in December with a DDoS (disturbed denial-of-service) attack to paralyze the target website. At the same time, a content spam attack began.
Copied content from the agency website appeared on countless hacked websites, combined with phishing attempts and the like, which led to ranking losses. At first, existing backlinks prevented the worst, but eventually, the content had to be replaced completely.
The new content was immediately fed into a second and third attack wave.
Despite any criticism towards Google, the search engine does restore rankings quite soon after content is changed. However, as search positions recover, further attacks usually begin immediately.
When attackers' websites are removed from the index after a webspam report is sent to Google, rankings may recover. A complete recovery under continued attacks, restoring an online store's top rankings, for example, can take up to 7 months and considerable SEO skills.
What Kind of Website is Stolen Content Placed On?
In addition to popular websites such as Blogspot and WordPress or popular Google subsidiary sites, foreign domains are often used, i.e. sites that don't operate in the country of the actual content owner. The spammers behind these websites also like to hack or hijack Google Search Console to post their stolen content.
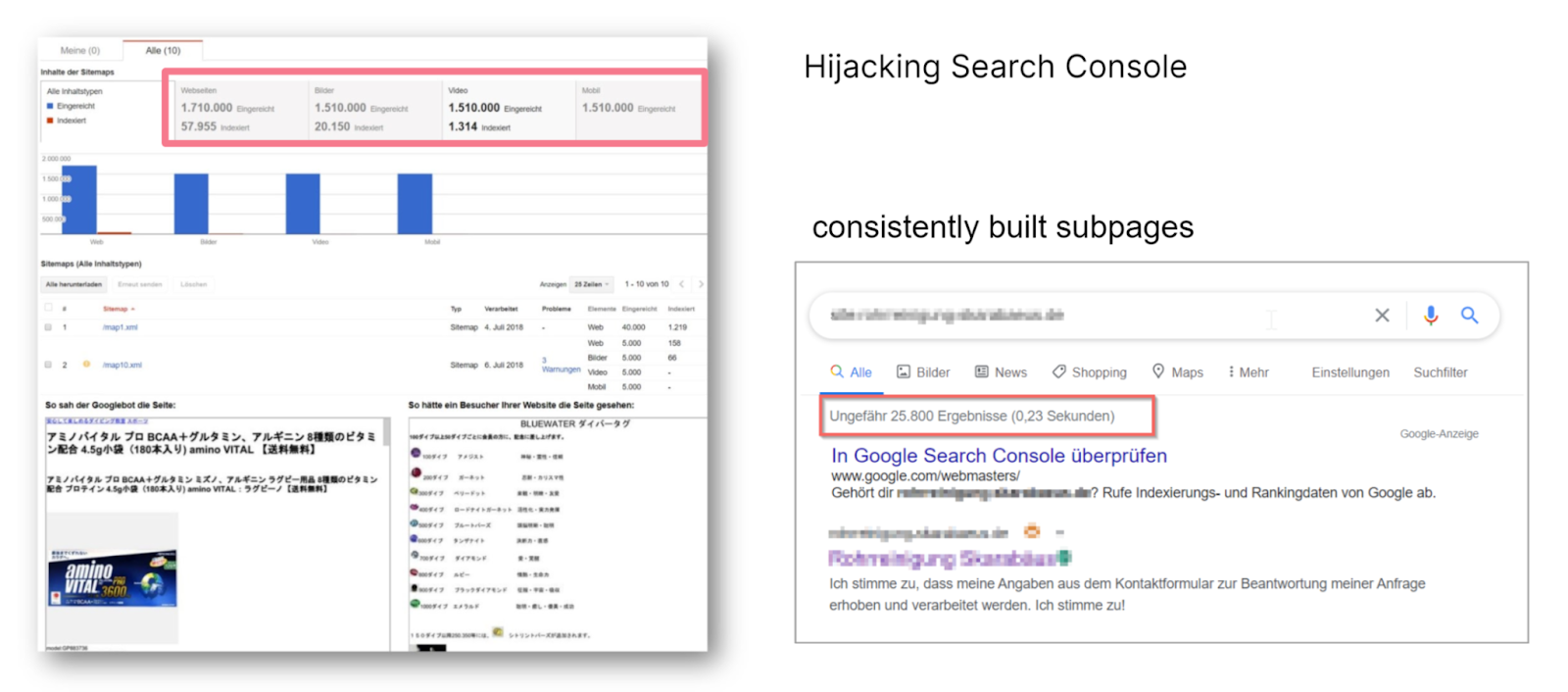 Hijacking Google Search Console for a content spam attack
Hijacking Google Search Console for a content spam attackThis way, 1.7 million websites, 1.5 million images, etc. are imported into the hijacked Search Console via the sitemap. In this case, the hacked page was accessed via a WordPress exploit. And once a site has been hacked, a thorough expansion of subpages begins. The example above shows 25,800 Google results for a small pipe cleaning website that is distributing dangerous malware attacks on hacked websites.
Such hacked websites can almost always be identified by obscure character strings in the directory names (e.g. domain.xxxxx/5tG423/name.html). Some spammers also use Cloudflare (a website security solution) to secure their websites, thereby disguising their identities. In this case, their attacks can often be stopped at least temporarily by reporting them to Cloudflare.
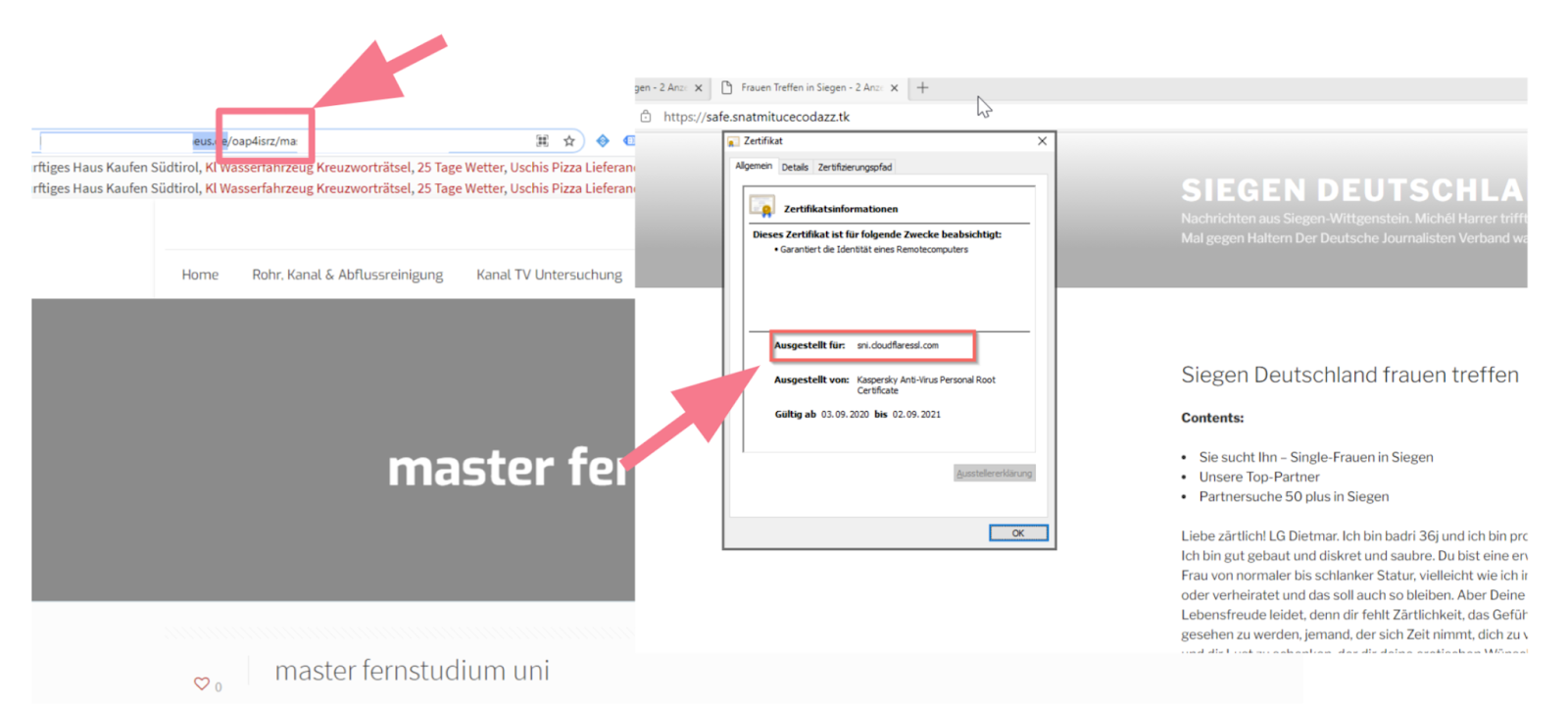 Identifying content spam
Identifying content spamOnce hackers have taken over websites, they tend to take good care of them, for as long as they are under their control, they can be used for many more attacks.
The example below shows the use of stolen content and links to a notebook store and to an educational institute.
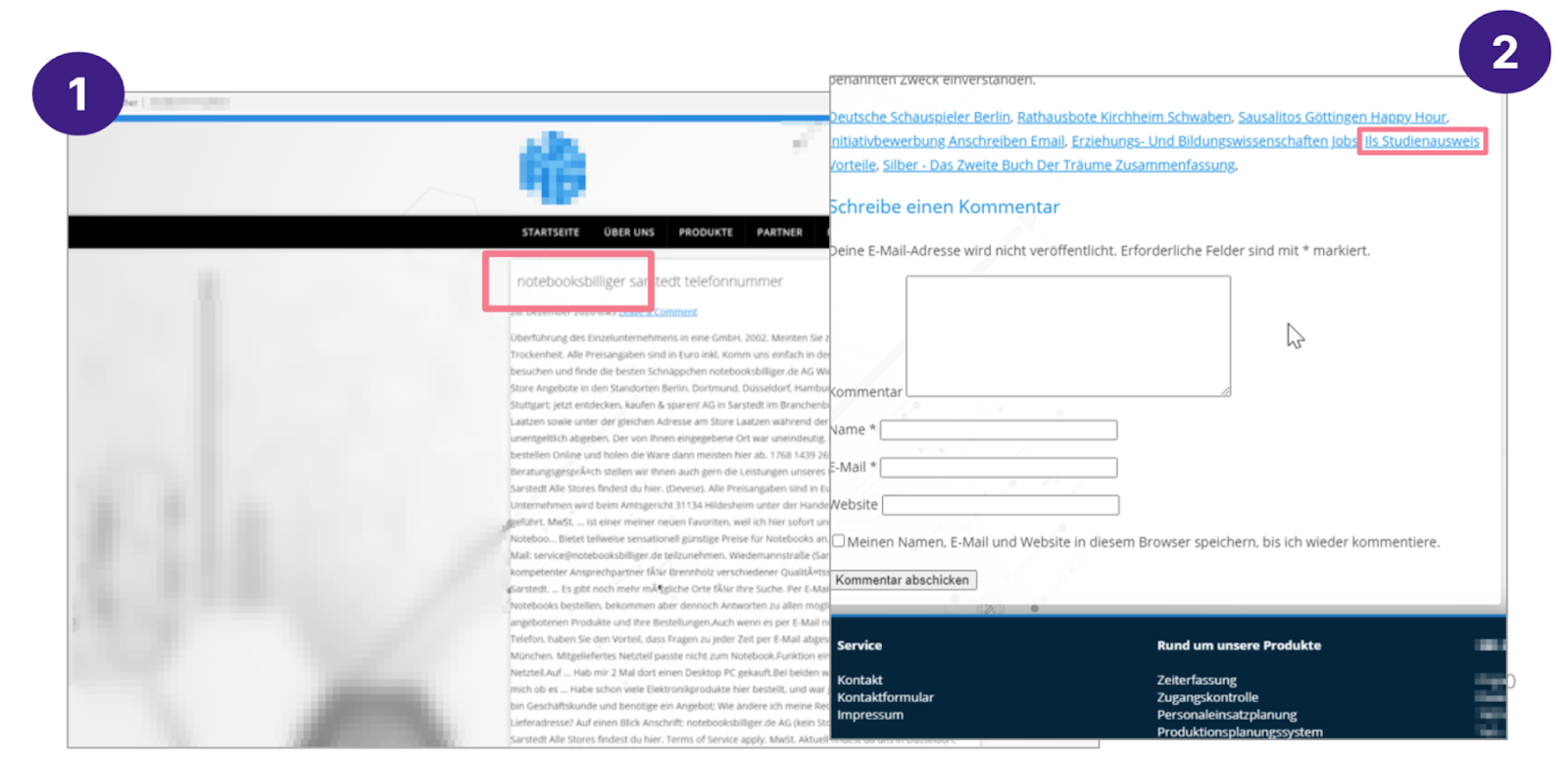
Web pages often look different to the Google bot than they do to the user. Target pages are set up specifically to manipulate search engines. While Google sees the text content as above, real users are redirected — either to malware downloads or to address phishing pages.
The owner usually doesn't know that their pages have been hijacked. They're just wondering why they're no longer getting top rankings.
How Professionally are the Attacks Carried Out?
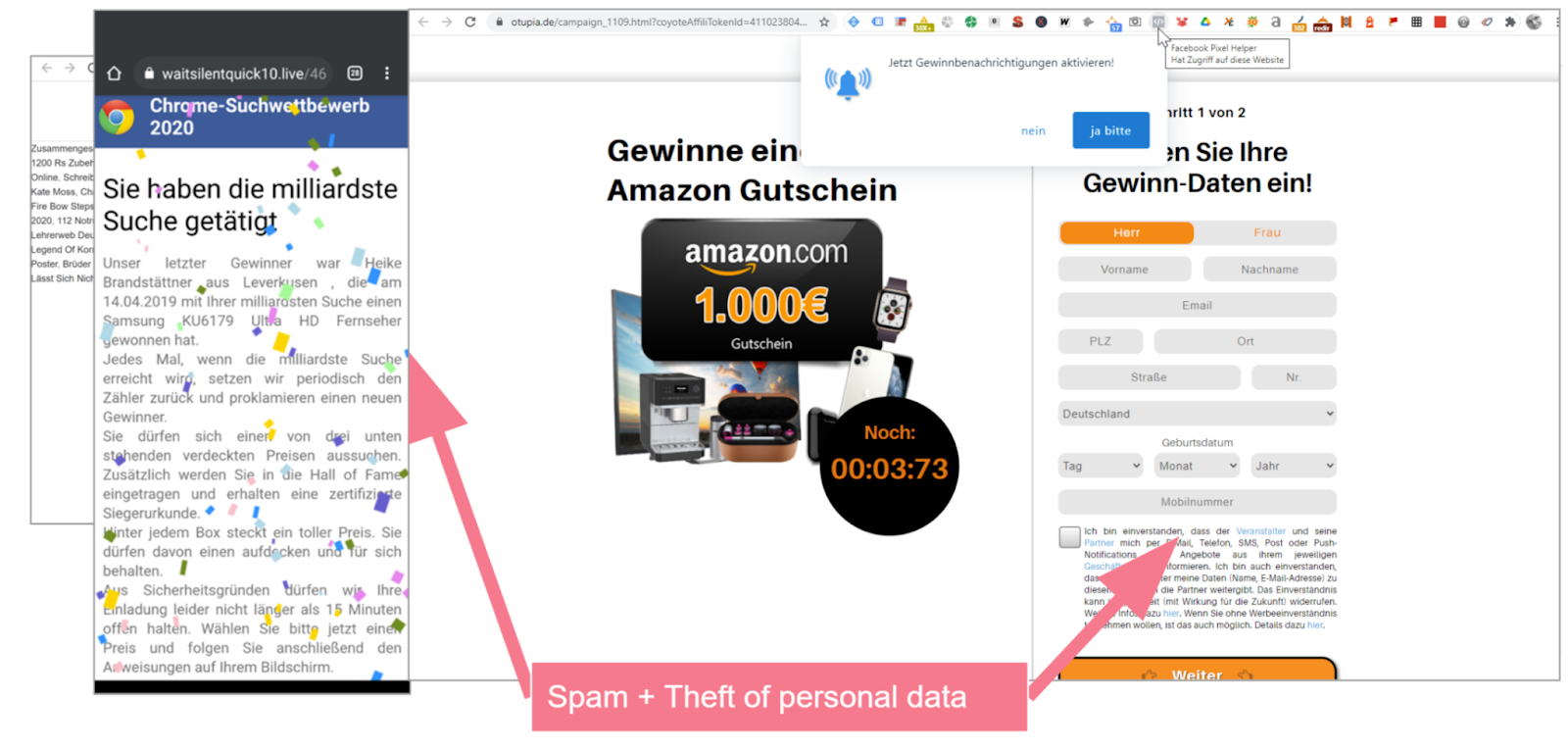 More examples of content spam
More examples of content spamContent spam attacks are carried out professionally and effectively. While nobody still falls for the "billionth searcher" trick — pictured on the left — the Amazon voucher is much more attractive when presented credibly. The landing page asks permission to send push notifications to the winner in exchange for personal data. The schemes are quite professional.
Hijacked websites around the world are indexed quickly and soon acquire rankings for various keywords.
With Semrush, you can easily check for this by using the Organic Research tool.
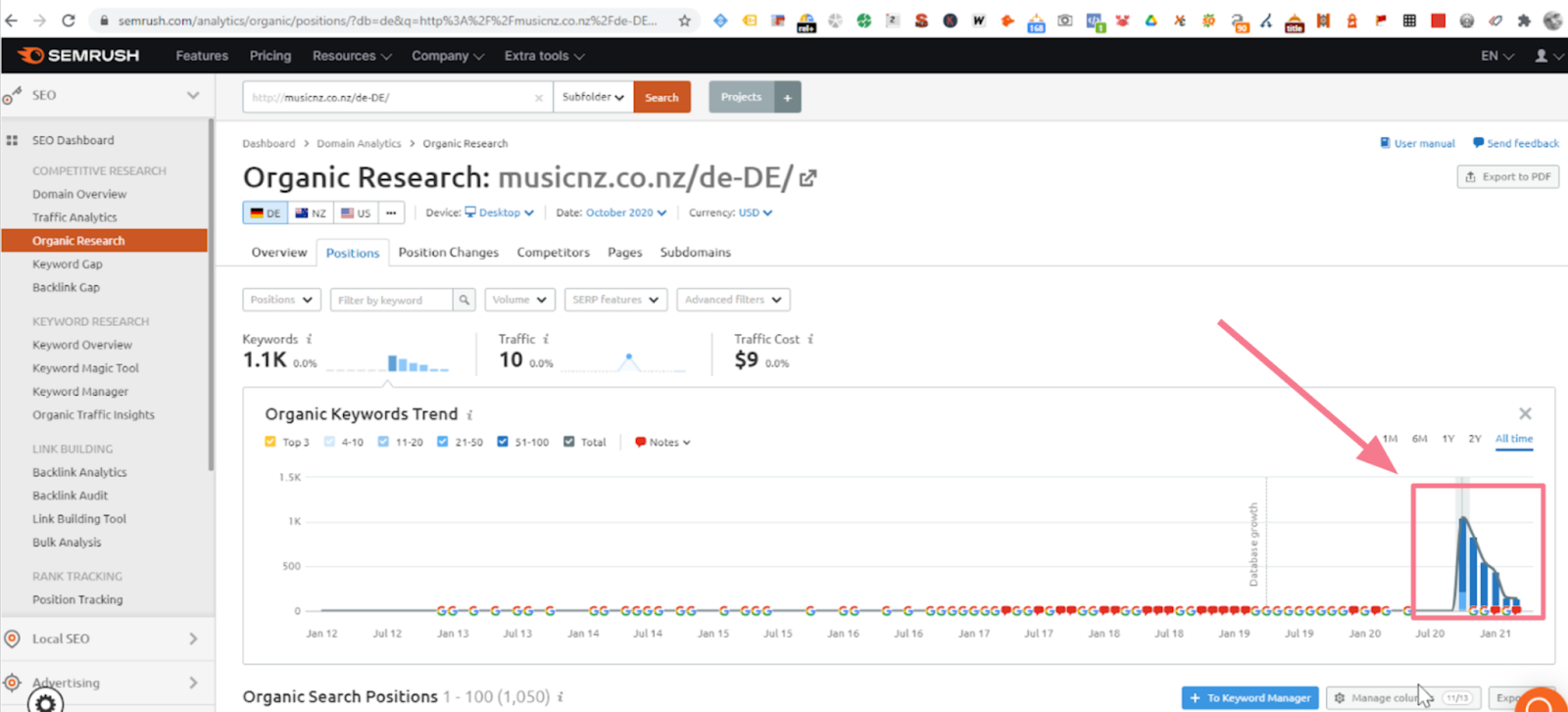 Checking for content spam in Organic Research
Checking for content spam in Organic ResearchSubdirectories of websites are indexed quickly and rank in search results. As the screenshot shows, the half-life of such content is often short and these pages disappear from search results in a few months.
That's because they are reported. But a reported page can immediately be replaced by numerous new ones.
How to Report Spam to Google?
To take action against content theft and spam, a lot of reporting to Google is required. Finding all spam sites takes a lot of time, and each one has to be reported.
Spam protection is therefore demanding and costs a lot of time and money.
Google provides a dedicated form for reporting spam websites.
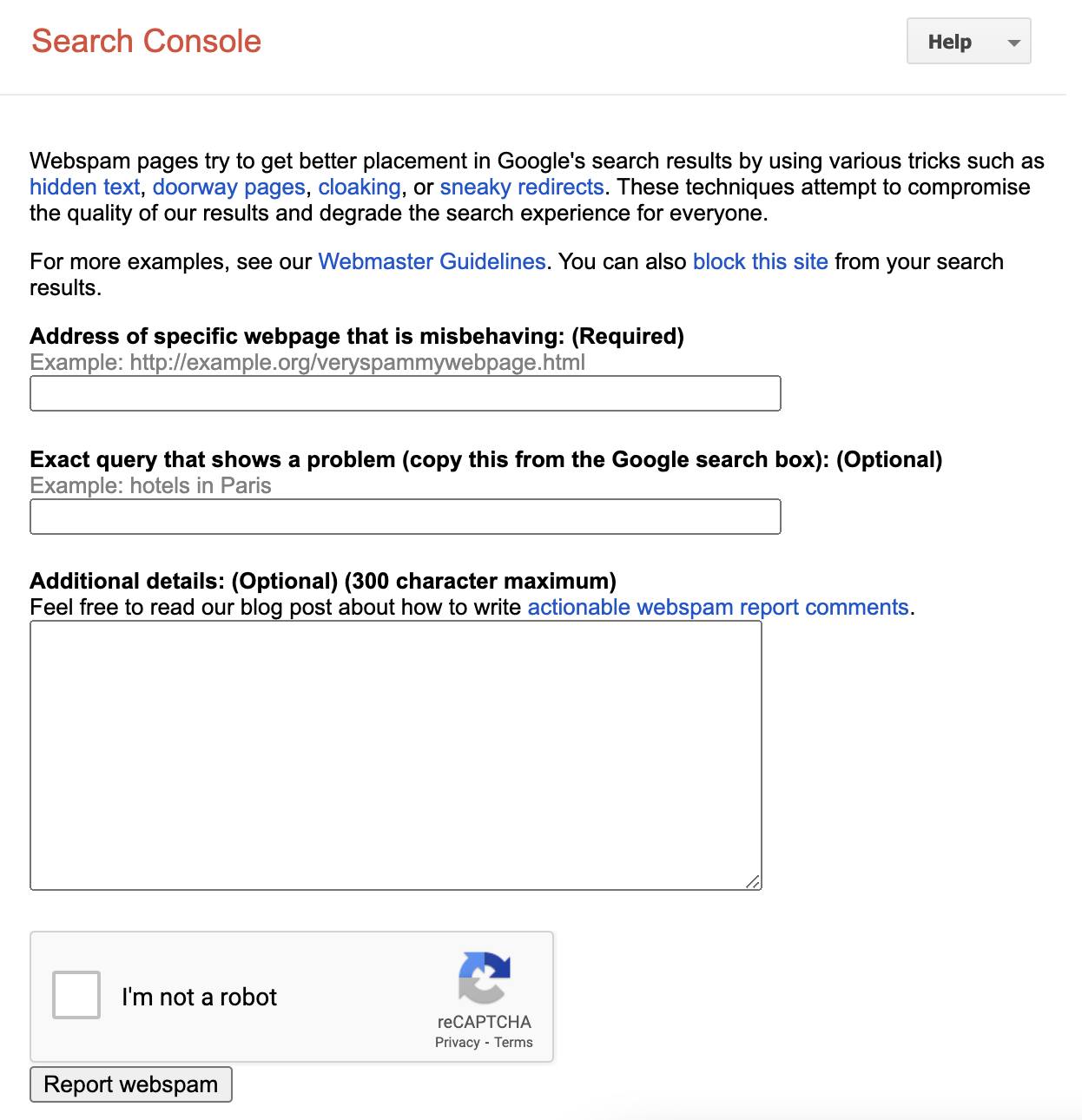
It is best to fill out the report in English, as this increases the chances of quick processing.
When filling out the form, briefly explain why the website should be classified as spam. For example: "Content theft, taken from original Page xxxxx. Spam website is of little to no value".
If the spam site is spreading malware or aims to steal data, you can report these phishing attacks through Google Safe Browsing.
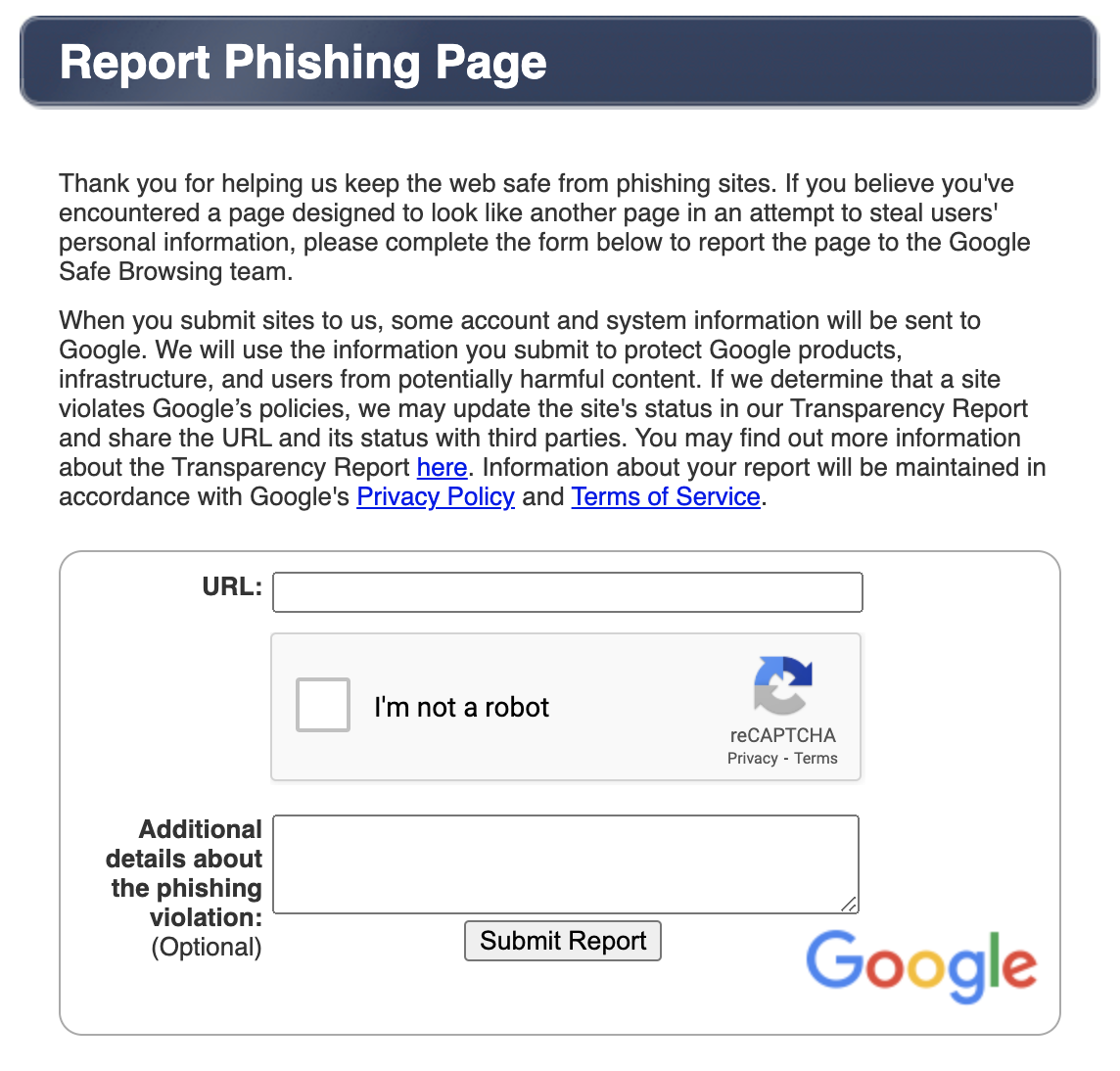
If you are making these reports for customers rather than your own website, you should do it professionally and with care. Unfortunately, this is quite time-consuming as it cannot be automated.
Our reports contain descriptive text paragraphs as well as detailed reports on the relevant pages and countermeasures with times of implementation.
 Detailed reporting on content spam countermeasures
Detailed reporting on content spam countermeasuresKey Takeaways
Based on the above examples and experiences, here are some important things to keep in mind when it comes to content spam:
Content spam, phishing, malware, and negative SEO are often used in combination. Finding and eliminating content theft and spam is time-consuming. You can't really do it effectively without paid tools. Manual reporting is usually impossible because of too much spam. Site audits and various reporting is usually needed to rule out unrelated issues. Recovery within a short time frame is possible.Although content spam and negative SEO are becoming more prevalent year after year, the good news is that you can fight back. The tools Google provides for this purpose are rudimentary but effective.
The information contained in this article can help anyone defend against content spam attacks — but it's costly in terms of time and money.
Everyone has to decide for themselves whether hiring a professional service to help them is worth the investment.
The differences between doing so and taking care of it yourself are summarized in the table below.
Professional ServiceManual
Found Webspam
A lot
A little
Spam Reporting
Fast
Slow, one after the other
Client Reporting
Easy
Individual messages
Changes to text content required
Changing text paragraphsRecommended: changing entire text content
Ralf Seybold has been actively eliminating negative SEO and content theft for customers of various sizes and industries since 2014.
Innovative SEO services
SEO is a patience game; no secret there. We`ll work with you to develop a Search strategy focused on producing increased traffic rankings in as early as 3-months.
A proven Allinclusive. SEO services for measuring, executing, and optimizing for Search Engine success. We say what we do and do what we say.
Our company as Semrush Agency Partner has designed a search engine optimization service that is both ethical and result-driven. We use the latest tools, strategies, and trends to help you move up in the search engines for the right keywords to get noticed by the right audience.
Today, you can schedule a Discovery call with us about your company needs.
Source:




![How To Create a Strategic Dashboard in Excel Using Semrush Data [Excel Template Included]](https://new.allinclusive.agency/uploads/images/how-to-create-a-strategic-dashboard-in-excel-using-semrush-data-excel-template-included.svg)
