Looking for a complete SEO checklist that will help you to increase your site’s organic traffic and rank on Google? Look no further.
We’ve put together the ultimate checklist that you need to drive SEO success, covering 41 best practice points and tasks that you need to know about.
From the SEO basics to must-knows when analyzing your off-page signals, use this as your go-to reference point.

Download a copy of the checklist here.
How to Use This SEO Checklist
We’ve broken this checklist down into sections that cover the main focus areas of SEO:
SEO basics Keyword Research Technical SEO On-page SEO Content Off-page SEOYou’ll need to focus on all of the above for a holistic SEO strategy. Make your way through our checklist to ensure you’re following SEO best practices in each area.
By implementing best practices and resolving any current issues, you’ll likely have a better chance at SEO success.
SEO Basics Checklist
Still learning exactly what SEO is? If you haven’t got the basics covered, your site may struggle to rank for competitive terms.
The following points are very much housekeeping tasks but form the basics of implementing a successful SEO strategy.
1. Set Up Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools
Google Search Console is an essential tool that provides you with invaluable insights into your site’s performance as well as a wealth of data that you can use to grow your site’s organic visibility and traffic.
You can learn more about why it is so important to use, how to set it up, and more in our definitive guide.
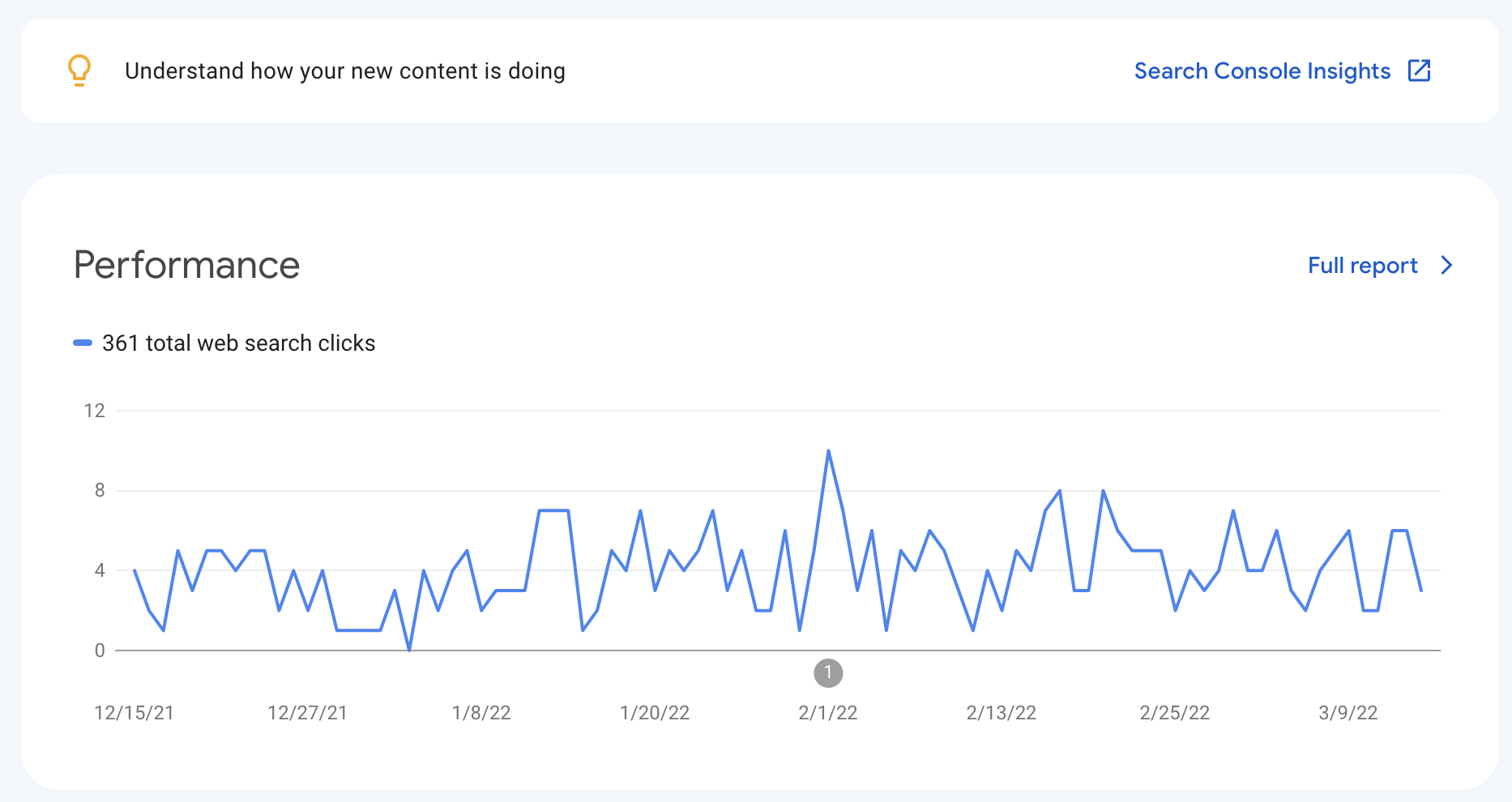
Bing Webmaster Tools is the equivalent platform, providing data and insights for their search engine.
These all-important tools allow you to view the search terms and keywords that users are finding your site on the SERPs for, submit sitemaps, identify crawl errors, and much more.
If you have not got these set up, do so now, and thank us later.
2. Set Up Google Analytics
Without the right data, you can’t make the right decisions.
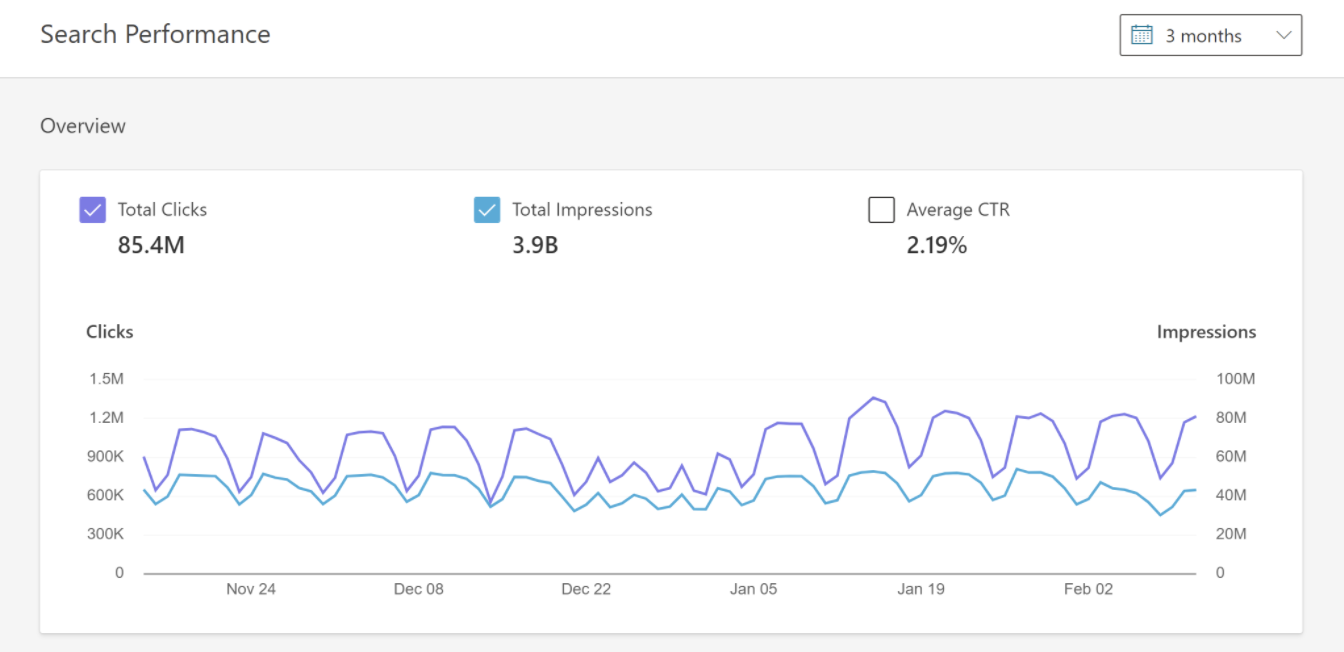
Google Analytics is a free marketing analytics tool that allows you to view data and insights about how many people are visiting your site, who they are, and how they are engaging with it.
Our Google Analytics guide will walk you through everything you need to know about the tool as a beginner, including how to set it up and the reports that you will find the most useful, but one this is for sure, and that is that you can’t run a successful SEO strategy without it.
You will also need to connect Google Analytics and Google Search Console to import data from the latter.
3. Install and Configure an SEO Plugin (If You’re Using WordPress)
If you are using WordPress as your CMS (which there is a pretty good chance that you are, given that it now powers 39.5% of the web), you should install and configure an SEO plugin to provide the functionality and features that you need to properly optimize your site.
In our WordPress SEO checklist, we have SEO plugin suggestions for you. Whichever plugin you choose pretty much comes down to personal preference, but these are three great options.
If you are using a different CMS to WordPress, speak with your developer to see whether you need to install a dedicated SEO plugin or module or whether the features that you need are included out of the box.
Plug in SEO, as an example, is one of the most popular Shopify SEO apps.
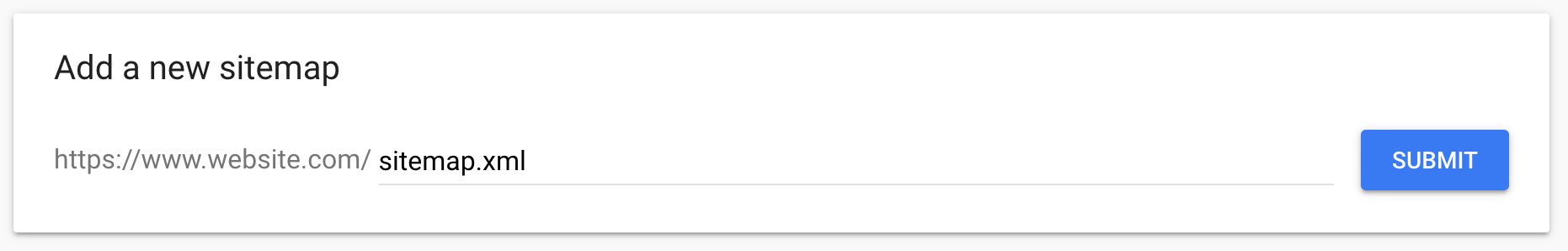
4. Generate and Submit a Sitemap
The purpose of a sitemap is to help search engines decide which pages should be crawled and which the canonical version of each is.
It is simply a list of URLs that specify your site’s main content to make sure that it gets crawled and indexed.
In Google’s own words:
A sitemap tells the crawler which files you think are important in your site, and also provides valuable information about these files: for example, for pages, when the page was last updated, how often the page is changed, and any alternate language versions of a page.
Google supports a number of different sitemap formats, but XML is the most commonly used. You will usually find your site’s sitemap at https://www.domain.com/sitemap.xml.
If you’re using WordPress and one of the plugins mentioned above, you’ll find that generating a sitemap is standard functionality.
Otherwise, you can generate an XML sitemap with one of the many sitemap generator tools that are available. In fact, we recently updated our ultimate guide to sitemaps, which includes our top recommendations.
Once you have generated your sitemap, make sure that this is submitted to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
Make sure to also reference your sitemap in your robots.txt file.
5. Create a Robots.txt File
Quite simply, your site’s robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers the pages and files that web crawlers can or can’t request from your site.
Most commonly, it is used to prevent certain sections of your site from being crawled and is not intended to be used as a way to de-index a webpage and stop it from showing on Google.
You can find your site’s robots.txt file at https://www.domain.com/robots.txt.
Check whether you already have one in place.
If you don’t, you need to create one—even if you are not currently needing to prevent any web pages from being crawled.
Several WordPress SEO plugins allow users to create and edit their robots.txt file, but if you are using a different CMS, you might need to manually create the file using a text editor and upload it to the root of your domain.
You can learn more about how to use robots.txt files in this beginner’s guide.
6. Check Search Console for Manual Actions
In rare instances, you might find that your site has been negatively affected by having a manual action imposed upon it.
Manual actions are typically caused by a clear attempt to violate or manipulate Google’s Webmaster Guidelines—this includes things like user-generated spam, structured data issues, unnatural links (both to and from your site), thin content, hidden text, and even what is referred to as pure spam.
Most sites won’t be affected by a manual action and never will be.
That said, you can check for these in the manual actions tab in Google Search Console.
You will be notified if your site received a manual action, but if you are working on a new project or taking over a site, it should always be one of the first things that you check.
7. Make Sure That Google Can Actually Index Your Website
Part of having your SEO basics covered is making sure that your site can be indexed by Google. It is not as uncommon as you may think that a website isn’t actually able to be indexed by Google.
In fact, you’d be surprised at how often a sudden de-indexing of a site is caused by developers accidentally leaving noindex tags in place when moving code from a staging environment to a live one.
You can use the Site Audit Tool to ensure that your website can actually be crawled and indexed.
Set up a Site Audit for your project. Once you run the audit, you can navigate to the Crawlability report for more insight.
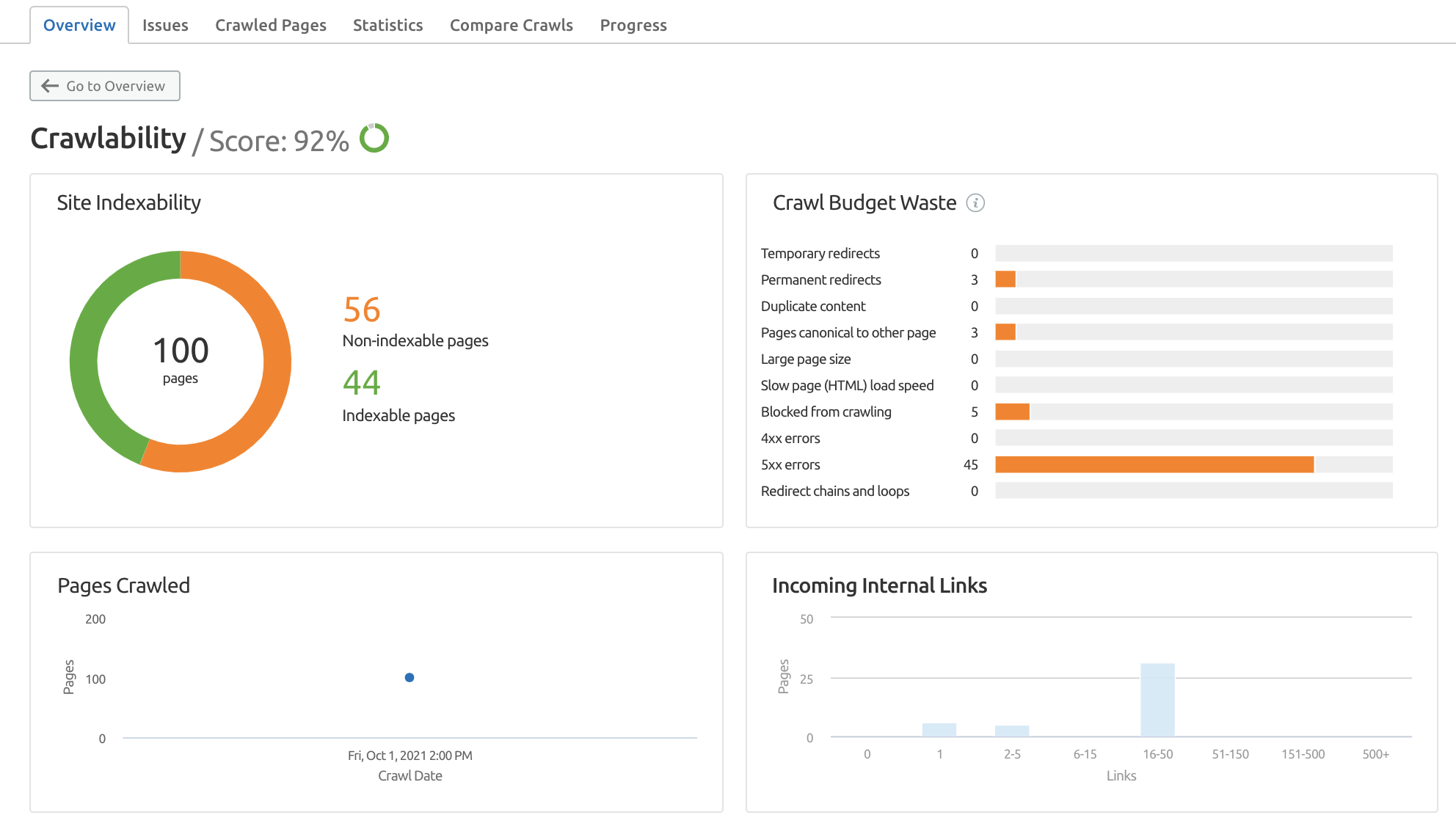
Double checking that your site’s main pages that should be indexed are actually able to be indexed can save a lot of troubleshooting problems if you find issues later down the line.
Unsure if your site is correctly indexed by Google? Let Jason Barnard take you through the steps of properly indexing your website.

Keyword Research Checklist
Without a solid keyword research process, it will be difficult to rank for the right terms. If you are not ranking for the right terms, your traffic isn’t going to convert at the rate it could.
Here is a checklist of the essential keyword research tasks you need to ensure you are covering to see success from your SEO efforts.
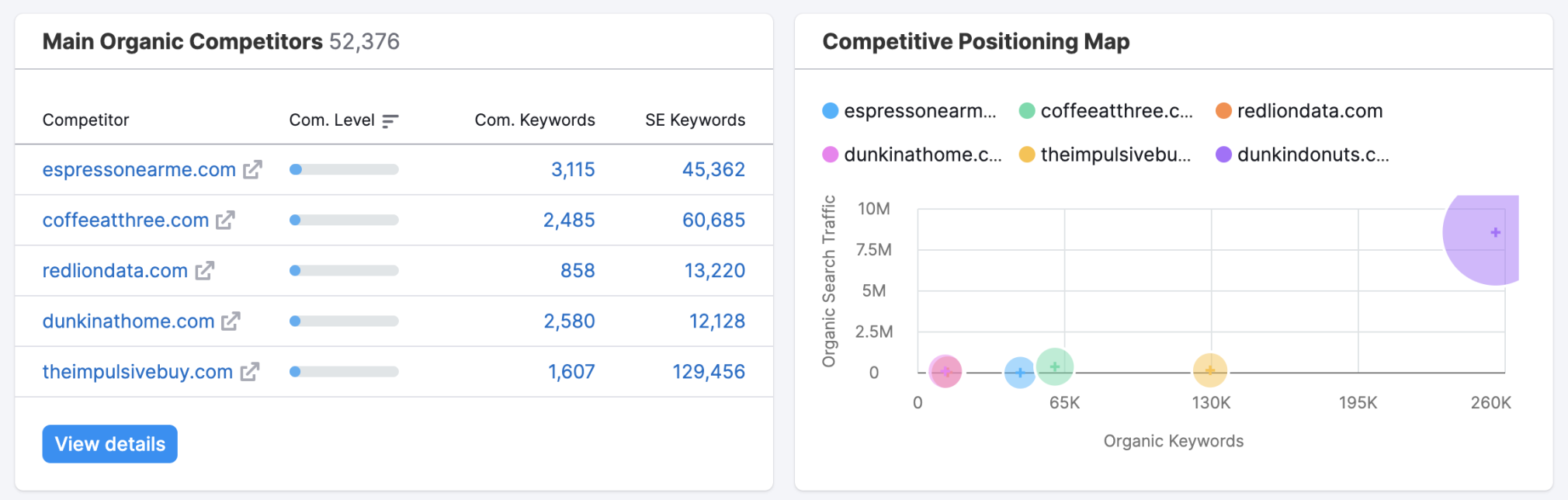
8. Identify Your Competitors
One of the quickest ways to get started with keyword research is to find the terms that are working for your competitors (i.e., competitor keywords).
In our opinion, no time spent doing competitor analysis is wasted time.
Run your own domain (and your key competitors) through the Semrush Domain Overview tool, and you will be able to quickly identify those competitors who are competing in the same space as you are and how your visibility compares.
9. Find Your Main “Money” Keywords
You need to know what your main “money” keywords are. If you hadn’t guessed, these are the ones that are going to drive you leads, sales, and conversions.
You will also find these referred to as head terms and pillar page keywords.
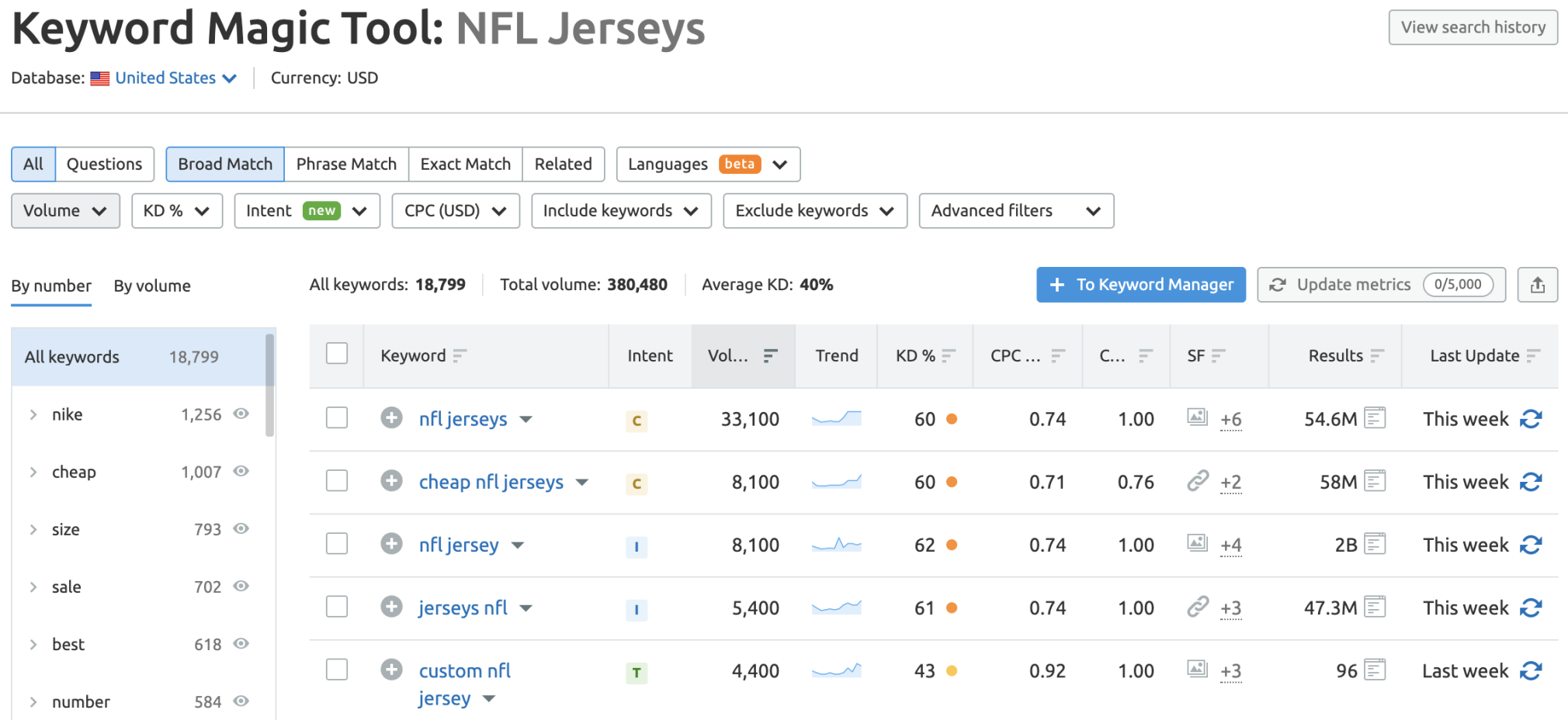
Generally, these are the high volume, high competition keywords that really summarize what you offer, either at a topic or category level. Let’s take the term “NFL Jerseys” as an example—FYI, that is considered a head term.
You can use the Keyword Overview tool to conduct keyword research around your products and services, and identify your head terms.
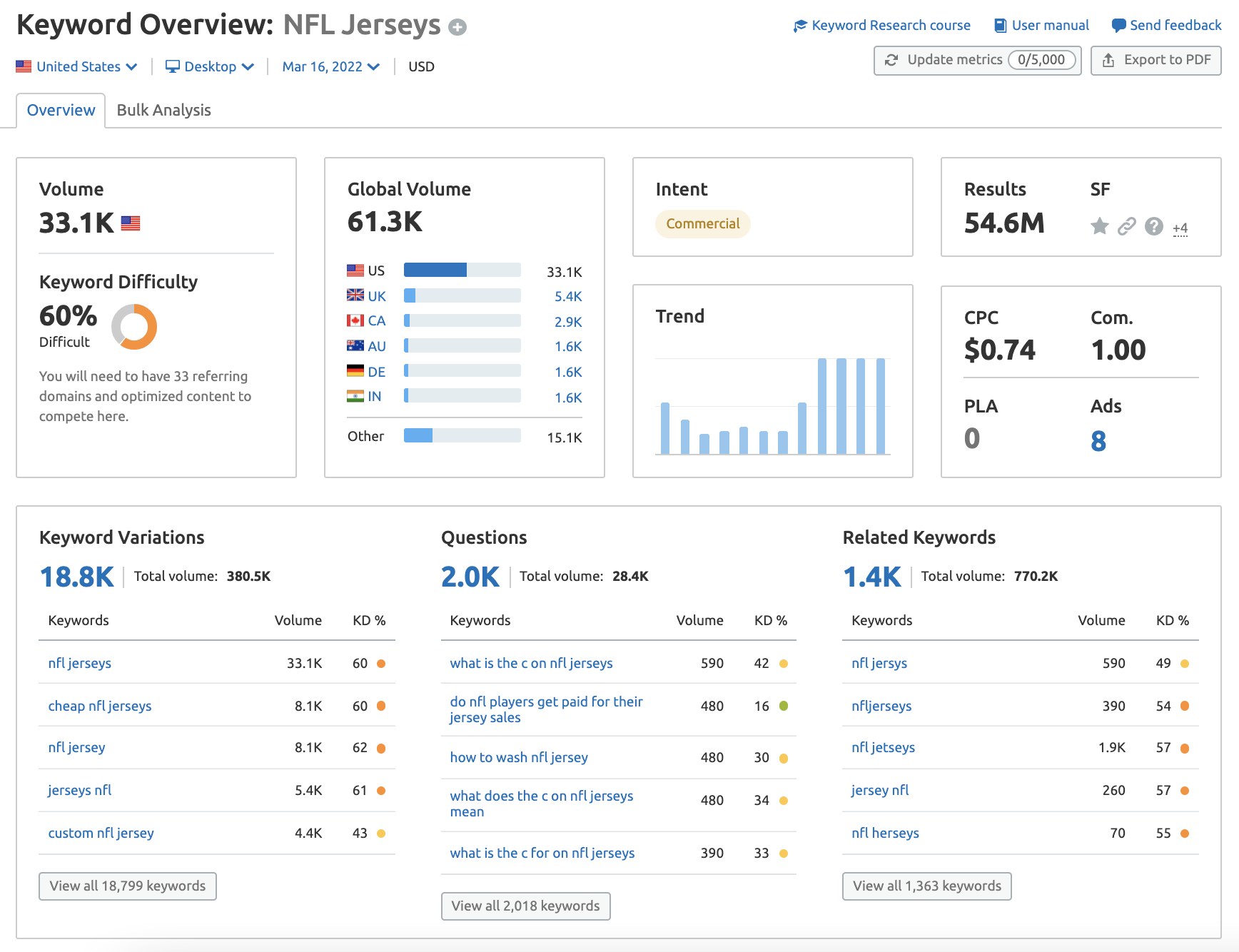
If you’re looking for a comprehensive guide to learn how to pull together a content strategy based on priority terms, check out our ultimate keyword research guide.
10. Find Long-Tail Keyword Variations
A keyword strategy without long-tail keywords isn’t really a keyword strategy.
In fact, long-tail keywords, despite typically being lower volume than head terms, deliver a higher conversion rate.
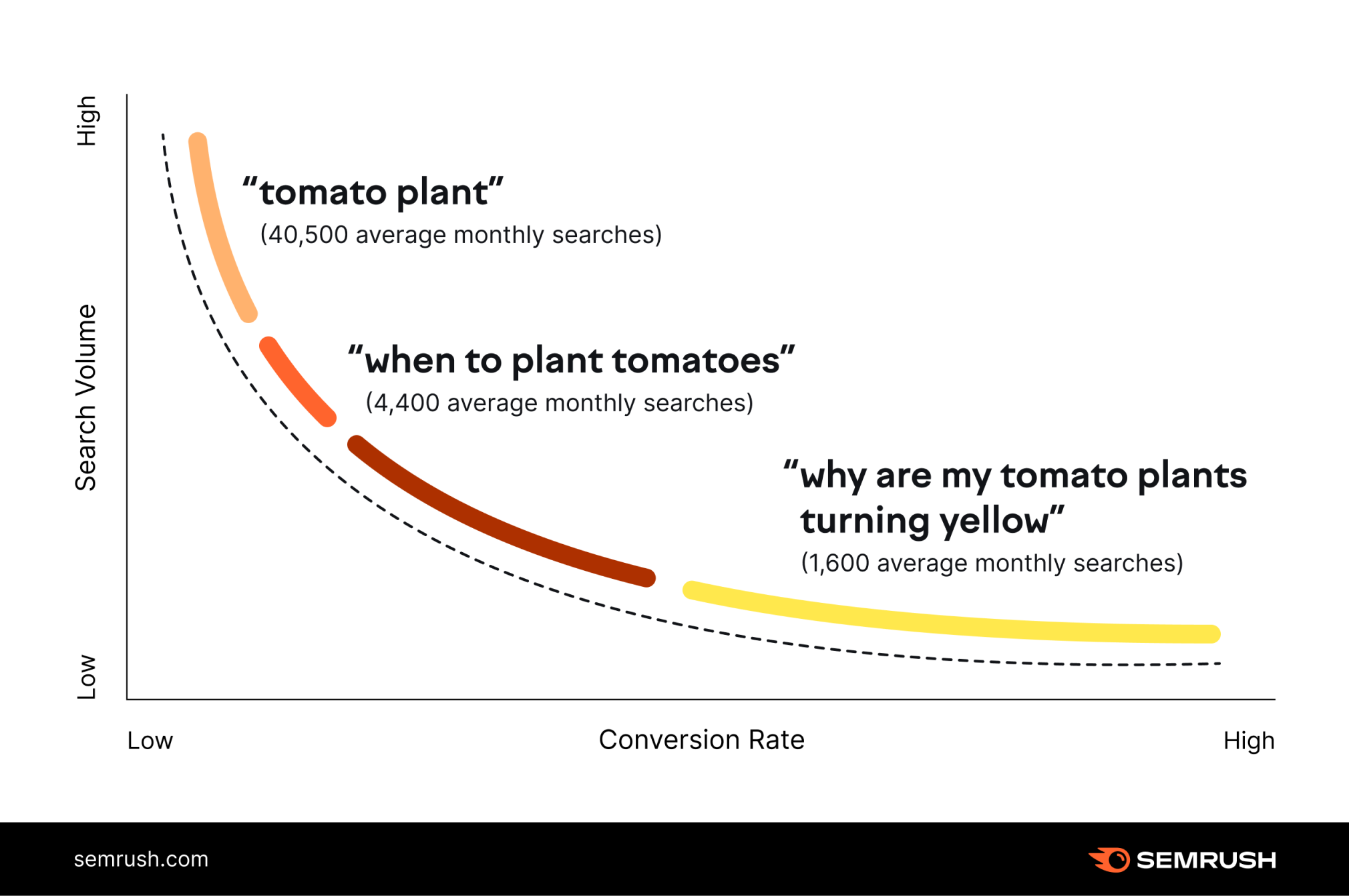
You need to ensure that your SEO strategy targets long-tail keyword variants as well as head terms.
It can be helpful to start by finding what head term you plan to target, then focus on more specific long-tail keywords that are more likely to bring in conversions.
You can use the Keyword Magic Tool to help you find long-tail keywords.
Simply enter your main keywords and choose your country, and the tool will return a list of keywords where you can modify the match type by broad, phrase, exact, or related keywords.
11. Create a Keyword Map
Once you have identified your target keywords, you need to “map” or pair these to pages on your site and also identify any gaps.
Our guide to keyword mapping outlines it as:
In its simplest form, keyword mapping is a framework for the keywords you have chosen to target that mirrors your site’s structure. Driven by research, the ultimate goals of the map are to help you discover where to optimize, what content to build, and where you can add new pages to attract more traffic.
Andrea Lehr
It’s important that you put in the time to ensure that you’re targeting the right pages with the right keywords, and the process outlined in the guide can help you to get this right first time and use this to power your strategy.
12. Analyze the Intent of Pages That Rank
You need to make sure that your page’s content matches the searcher’s intent.
This means taking the time to analyze the pages that rank for your target terms and making sure that your content aligns.
Let’s say you are looking to target a term at a nationwide level. You might have identified a high search volume and a realistic keyword difficulty, but if the SERPs return local results, you are not going to see yourself ranking in prominent positions.
If you don’t understand the intent of the content that Google is ranking, you won’t be able to ensure that yours aligns.
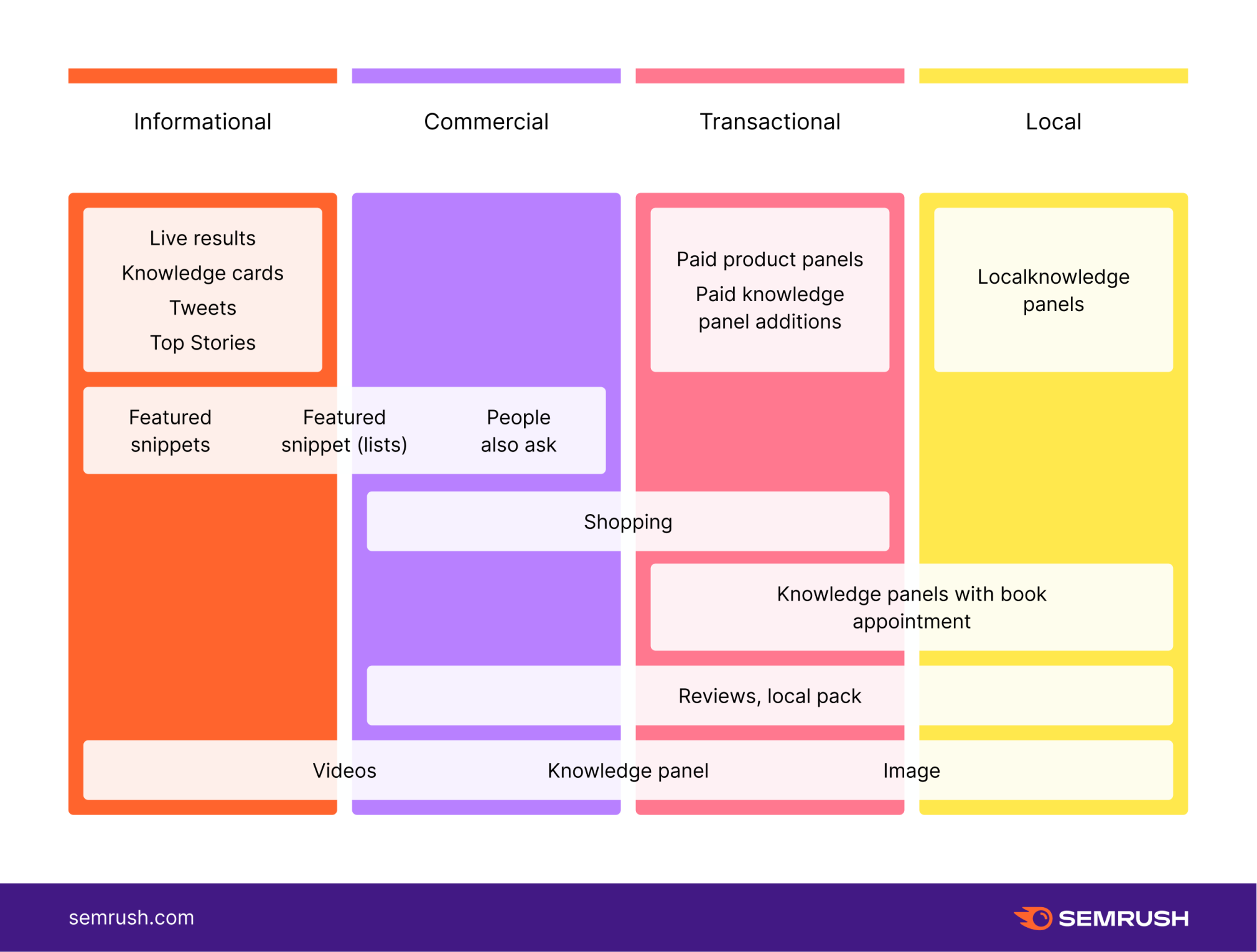
Learn more in this guide on how to identify intent in search and use this handy visual as a starting point to classify search features by intent type:
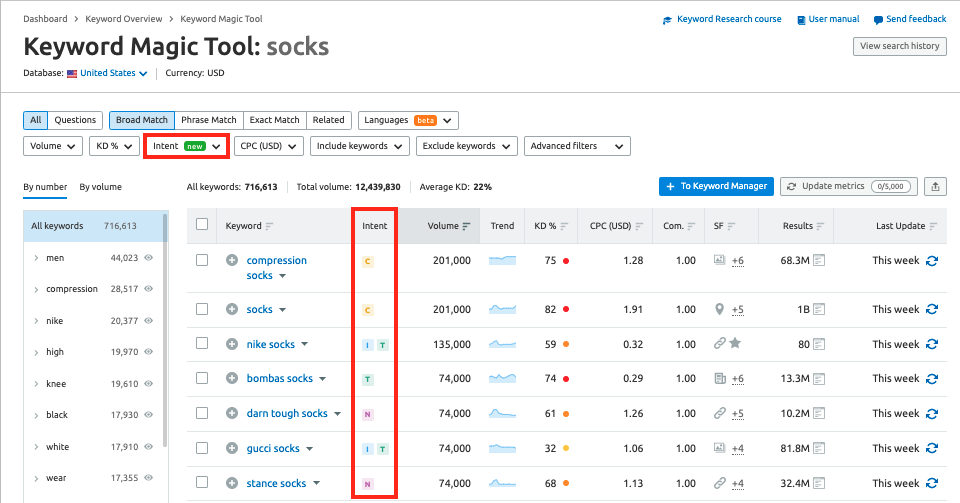
You can also use various Semrush Keyword Research tools to identify the intent of specific keywords.
The intent options vary slightly to help you determine where the searcher is in the buyer journey. Keywords are labeled Navigational, Informational, Commercial, or Transactional.
13. Identify Questions That Are Being Asked
Knowing the questions that your audience are asking can help you to better answer these through your site’s content.
Find a list of related questions for any keyword by busing the Keyword Magic Tool. Input a keyword and filter to "questions" to see results.
This is a great starting point and can provide great inspiration, especially if you enter more specific keywords as a starting point.
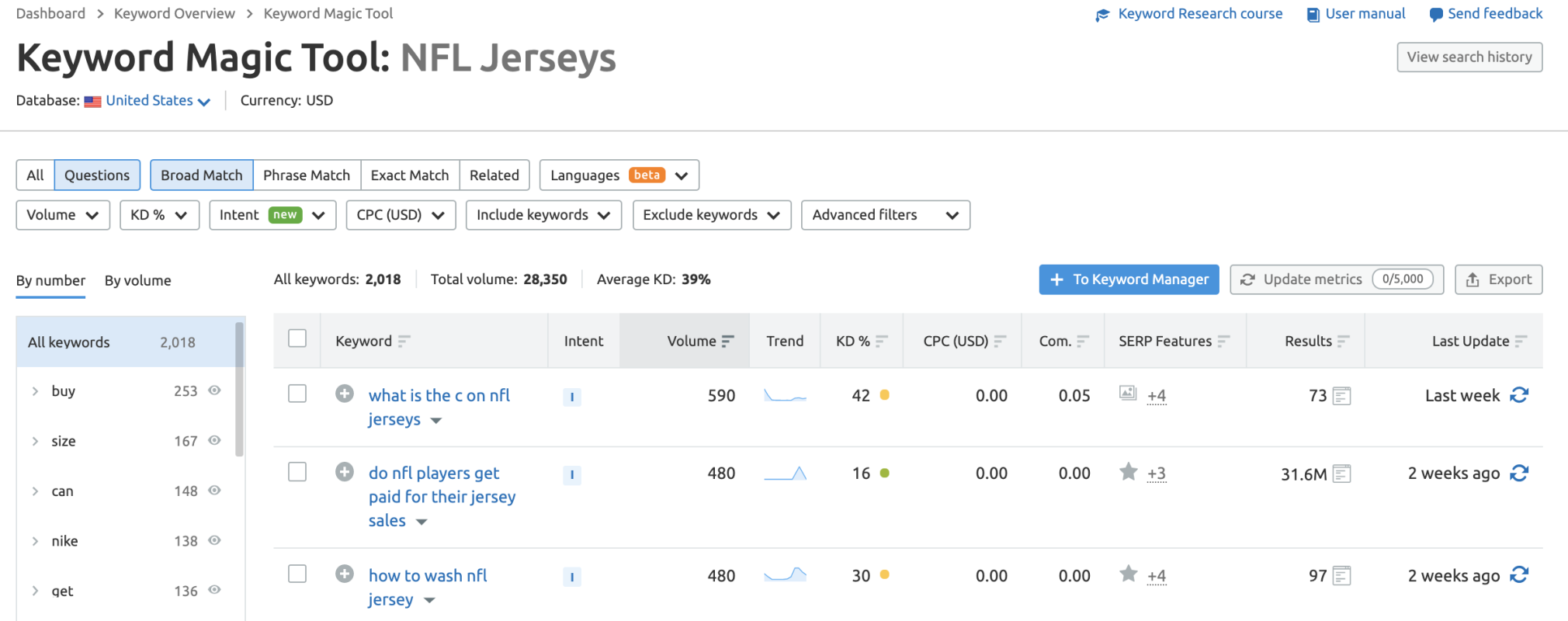
Additionally, you can use a tool like AlsoAsked.com that scrapes and returns “People Also Asked” results to find further ideas and questions to answer with your content.
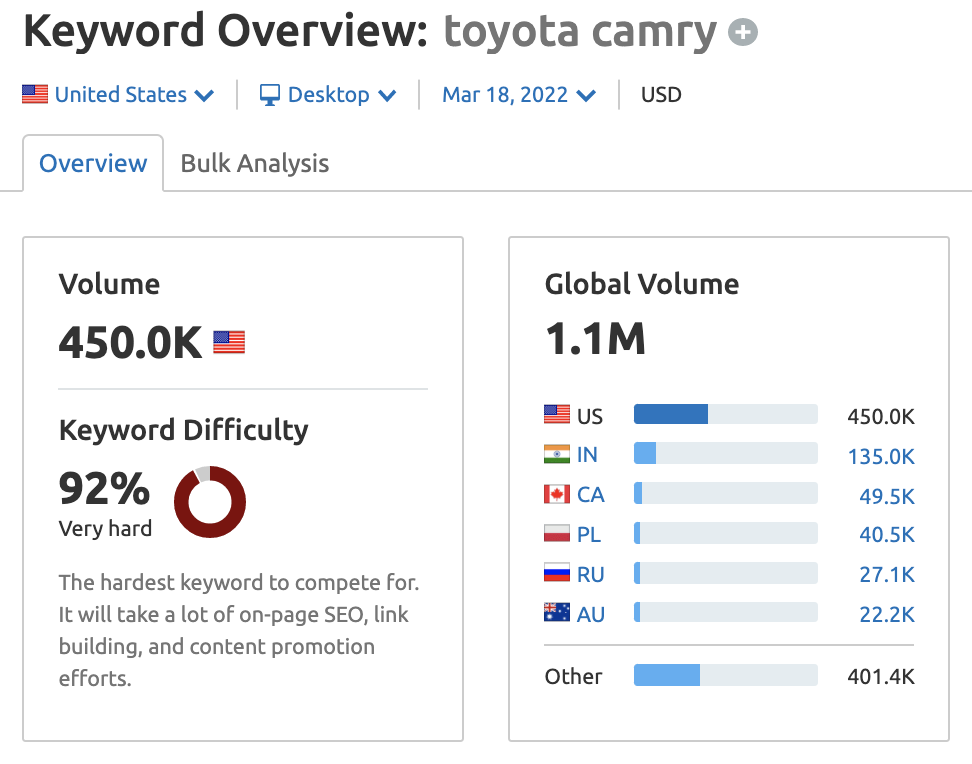
14. Understand How Difficult It Is to Rank for Your Target Keywords
A brand new website may struggle to rank for competitive keywords until it builds authority.
For that reason, you need to gauge the difficulty of keywords you plan to target. This can help manage your own (or your client’s) expectations when you begin your SEO strategy.
For example, a brand new site for a local car dealership will probably struggle to rank for the term “toyota camry.” Instead, it’s a better idea to target long-tail, localized keywords like “toyota camry for sale in san diego.” Local SEO services can help you do this.
Head to a tool like the Keyword Overview Tool (any tool that shows keyword difficulty will do), input your target keywords, and you can see the keyword difficulty; this is how hard it will be for a new website to rank in first page positions.
Technical SEO Checklist
Technical SEO helps you to create solid foundations and ensure that your site can be crawled and indexed.
Here are the most common technical best practices to keep in mind.
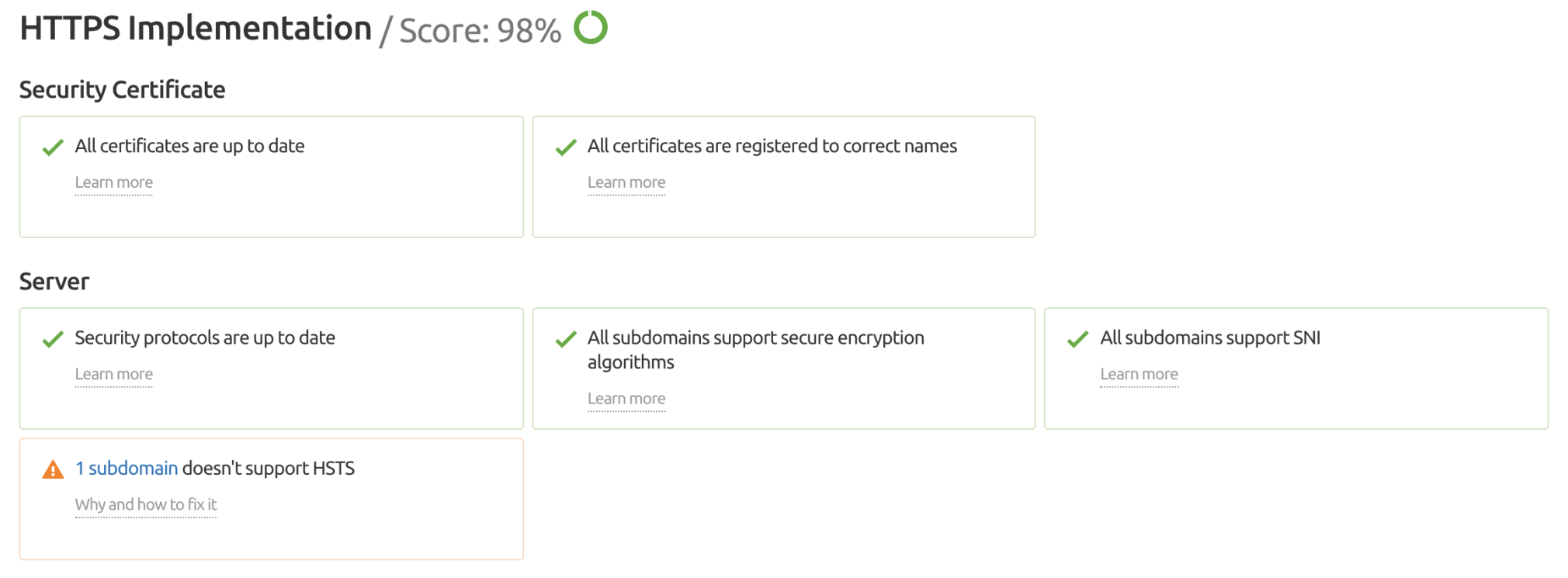
15. Make Sure You Are Using HTTPS
HTTPS has been known as a ranking factor since 2014.
There’s no good reason for not using HTTPS encryption on your site, and if you are still running on HTTP, it's time to migrate.
You can quickly confirm that your site sits on HTTPS by taking a look at your browser’s URL bar.
If you see a padlock to the left of the URL, you are using HTTPS. If you don’t, you are not.
For a more detailed report on possible issues, visit the Site Audit tool and view the dedicated HTTPS report.
16. Check for Duplicate Versions of Your Site in Google’s Index
It's important that you are only allowing Google to index one version of your site.
These are all different versions of your site and should all point to a single one.
https://www.domain.comhttps://domain.comhttp://www.domain.comhttps://domain.comWhether you choose a non-www or www version is up to you, but the most common one is https://www.domain.com.
All other versions should 301 redirect to the primary one, and you can check this by entering each variant into your browser bar.
If you’ve set up redirects without issue but you still find that you can access different versions, implement redirects ASAP.
17. Find and Fix Crawl Errors
You can quickly identify any crawl errors that exist through Google Search Console.
Head to the Coverage report, and you will see both errors and excluded pages, as well as those with warnings and those which are valid.
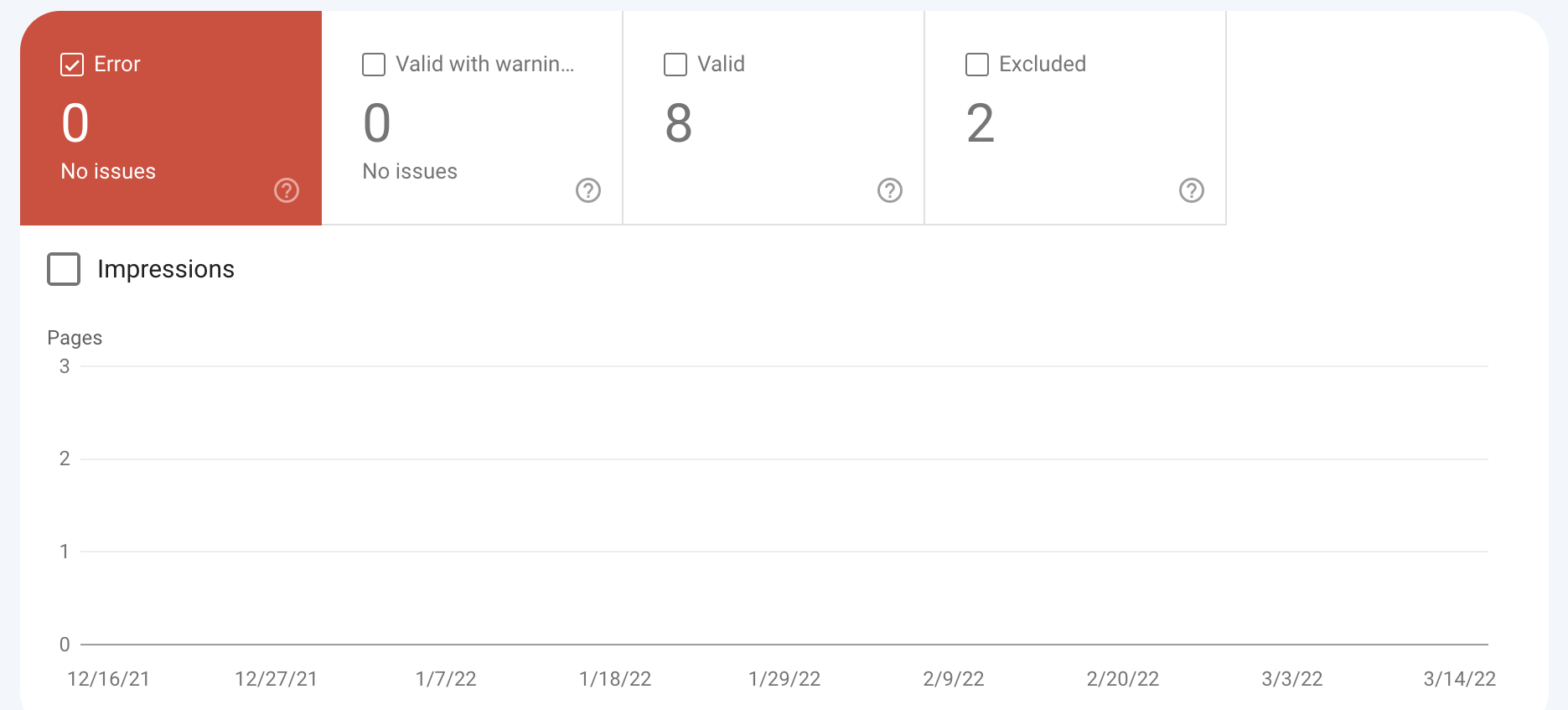
Take the time to resolve any errors that you find, and explore the cause of excluded URLs in more detail. Issues including 404 errors and incorrectly canonicalized pages may show up here, and these types of problems can negatively impact your website performance.
18. Improve Your Site Speed
Slow sites make for poor user experience.
In fact, Google confirmed in 2021 that page experience would become an even more important ranking factor.
You need to make sure your site loads quickly and acknowledge that users continue to expect more.
No one’s waiting around for a slow site these days.
You can use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool to gauge page performance and Core Web Vitals stats.
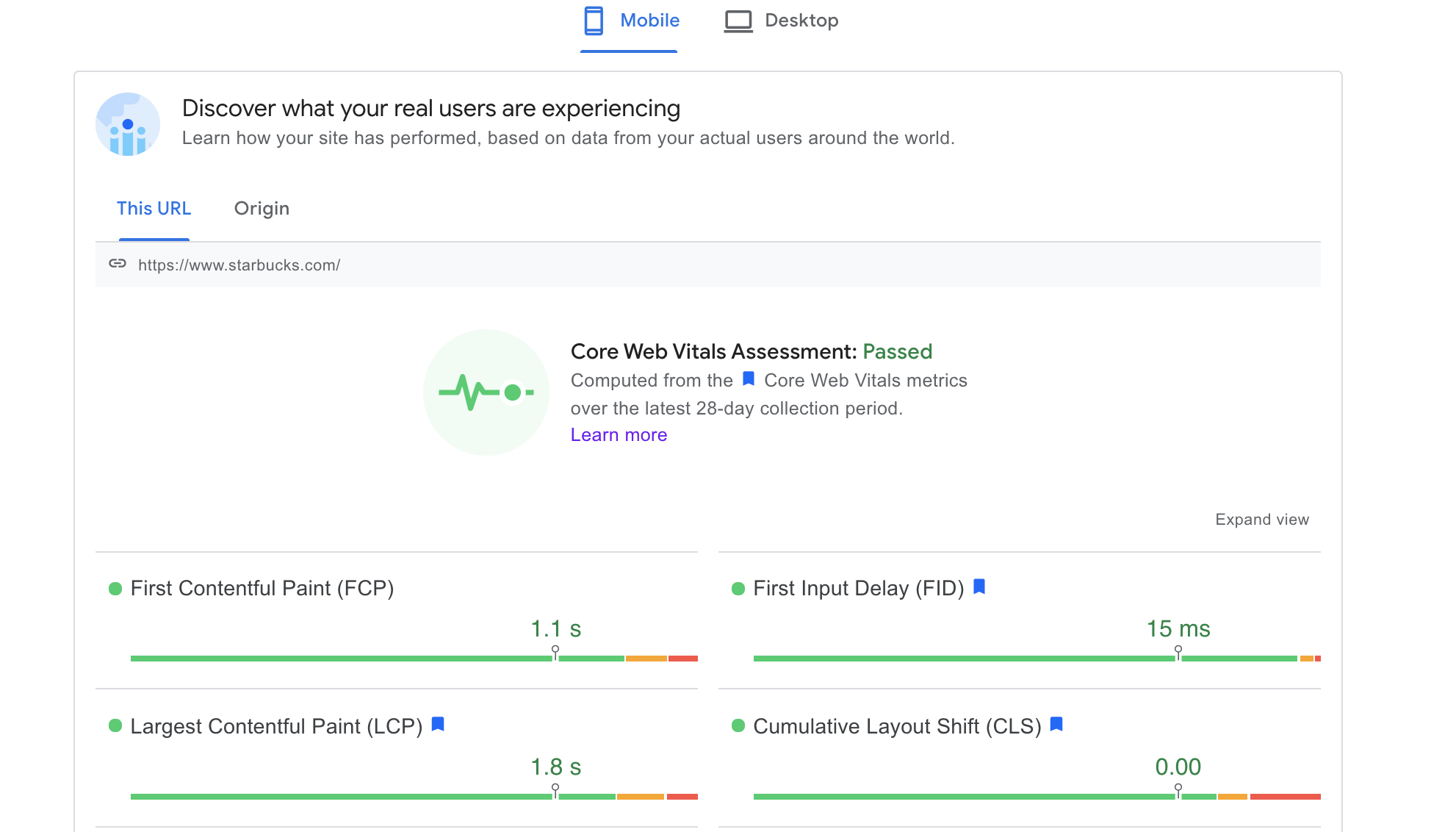
Scroll down to view an overall Performance score and a list of suggested actions for improvement.
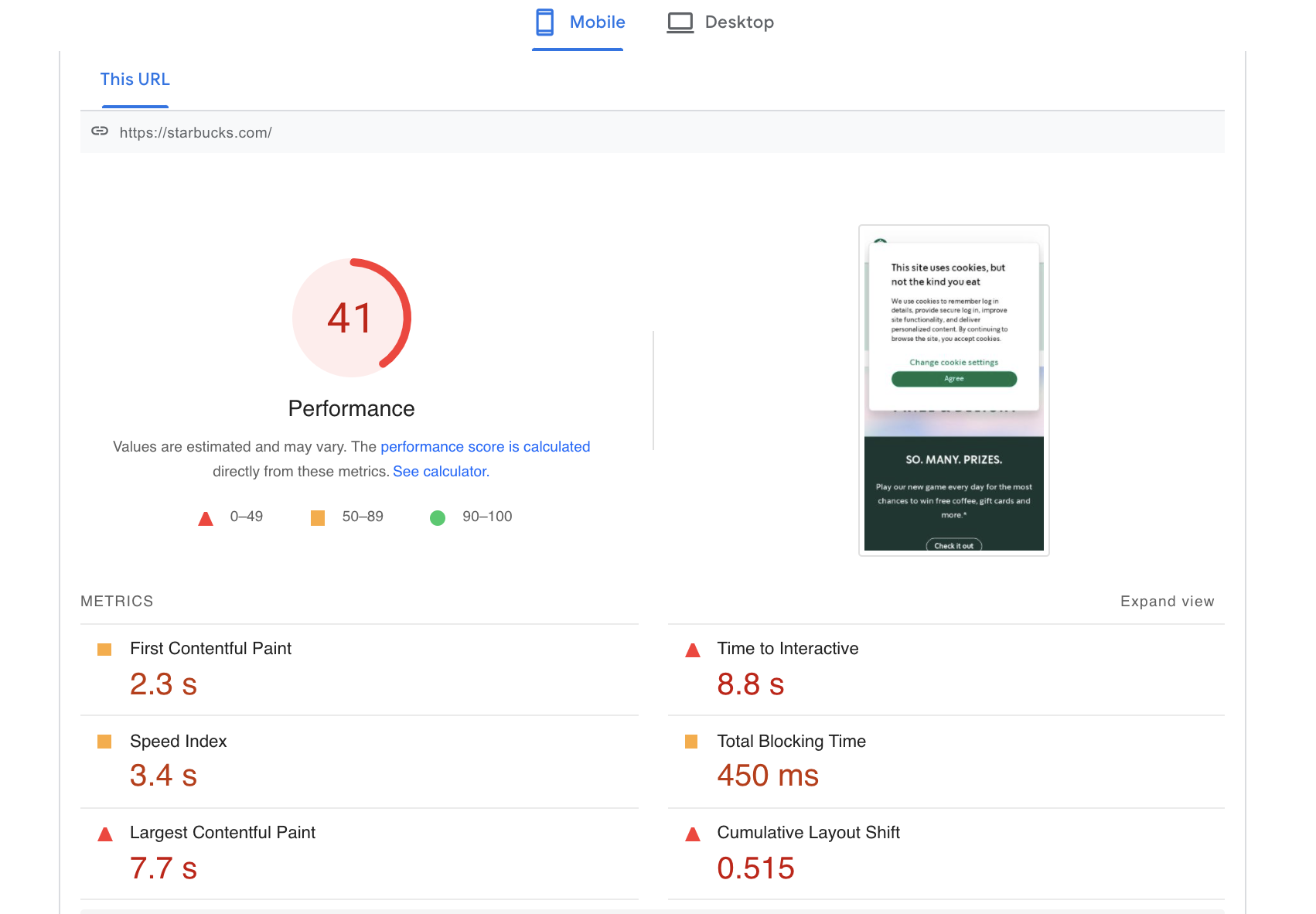
You can also use Site Audit to get a snapshot of your Core Web Vitals as well as recommendations for improvement.
Read our PageSpeed Insights guide for further information.
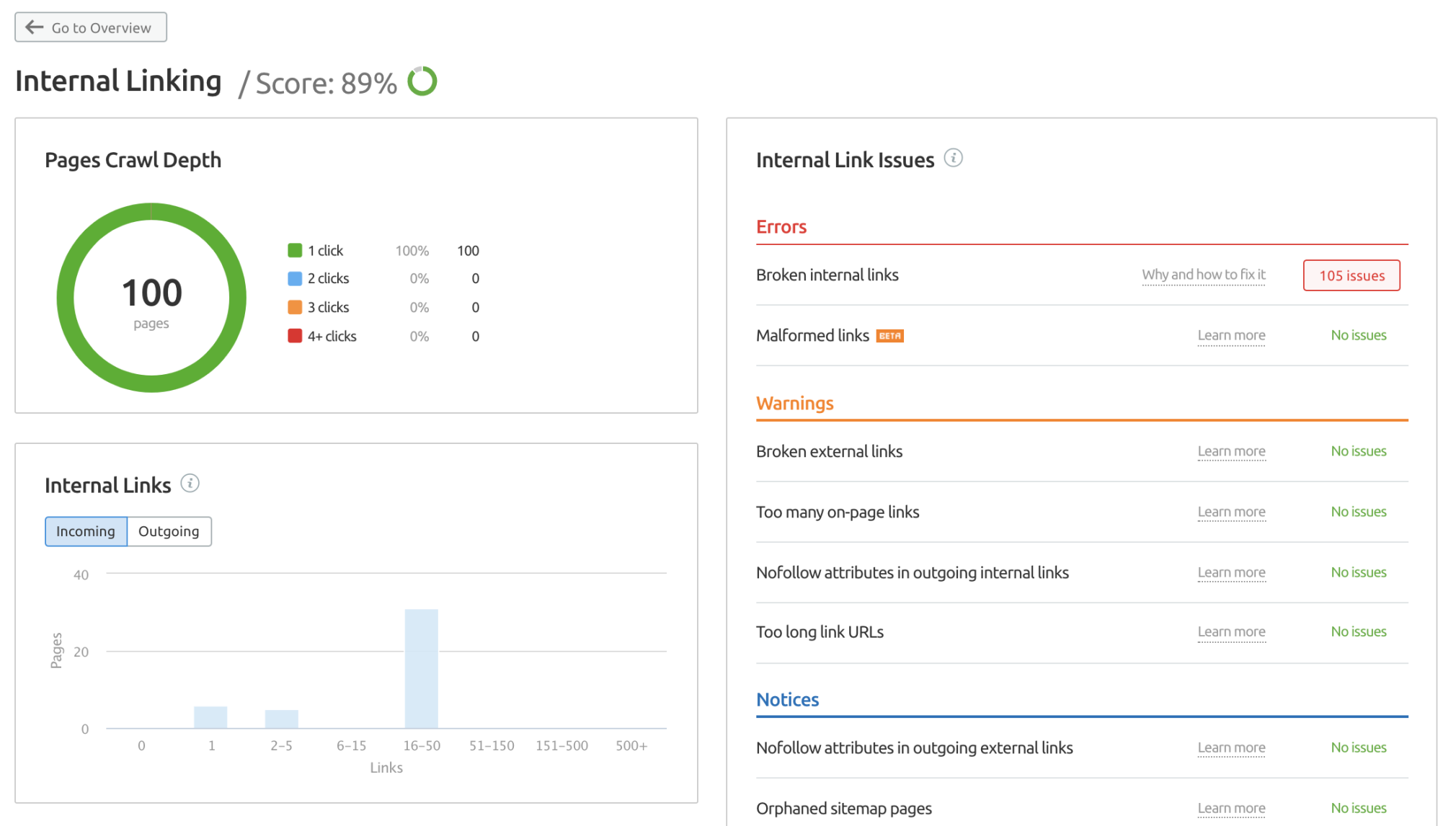
19. Fix Broken Internal and Outbound Links
Broken links are another signal of poor user experience. No one wants to click a link and find that it doesn’t take them to the page they’re expecting.
A list of broken internal links can be found in your Site Audit report, and you should fix and identified issues either by updating the target URL or removing the link.
20. Find and Fix HTTP Links on HTTPS Pages
Most sites migrated from HTTP to HTTPS quite some time back, yet it is still common to find that internal links point to HTTP pages, not the current version.
Even when there is a redirect in place to direct users to the new page, these are unnecessary, and you should aim to update these as soon as you can.
Take a look at the HTTPS Report in Site Audit to reveal any issues.
If there is only a small number of incorrect links, update these manually in your CMS. However, if these are site-wide (which they often are), you need to update page templates or run a search and replace on the database.
Speak to your developer if you are unsure.
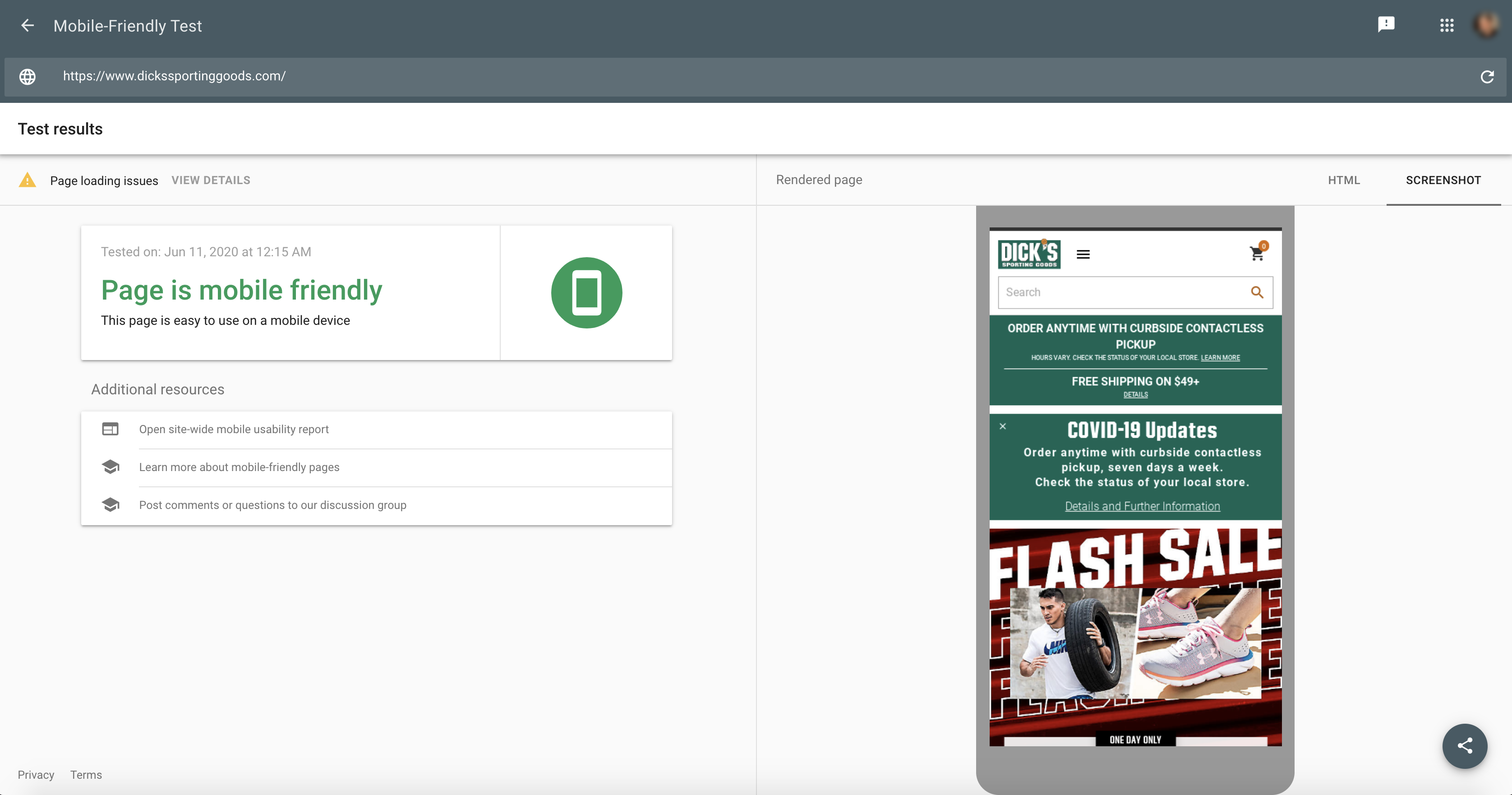
21. Make Sure That Your Website Is Mobile-Friendly
Mobile-friendliness is a key factor in Google rankings. Since mid-2019, Google officially switched to mobile-first indexing for all sites.
If you are not serving a mobile-friendly experience, you will find that your organic visibility suffers because of this.
You can test your site’s mobile-friendliness with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
22. Use an SEO-Friendly URL Structure
An SEO-friendly URL structure makes it easier for search engines to crawl your pages and understand what they are about. Your page URLs should be simple and descriptive for users as well.
Here is what an SEO-friendly URL looks like:
https://www.domain.com/red-shoes/As opposed to a query string that isn’t descriptive:
https://www.domain.com/category.php?id=32
Do use hyphens in your URLs to separate words; don’t use underscores.
Do keep URLs as short as possible ( a study by Backlinko showed that shorter URLs tend to rank higher).
23. Add Structured Data
As Google continues to build a more semantic web, structured data markup becomes increasingly valuable.
If you are not already using structured data, you should be.
In fact, the Schema.org vocabulary includes formats for structuring data for people, places, organizations, local businesses, reviews, and so much more.
Structured data helps your organic listings stand out on the SERPs, and in the example below, you will see both the review stars and the price that enhances the result.
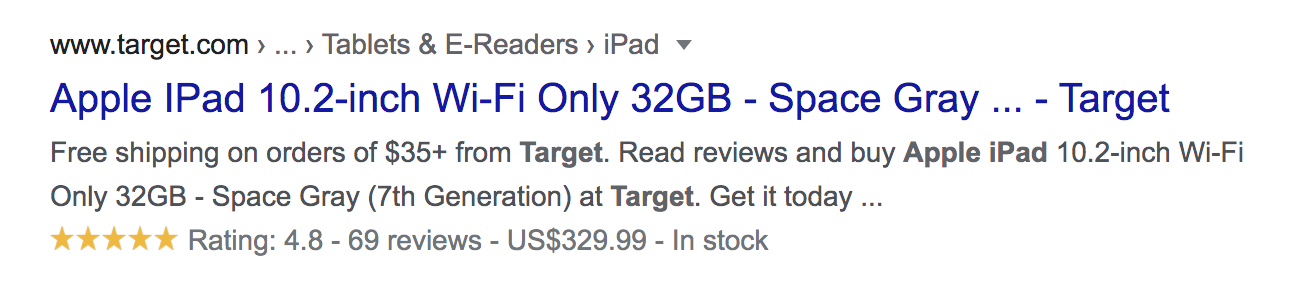
Check out our guide on structured data for beginners to learn more about how you can leverage this for success, or head to Google’s structured data testing tool to analyze whether or not your site currently uses this at all.
24. Check the Page Depth of Your Site
Ideally, pages shouldn’t be any further into your site than three clicks deep.
If they are, this is a sign that you need to spend time reworking your site structure to flatten it. The deeper a page is in your website structure, the less likely users or search engines are going to find it.
You can find the “crawl depth,” or number of clicks it takes to reach a page, in the Internal Linking report in the Site Audit tool.
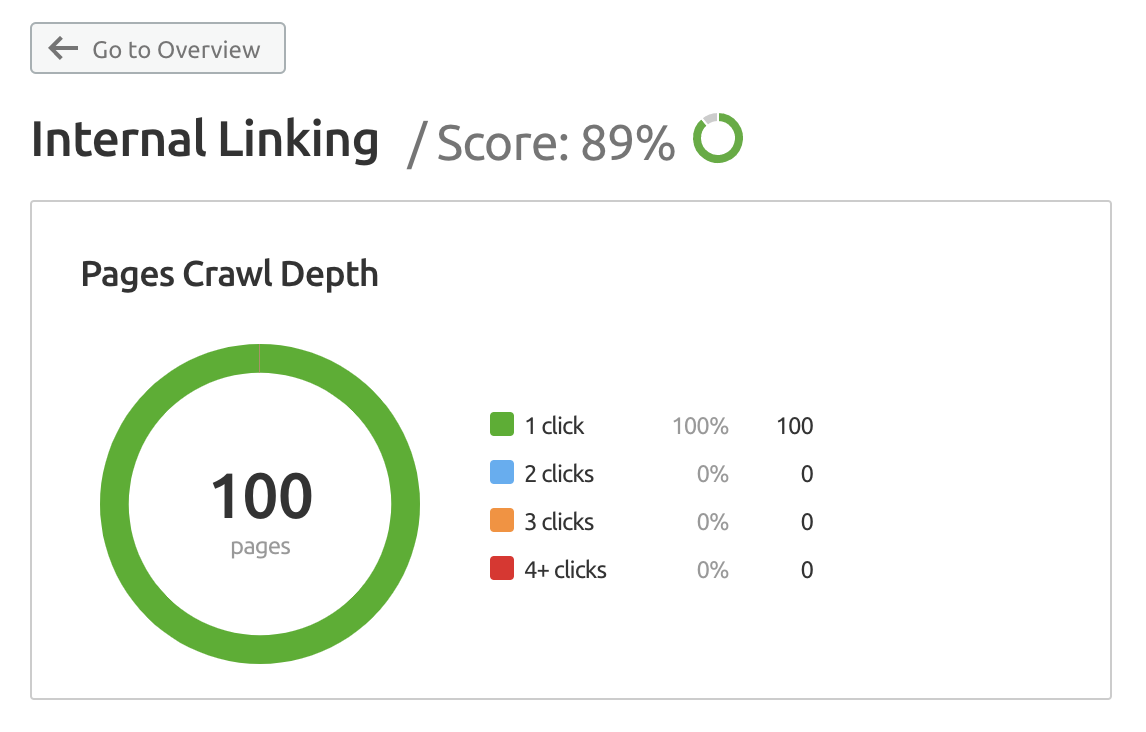
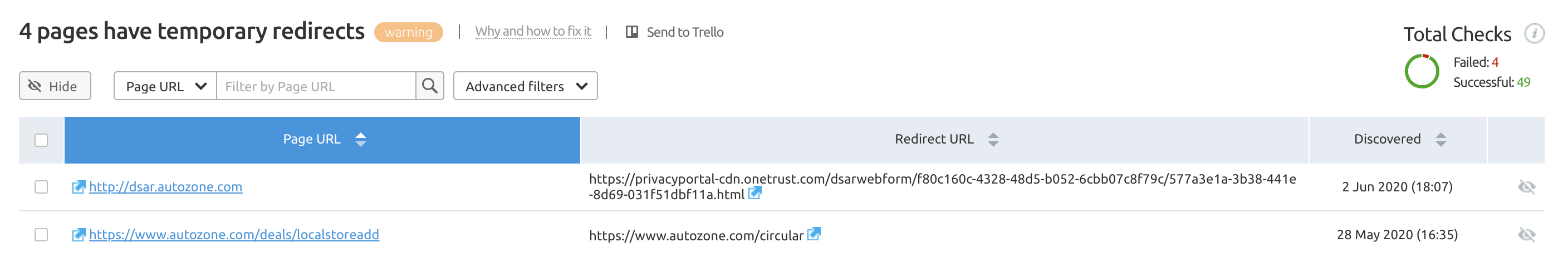
25. Check Temporary 302 Redirects
302 redirects indicate that a redirect is temporary, while 301s signal that the move is permanent.
It’s fairly common to find 302s used in place of 301s, and while Google has confirmed that 302s pass PageRank, the fact remains that if a 302 redirect isn’t expected to be removed at any point in the future, it needs updating to a 301.
You will find any 302 redirects clearly highlighted in the Site Audit report as pages that have temporary redirects.
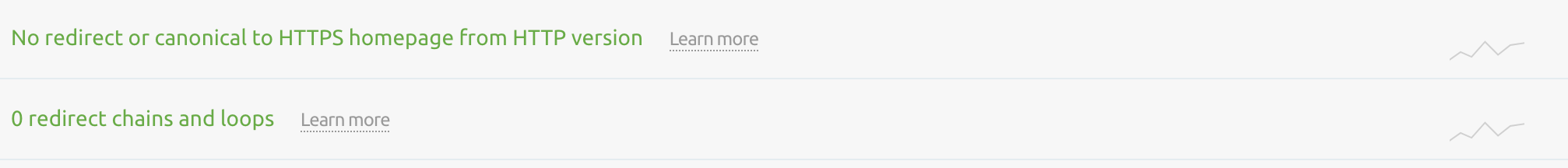
26. Find and Fix Redirect Chains and Loops
Your site shouldn’t send users or search engines via multiple redirects (a redirect chain), nor should redirects create a loop.
Simply, redirects should go from page A to page B.
The Issues tab in Site Audit will highlight any issues that exist in relation to redirect chains and loops. You can resolve these issues by updating all redirects in a chain to point to the end target, or by removing and updating the redirect causing the loop.
On-Page SEO and Content Checklist
Without useful content and a great on-page experience, your site will struggle to rank and get organic traffic. This applies to website pages and blog posts. There’s a lot of competition for blog posts these days, so it’s crucial to take every possible step to outrank competitors for important keywords.
For further reading, you can check out our guide on blog SEO.
Make sure that your site ticks the boxes below and focus on creating great content for users rather than focusing only on search engines.
27. Find and Fix Duplicate, Missing, and Truncated Title Tags
Optimized title tags are an important part of SEO basics. In fact, they are often the first thing any SEO would take a look at to help a page to rank.
Title tags inform search engines what a page is about and impact whether or not a user will click on yoru page.
Avoid duplicate title tags—ideally you shouldn’t have duplicate content on your site, and title tags should be specific enough that users can tell what type of page they’re gong to land on.
Also avoid title tags that are too long, as they may be cut off on the SERPs (you will see three dots after the title tag and part of it missing). Generally, title tags over 70 characters will get cut off.
You also need to ensure that title tags aren’t missing (where the title tag is blank).
All of these issues can be found flagged in the Issues section of the Site Audit report and can be fixed by updating and improving your page’s title tags.
28. Find and Fix Duplicate and Missing Meta Descriptions
While meta descriptions are not a ranking factor, they appear below the title tag in the SERPs and help users find out what your page is about.
Quite simply, it is your meta description that encourages a user to click on your listing over someone else’s and can either positively or negatively affect your organic click-through rate (CTR).
If you don’t have a meta description in place, Google will display part of your page’s content, but this could include navigation text and other elements and be far from enticing. If you have duplicates, there is a good chance that you are not presenting a unique description that encourages clicks.
Keep in mind that Google rewrites meta descriptions over 70% of the time to best match search intent. However, you should always write one that encourages users to learn more.
29. Find and Fix Multiple H1 Tags
A page’s H1 tag is your content’s main heading, and there should only be one in place per page.
Site Audit’s Issues tab will flag pages that have more than one H1 tag in place, and you should take the time to resolve these to ensure only one exists on each page.
The most common reason why multiple H1 tags exist is that your site’s logo is wrapped in one, as well as the main heading on the page.
Primarily, H1 tags should include a page’s main target keyword, so be sure to make sure that you are tagging the right content.

30. Improve Title Tags, Meta Tags, and Page Content
If you aren’t properly optimizing your page titles and meta tags, you’re missing out on an opportunity to rank not just for your main keywords, but also keyword variations.
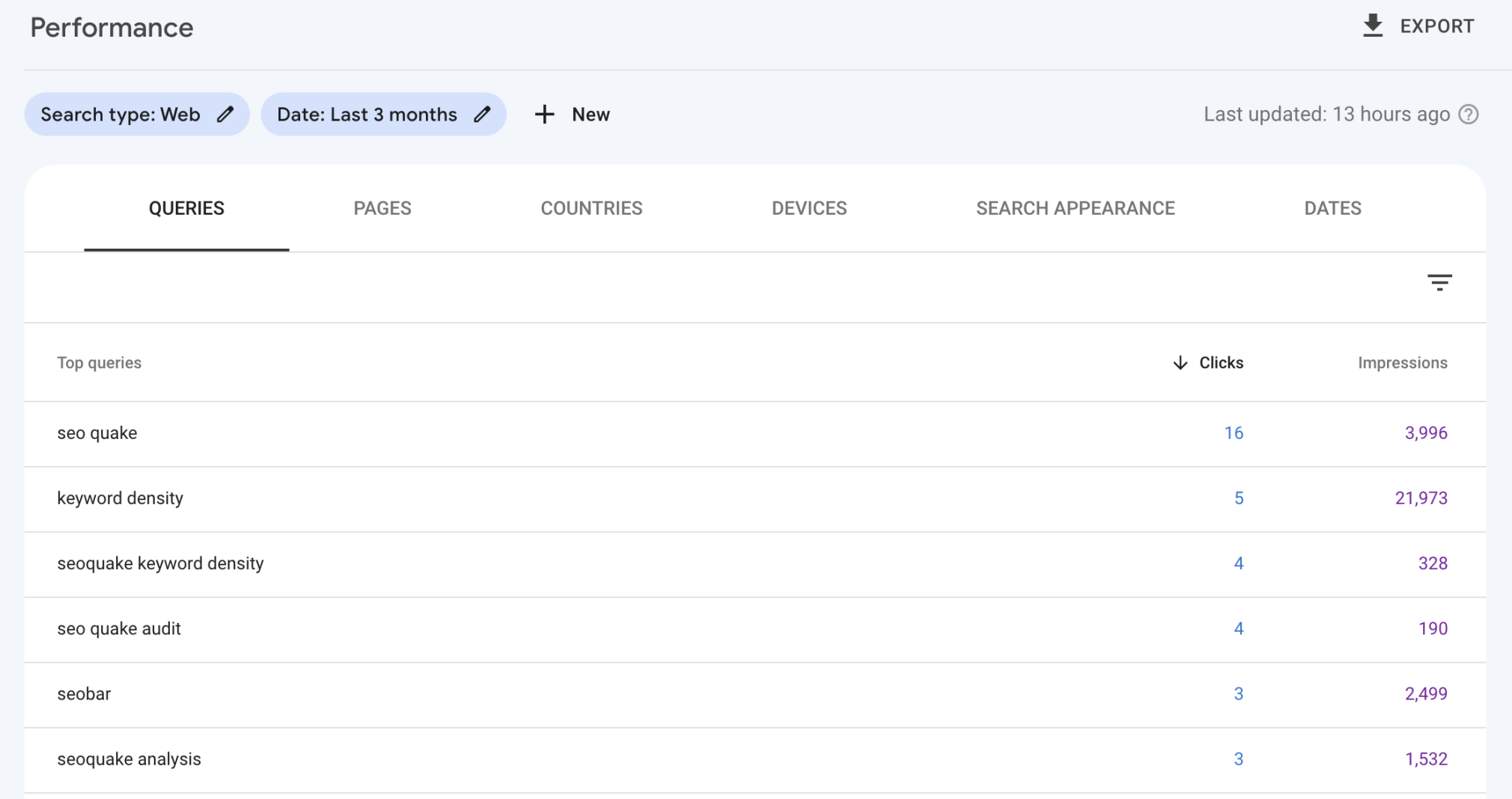
Head to the performance report in Google Search Console and identify keywords on each page that have a significant number of impressions but low clicks and a low average position.
This usually means that your page is deemed relevant for the queries, and is ranking in some capactiy, but you have not optimized the page by including these variations in your content or tags.
Keep in mind that simply adding in keyword mentions won’t do much. Think of these additional keywords as topics for additional H2s or subsections.
Rework and re-optimize your page with this in mind, and you will almost certainly see an uplift in clicks and ranking position.
31. Run a Content Audit and Prune Content
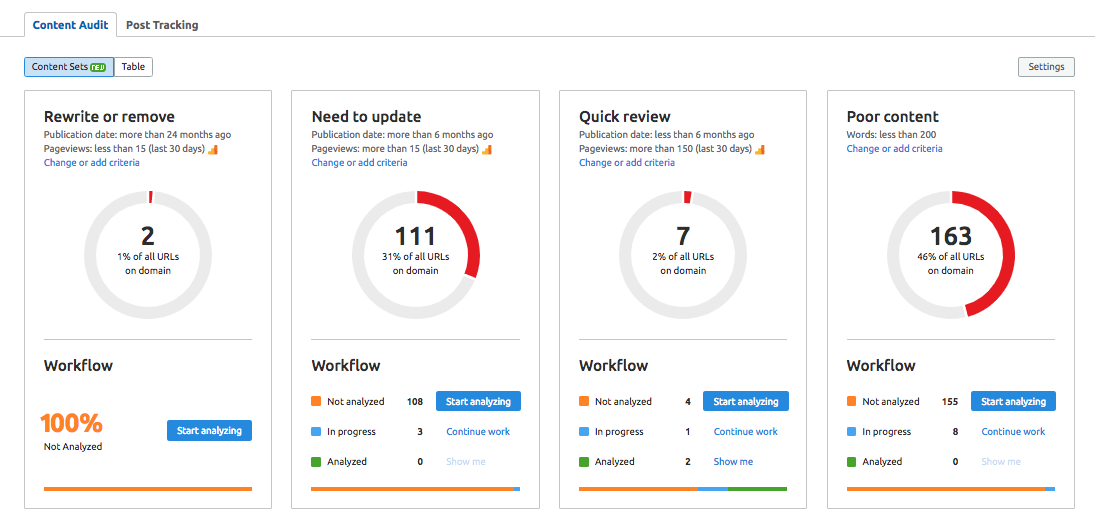
Running a content audit is a handy way to find out what content is doing well and what content isn’t adding value.
Essentially, this means getting rid of content that doesn’t rank, doesn’t add value, and shouldn’t really be on your site.
We can’t stress enough that time spent running a content audit and pruning thin, duplicate, or low-quality content is massively underrated.
If any content isn’t adding value to your site, it needs to go. It’s as simple as that. Kevin Indig’s guide to using Semrush for SEO pruning is a great starting point and will give you the insights you need to undertake this process effectively.
You can also run our Content Audit tool to find out which pages to rewrite, remove, or update based on how the content is performing.
32. Ensure Images Use Alt Tags
Always pay attention to image optimization. From properly naming images with a descriptive file naming convention through to optimizing the size and quality, it is an area of SEO that is often neglected.
At the very minimum, you should ensure that the main images on each page of your site use alt tags to properly describe the content of it.
Alt tags are not only useful for search engines in identifying images, but also useful for those who are visually impaired.
Use the Site Audit Issues tab to find out if you have any images with missing alt text on your site.
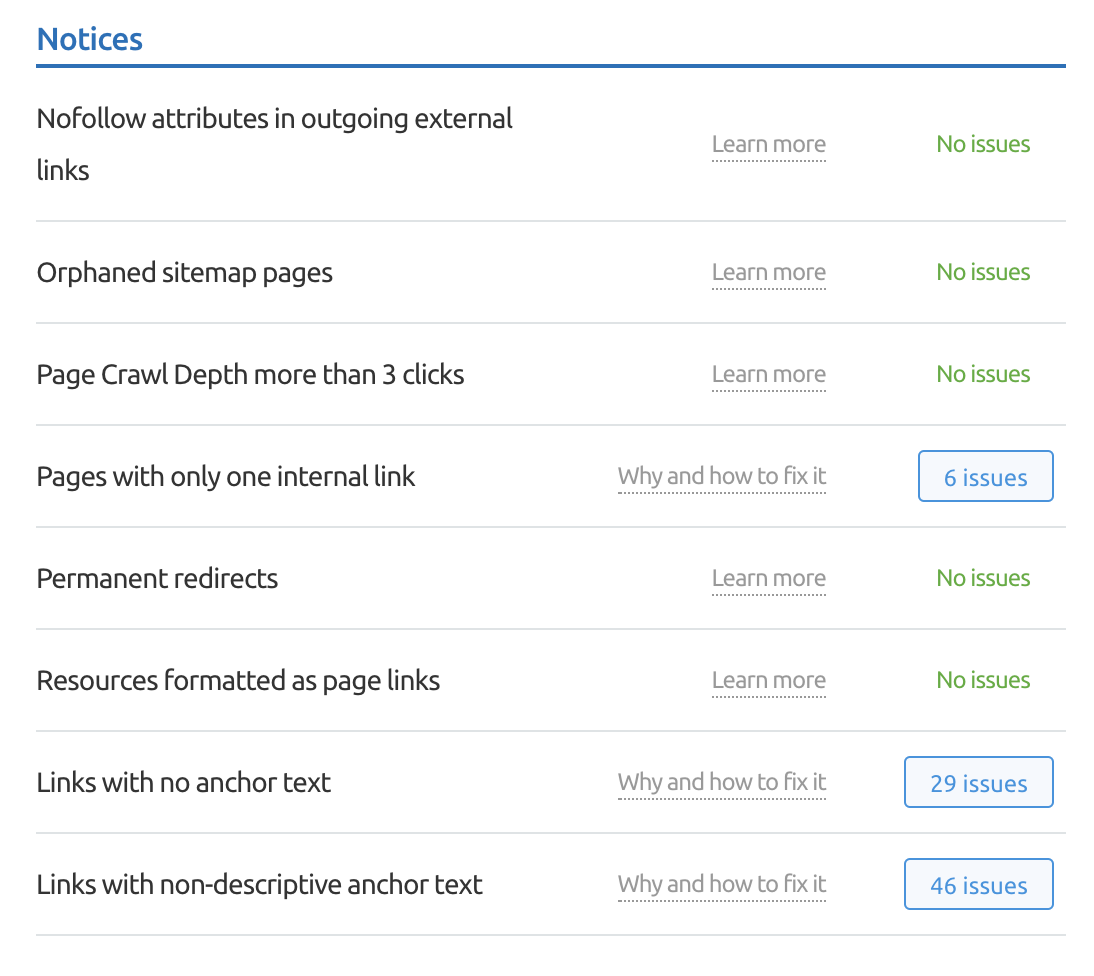
33. Improve Internal Linking
Internal links are arguably one of the most neglected link building tactics in SEO marketing. Spending time improving your site’s internal linking strategy can drive noticeable gains quite quickly.
Some marketers see quick wins from adding even one or two internal links from authoritative pages elsewhere on your site.
When you add an internal link and almost immediately see the benefit #seo pic.twitter.com/NRaINuDBTU
— Louise (@louise_sarah) June 10, 2020You can read this guide to executing an internal links strategy that works and begin to identify pages that need to be linked to from other pages or which hold authority that could be distributed elsewhere across your site.
You can find a list of pages that have only one internal link pointing to them in the “Notices” section of the Site Audit Internal Linking report.
Related topic: What is Anchor Text? Everything You Need to Know for SEO
34. Find and Fix Keyword Cannibalization Issues
Keyword cannibalization happens when multiple pages on the same site rank for the same keywords, therefore competing with one another.
Keyword cannibalization is one of the most misunderstood SEO concepts. Pages often rank for many keywords, so it isn't always a monumental issue.
Let’s say you have two pages ranking for the term “SEO checklist”—one forgotten, out-of-date page and one new page with useful content. If Google prefers the older page, it may decide not to rank the newer, more useful page. In this case, it would be a good idea to combine the two pages so you aren’t dividing the traffic.
Essentially, if your site is suffering from cannibalization, you’ll struggle to rank for competitive terms because search engines have a hard time figuring out which page to show.
To find out if your site has keyword cannibalization issues, set up a Position Tracking campaign and review the Cannibalization tab.
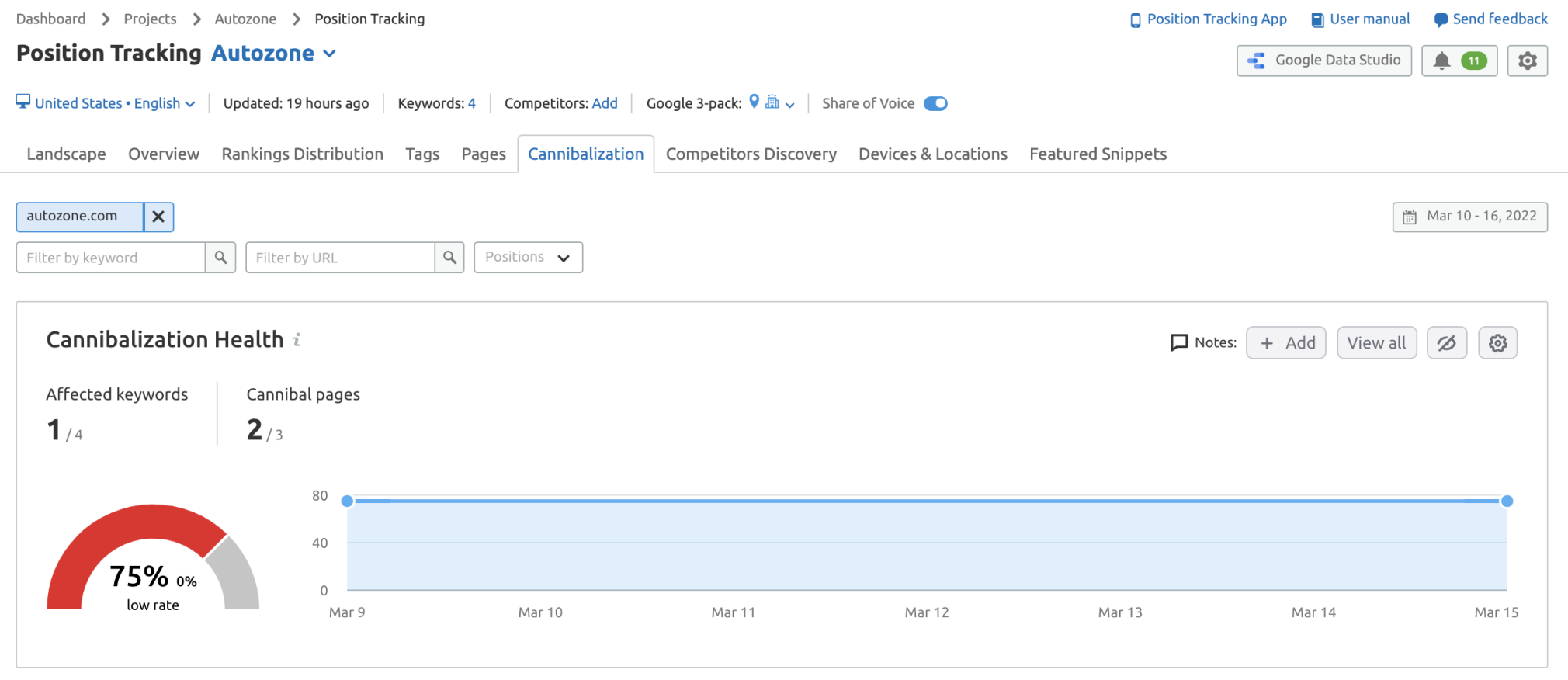
This cannibalization guide walks you through the most common ways to find and fix these issues.
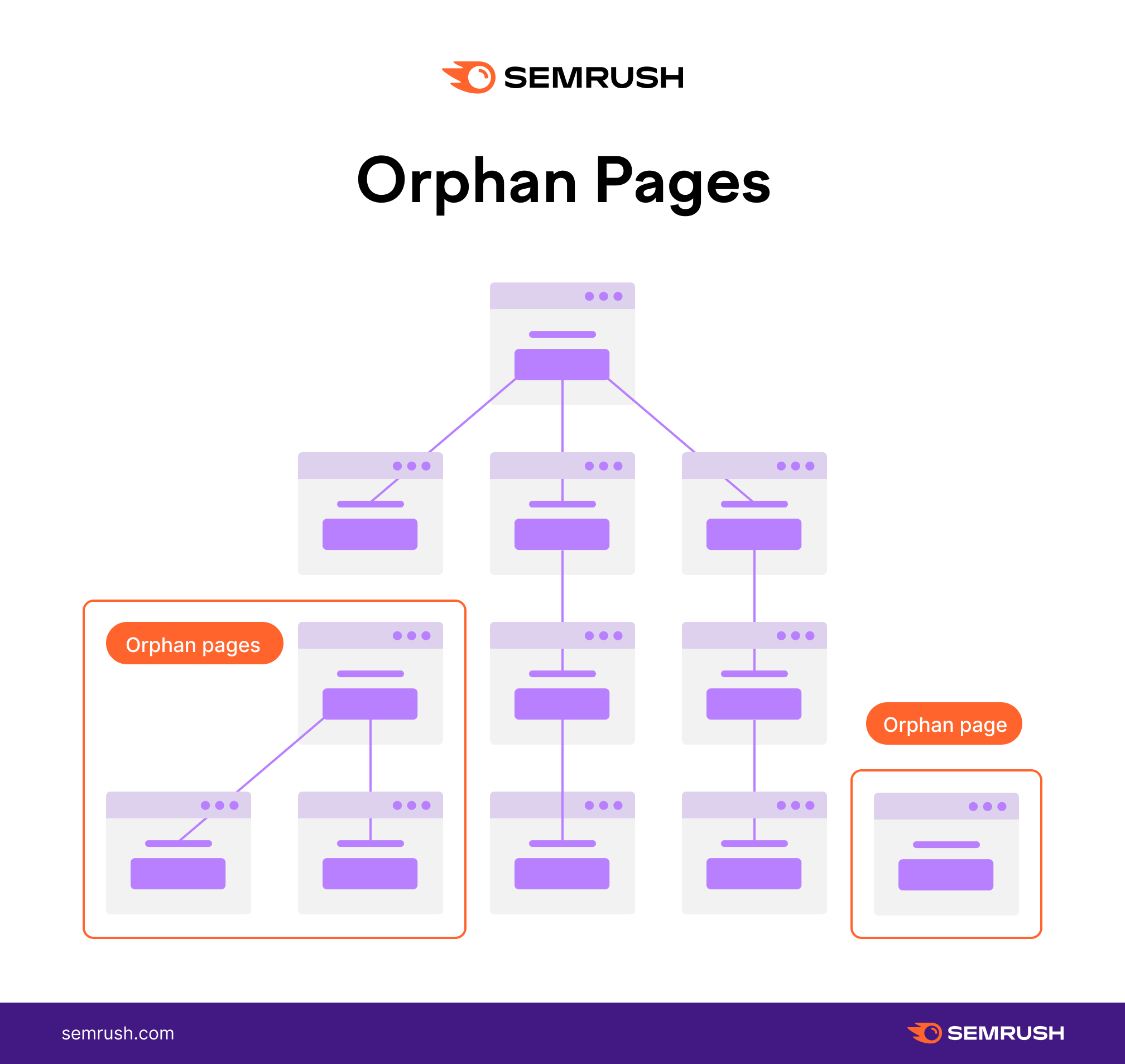
35. Find and Fix Orphaned Site Pages
Pages on your site should always be linked to from at least one other page.
After all, if Google isn’t able to crawl a page through other links on your site, it is likely that it is not inserting the authority that it otherwise could and not ranking as well as it could be.
If you are serving pages in your sitemap that are not accessible via at least one link from another page, you will find these flagged as “ orphaned pages in sitemaps” in your Site Audit Issues tab. It’s also highlighted in the Internal Linking report.
Go ahead and link to these pages from at least one other relevant page.
36. Ensure Your Site’s Content Up to Date
Content naturally ages and becomes outdated.
But updating old content is one of the easiest tasks that you can implement to see big wins.
Andy Crestodina of Orbit Media comments:
Updating old blog posts has been one of the most effective SEO strategies we’ve found.
If the content on your page contains outdated information or could simply do with being brought up to date with a fresh perspective, it is time well spent.
After all, content that is outdated usually doesn’t offer the best experience for users, so why would Google continue to rank it unless it’s brought up to date?
Off-Page SEO Checklist
If you want to drive SEO success, you can’t turn a blind eye to off-page SEO factors. While these are often thought of simply as link building, there is more to it than that—which we’ll cover below.
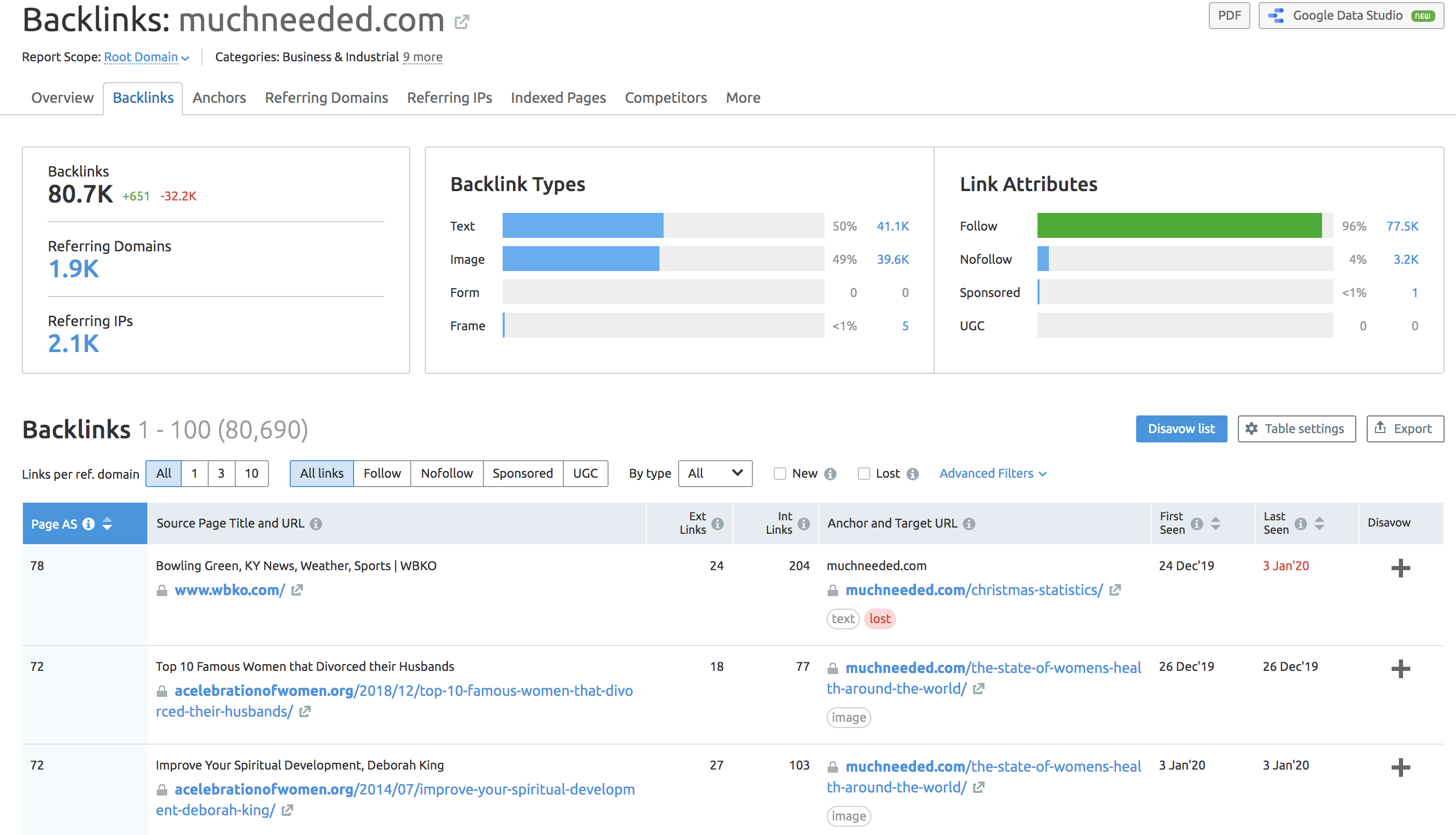
37. Analyze Your Competitor’s Link Profile
If you don’t have insight into your competitor’s link profile, how can you plan a strategy to outrank them?
Just as it is important to spend time analyzing your competitor’s content, you should also invest resources into digging deep into their link profile.
Run any URL through the Backlink Analytics tool, and you can analyze any competitor’s link profile and start to understand the overall quality and authority of the links that point to their site.
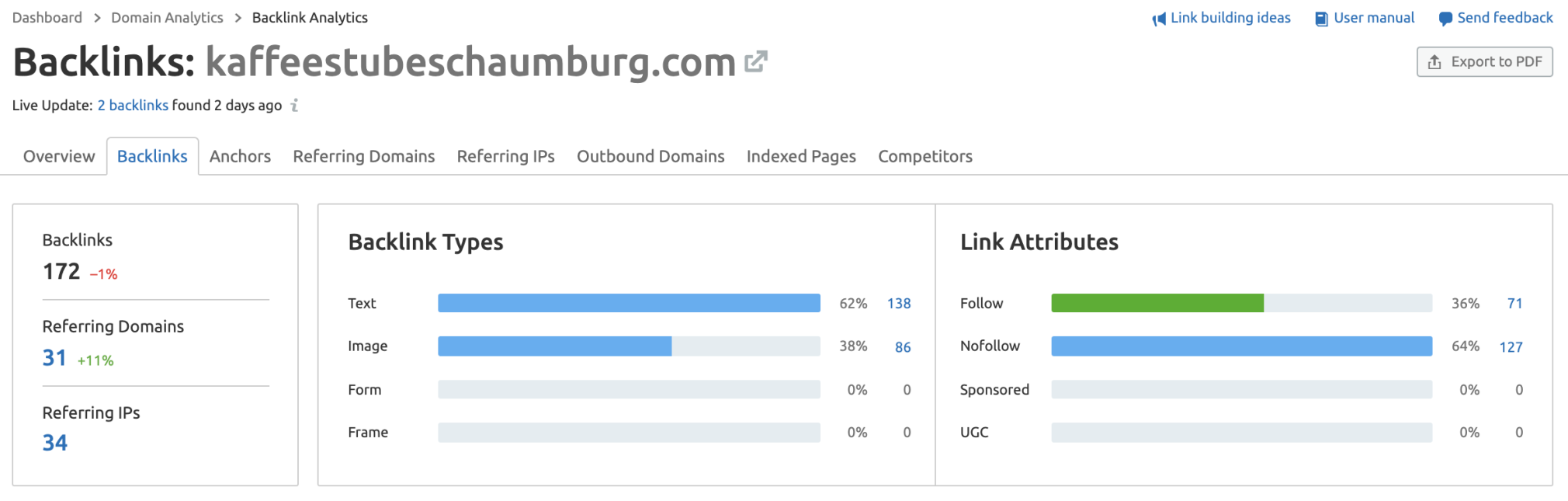
38. Conduct a Link Intersect Analysis
Are you missing out on links that your competitors are benefiting from?
Conducting a link intersect analysis can help you to find quick-win opportunities.
Using Backlink Analytics, you can enter up to five different domains to gain insight into which domains are linking to which of your competitors.
If there is, let’s say, a resource page that links to all others in your space except you, a great starting point would be to reach out to ask to be added.
39. Turn Unlinked Mentions Into Links
If you have a PR team that lands coverage in the press, there is a good chance that you will find articles that mention your business but don’t link.
These are known as unlinked brand mentions. The Brand Monitoring tool can help you to quickly identify mentions of your brand that don’t link, and this guide shows you how to ask for a link when there’s an existing unlinked brand mention.
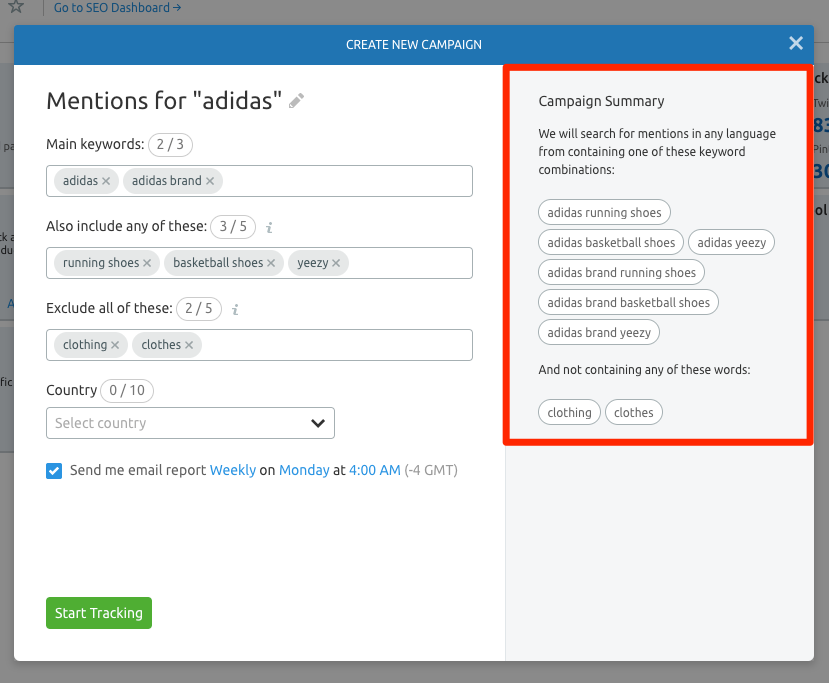 Choose which specific related keywords to monitor with the Brand Monitoring tool.
Choose which specific related keywords to monitor with the Brand Monitoring tool.40. Find New Link Building Opportunities
There are always new link building opportunities that you can explore and act upon, but finding these often takes time.
It’s important to build a high-quality backlink profile, and using the right SEO tools can make the task of finding these opportunities a little bit easier.
The Link Building Tool, for example, is a simple and straightforward way to see a continual stream of new opportunities that you can look into and websites that you can reach out to.
In minutes, you will have a whole host of new opportunities and can put in place a solid strategy to make great gains on the competition.
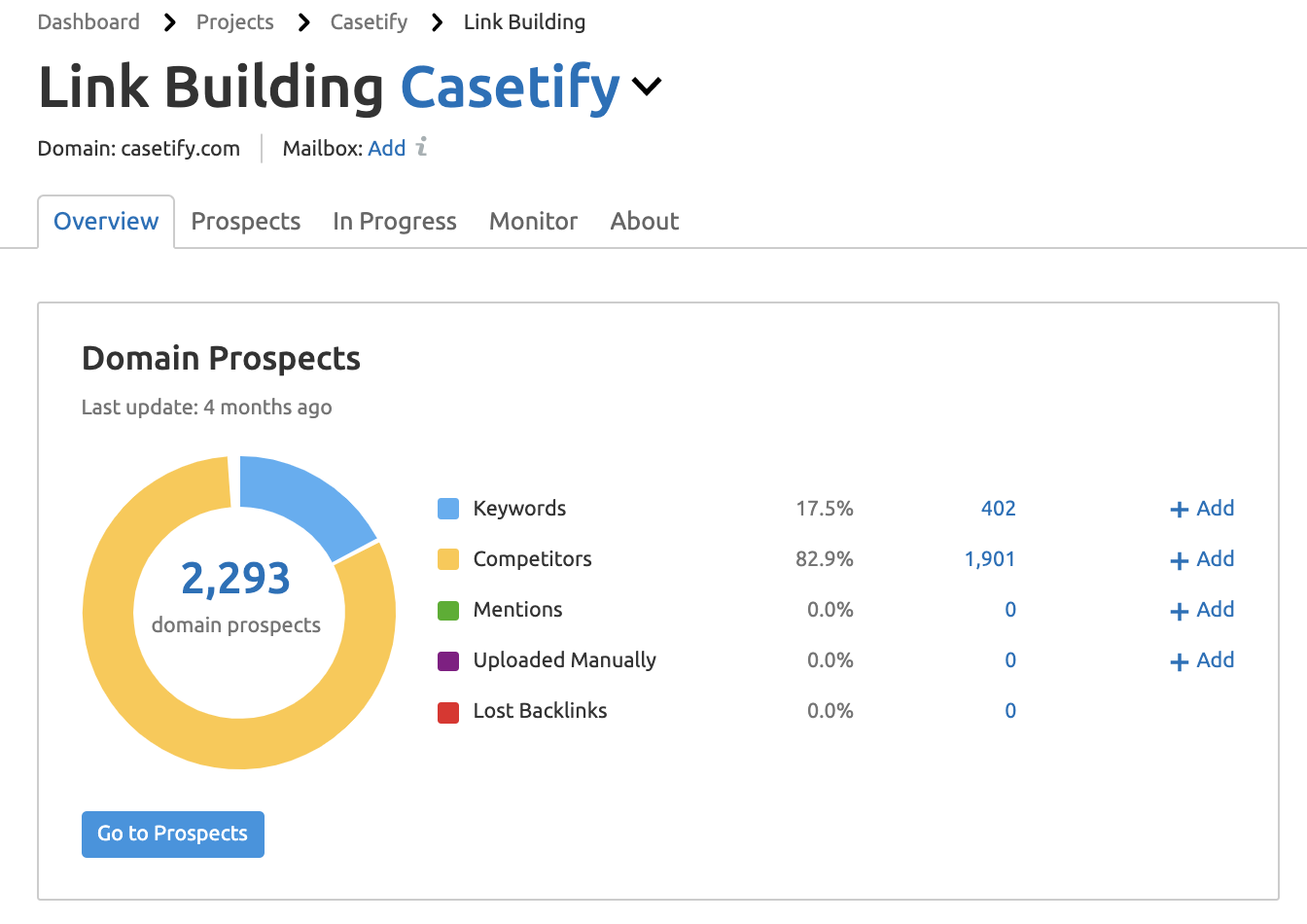
Review our L ink Building Guide to review specific link building strategies.
41. Set Up and Optimize Google Business Profile
Off-page factors go way beyond just links, despite these being a key ranking factor.
If you run local business, make sure that your business is listed (and ranking) on Google Business Profile (GBP). Otherwise, you'll essentially be handing visits to a competitor.
There is no denying that it takes time to optimize your GBP listing to a decent standard and keep it up to date. But if you are serving customers at their location or they are visiting you, there is no reason why you won’t stand to gain from the time you put in here.
To get started with improving your brand’s local visibility through GBP, take a check out our GBP (formerly Google My Business) guide.
Improve Your SEO Presence Today
There you go; a 41-step SEO checklist that both beginners who may just be learning SEO and more advanced SEOs can follow and hopefully find at least a few ways to improve their site’s optimization. SEO success doesn’t come from simply following a checklist. However, to outrank your competitors you need to make sure you are working on these steps to improve your SEO.
Have any steps that you would add to the list? Let us know on social media.

Innovative SEO services
SEO is a patience game; no secret there. We`ll work with you to develop a Search strategy focused on producing increased traffic rankings in as early as 3-months.
A proven Allinclusive. SEO services for measuring, executing, and optimizing for Search Engine success. We say what we do and do what we say.
Our company as Semrush Agency Partner has designed a search engine optimization service that is both ethical and result-driven. We use the latest tools, strategies, and trends to help you move up in the search engines for the right keywords to get noticed by the right audience.
Today, you can schedule a Discovery call with us about your company needs.
Source:





