What Is Technical SEO?
Technical search engine optimization (SEO) refers to the tactics involved in creating and optimizing a website so that search engines can readily crawl, index, and render it. Technical SEO is just one piece of the whole SEO puzzle.
Most marketers and business owners leverage technical SEO to better their website's chances to rank well in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
Learning Technical SEO
Looking to dive into the world of technical SEO? Then this is the beginner’s guide for you. In this article, we will cover:
What technical SEO is Website creation HTML, JavaScript, and CSS (programming languages) Crawling, rendering, and indexing (how Google organizes itself) Page speed User-friendly sites Thin/duplicate content Canonical tags Hreflang tagsRead on to build your technical SEO skills and set your website up for success.
Why Is Technical SEO Important?
You could be making the world’s most engaging, thoughtful content on your website — the kind of content that immediately converts casual users into customers. But, if search engines can’t properly browse your website and index it, your efforts will be wasted. That’s why technical SEO is important.
Think of it like trying to sell a house. You could have an interior (content) worthy of “Architectural Digest,” but if your siding is falling off (bad programming) or your house is full of wiring that leads to nowhere (broken links), your house isn’t going to pass inspection (Googlebots), and it’s doubtful that it will sell (rank well enough for users to find).
To see how your existing site is performing in the technical SEO realm, you’ll want to do a comprehensive technical SEO audit.
What Is an Example of Technical SEO?
An example of technical SEO would be building structured data. We will get into this in a bit more detail later on, but structured data is the act of describing your website in a language that search engines can recognize. The most recognized type of structured data vocabulary is schema markup.
Most major search engines rely on a standardized structure for websites. This structure needs to be orderly so that search engines can give searchers the most relevant and thorough results possible. That’s why structured data is one important example of technical SEO.
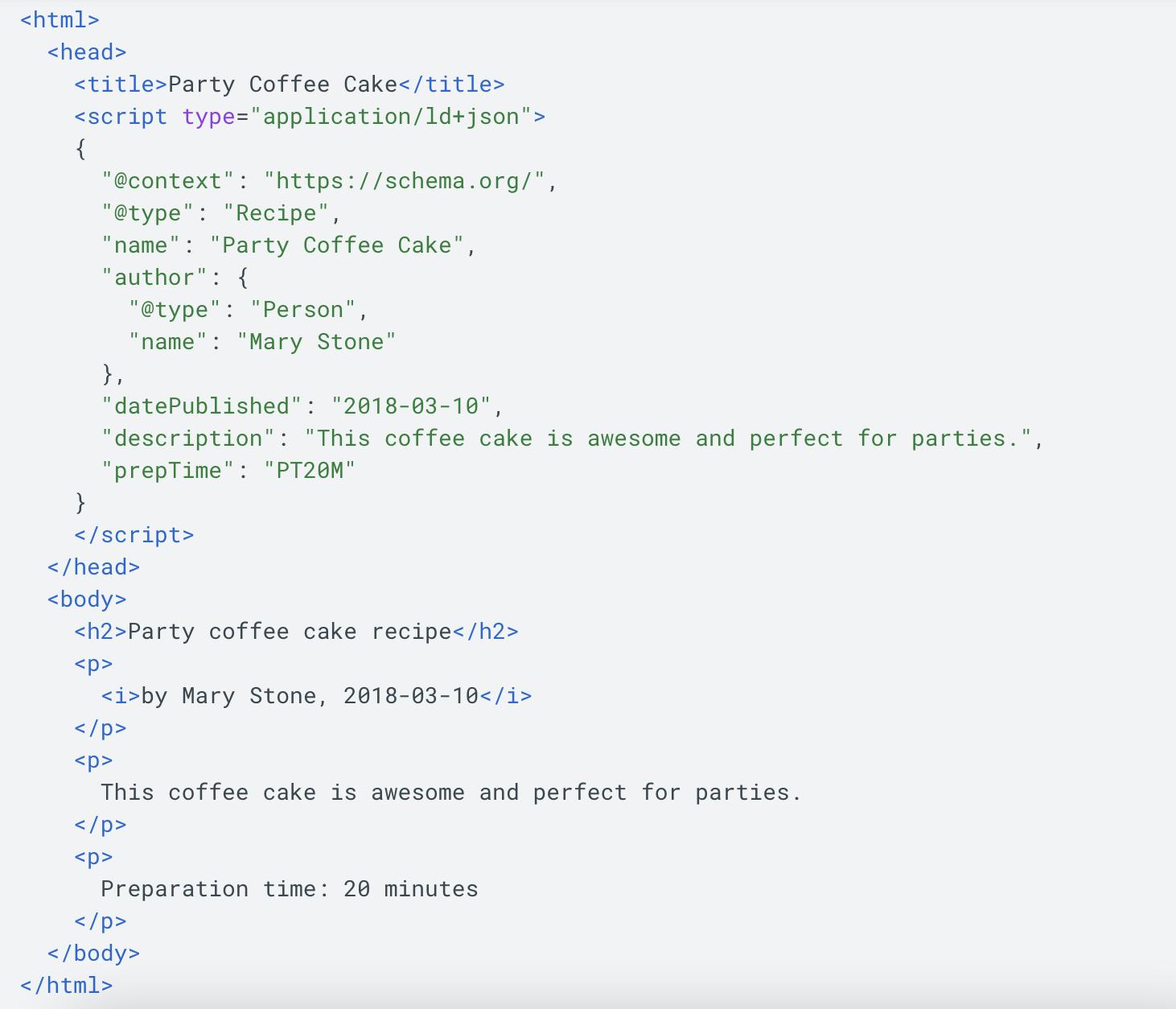 This is an example of JSON-LD markup (schema) for a recipe website. JSON is a common and highly successful schema format. Image courtesy of Google.
This is an example of JSON-LD markup (schema) for a recipe website. JSON is a common and highly successful schema format. Image courtesy of Google.Another example of technical SEO would be building an XML sitemap for your site. The first major step in establishing a technical SEO strategy is setting up your website correctly so every page functions as it should. Google (and other search engines) crawls this file to understand your site better.
 This is a simplistic XML sitemap that includes the location of a singular URL. You can see that the code provides information about when the page is modified or changed. Image courtesy of Google.
This is a simplistic XML sitemap that includes the location of a singular URL. You can see that the code provides information about when the page is modified or changed. Image courtesy of Google.Setting Up Your Website
The first major step in establishing a technical SEO strategy is setting up your website correctly so every page functions as it should.
Let’s go over some SEO basics and beginner steps to setting up a website from scratch:
Purchase a domain name: There are tons of domain registrars (businesses that organize and manage taken and available domain names) out there. Wix, GoDaddy, and Domain.com are some of the most popular registrars out there. Link up your domain name to an IP address: Internet protocol addresses (IPs) are a set of numbers that help the internet translate a domain name like “semrush.com” into something it can catalog and organize. A domain name server (DNS) organizes these IP addresses into an intricate map across the web.Once you’ve got those two parts down, you will need to start preparing your site to appear on searchers’ web browsers. There are several ways this happens:
A person searches for your site (example: a searcher wants to learn more about SEO, so they plug in “semrush.com” to their Chrome browser’s search bar). Their internet browser will begin contacting the DNS to convertn a domain name and IP address. It will also start requesting information about your website's type of programming/coding. Once the DNS has the request, it will begin building the website files that will appear in the user’s internet browser. The big show begins — rendering. Now that the DNS has delivered the right materials to the internet browser, the browser will begin building the web page requested. This is referred to as “rendering.” It allows typical users to see the polished website without sorting through a bunch of complex code. The browser does a final check by making any unfulfilled code requests to the server. Your website is displays successfully in the browser.And that is the gist of how a website goes from inception to browser-ready. For more comprehensive information, check out our article on How to Build Your Website Architecture for SEO.
URL Structure
Uniform Resource Locator (URL) structure describes the appearance of a URL. This structure gives important information about the web page to both search engines and searchers. For example, you’ve probably seen many URLs that start with “HTTPS.”
This group of letters refers to a URL structure that combines Hypertext Transfer Protocol and the Secure Socket Layer (SSL). That “S” at the end refers to a security protocol that many sites use to keep the contents of the webpage (and information users enter into the page) secure.
Let’s take a look at a structured URL example:
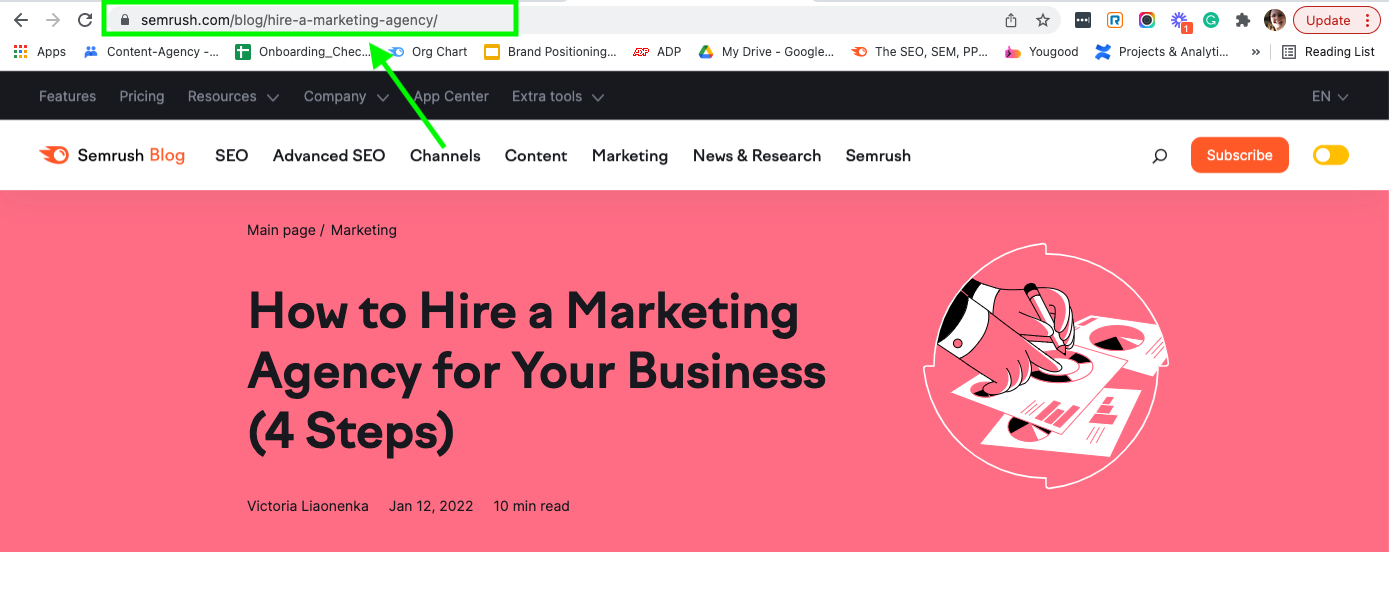
You can see from the content that this is a blog post about how to hire a marketing agency for your business. The URL structure also reflects this with “/blog/hire-a-marketing-agency.”
You can also see an SSL certificate at the top, indicated by the “S” at the end of “HTTPS” and the little lock icon in the left-hand corner of the search bar.
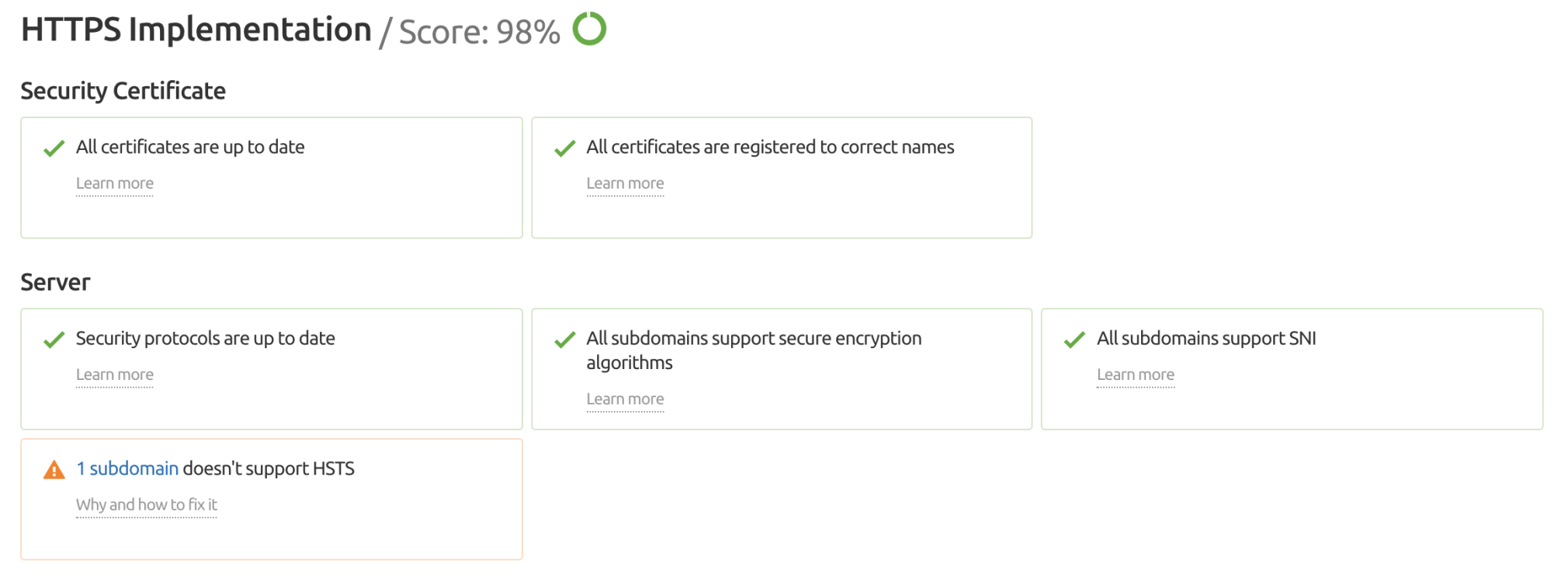
You can also audit HTTPS usage on your site using the Site Audit tool, which is helpful when checking for technical SEO issues.
Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumb navigation refers to a user’s “trail” when navigating a particular site. This breadcrumb navigation easily allows users to click to return to a previous page or to navigate several steps back in their journey through a website.
This type of navigation is good for maintaining an orderly site infrastructure, and it offers an additional layer of accessibility for the user. See the example below:
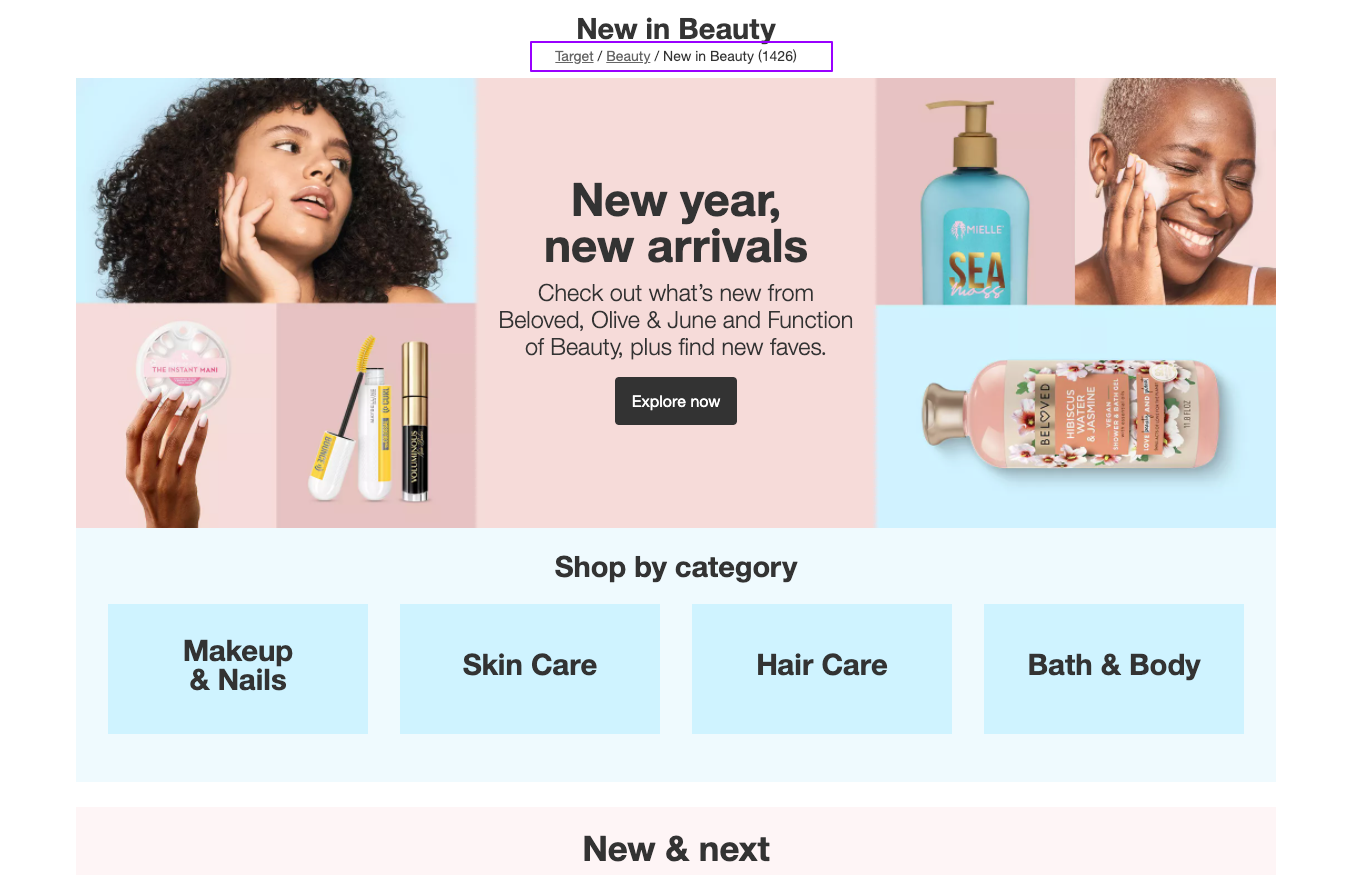
This image shows a specific page on Target’s website. The breadcrumb navigation is highlighted in purple at the top of the page. In this example, a customer could return to the “beauty” page or Target’s homepage with a click, if they like.
HTML, JavaScript, and CSS
You’ve probably heard of HTML, JavaScript, and CSS used in technical SEO spaces or around the internet before. If it feels like learning Latin to you, don’t worry; HTML, JavaScript, and CSS are all programming languages many individuals can learn with a lot of patience, practice, and support.
Let’s use the house example again to go over each programming language.
HTML: HyperText Markup Language is like a house’s foundation and load-bearing walls. This language provides the essential structure (code) browsers need to display your web content. When you see written content on a site, including headers and listicles, that’s HTML. JavaScript: This language is like the plumbing and electrical elements of the house. JavaScript provides the code that makes the functional parts of a site usable when searchers come to it. JavaScript makes elements of a website dynamic and flashy. With JavaScript, the options are essentially endless. For example, if you wanted to create a click-through quiz on one of your web pages, you could do that with JavaScript CSS: CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is the house’s exterior in this analogy. This programming is responsible for the colors, fonts, and overall look of your site. Without it, things would look very blank and boring on a webpage.To review:
HTML is the foundational code for your site JavaScript adds interactive elements to your web pages CSS makes everything look greatPro tip: Use our downloadable JavaScript Cheat Sheet to reference common JavaScript commands.
Crawling, Indexing, and Rendering
So, once you have your website connected to an IP address and you’ve added your HTML, JavaScript, and CSS programming into the mix, what happens next? To ensure that your website appears in the SERPs, you’ll want to pay close attention to what Google is doing when it’s crawling, indexing, and rendering your website.
The better you understand each of these steps, the more you can refine your technical SEO strategy to meet the needs of users and search engines. The more you meet the needs of search engines, the better chance you have at ranking well in the SERPs.

Note: We will be using the most popular search engine, Google, as the example for this section.
Crawling
When you visit a website you like, do you browse multiple pages and follow breadcrumb navigation to check out all the content the site has to offer? If you do, then you understand exactly how Google’s crawlers (bots) navigate public websites.
Once these Google bots begin scouring the web, they go to public websites and hop from link to link much as a person would do.
Important note: Make sure that your website isn’t blocking Googlebot from crawling your files. Your site will not appear in the search engine results if it is blocked. It’s also good to note that JavaScript files that are too complicated might make it nearly impossible for Google to render your web content correctly.
Indexing (and Why Sitemaps Matter)
Indexing is like Google’s filing cabinet. Once the Googlebot crawls a public site, it stores that content, and (when it’s finished indexing) that page will appear in the relevant search engine results that best match a searcher’s query.
One way to ensure that Google has correctly crawled and then indexed your content is to leverage a free Google tool called Google Search Console.
Once you create your free account, you can do several things like monitor when a new webpage you created is indexed. You can also submit sitemaps, making it easier for Google to identify and correctly catalog your site’s content.
Building a sitemap is very important because it makes Google’s life (and yours) much easier. Instead of aimlessly searching your website, you can tell Google where the important content is and how often you update it.
Tips:
Ensure your main navigation features are in the most simple code possible (HTML). If you do want to use more complex JavaScript to build your navigation menu, know that Google is not as adept at indexing complex navigation structures. Ensure your mobile and desktop versions of your site are the same. Having different content on each can keep Google from correctly indexing your site. Incomplete navigation (like missing an important contact page) will keep Googlebot from jumping easily from link to link.Open the Crawlability report in Site Audit to learn more about any issues or errors on your site.
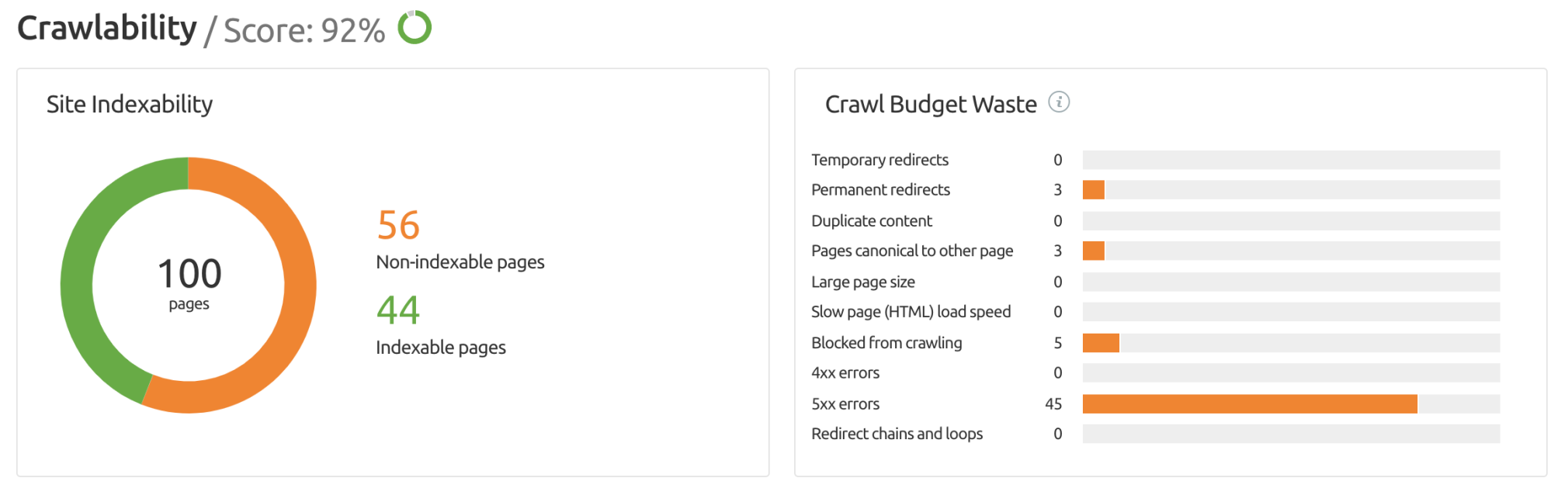
Rendering
Rendering is what happens once Google has finished crawling and indexing your website content into its filing cabinet. If all goes well and your content begins appearing in the SERPs, Google wants to make sure that users see and interact with your content, just as you intended them to.
In the early days of the internet, websites didn’t have JavaScript. This made them very easy to render because they used HTML — a very static programming language. Now, with JavaScript and colorful CSS, Google’s job has gotten a lot more complex.
The more JavaScript and other complex coding elements you apply to your website, the more likely that Google will have difficulty rendering your website as you intended.
Implementing Structured Data
We touched on structured data briefly earlier on in this guide. As a recap: building structured data is the act of helping Google understand your website content through creating a detailed site description in a language (code) that Google can readily understand.
For example, your structured data might include the title of the article or content, the description, and other elements baked into a code (schema) that Google likes.
If you want to learn how to create structured data, or you’d like some examples to build off of, check out Google’s Codelabs for examples and an in-depth explanation.
Google even has a Structured Data Markup Helper if you’re struggling with figuring out how it all works.
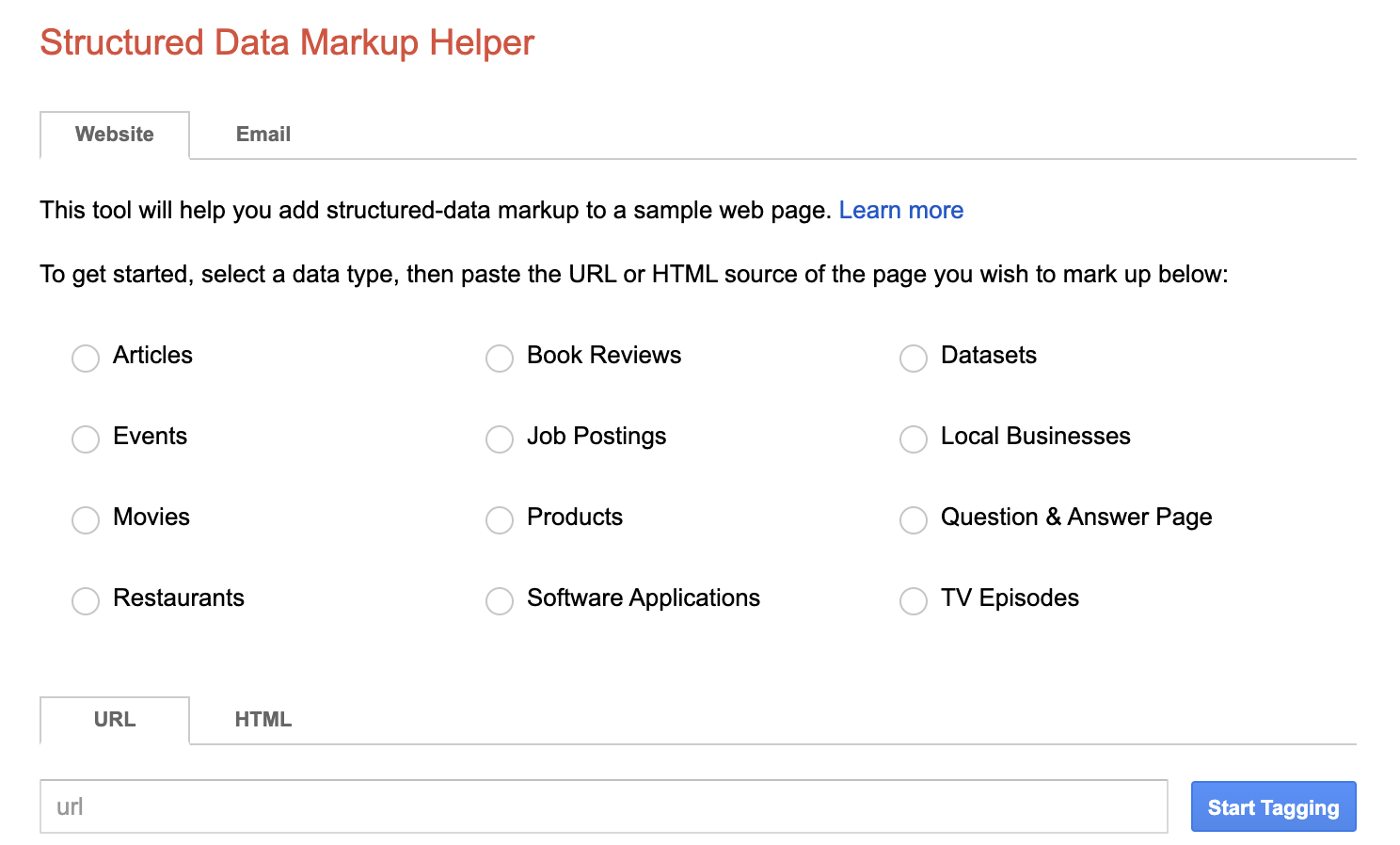 With Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper, you enter the URL you would like to begin tagging, along with a category that best describes the page. Here we have entered “veganshoes.com” and “Products” as examples. Image courtesy of Google.
With Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper, you enter the URL you would like to begin tagging, along with a category that best describes the page. Here we have entered “veganshoes.com” and “Products” as examples. Image courtesy of Google.The tool helps by walking you through building structured data to a sample web page. An example of the URL you entered will be rendered on the left. You tag items by clicking on them and providing context as to what that element of the page is about.
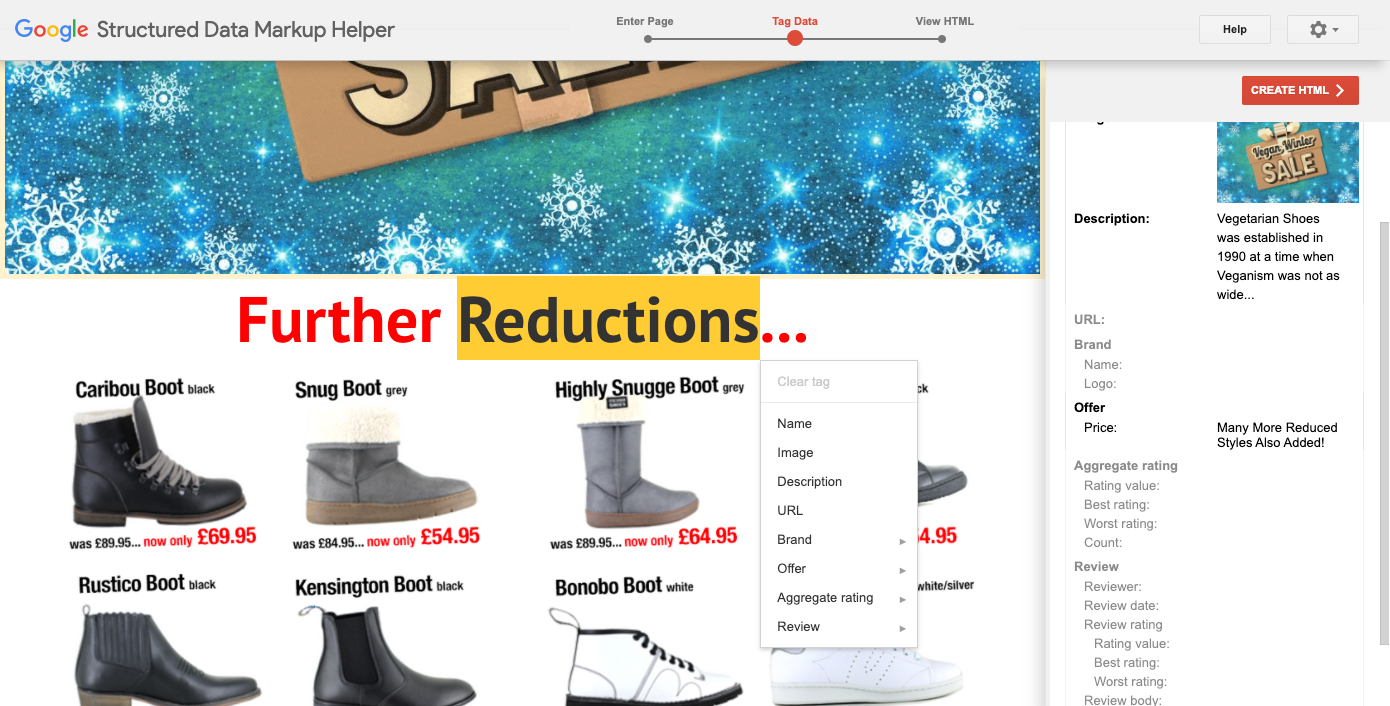 Here, we need to tag these shoes as “Offer” and then provide a price. Image courtesy of Google.
Here, we need to tag these shoes as “Offer” and then provide a price. Image courtesy of Google.Once you have tagged all of the page elements, Google will render the structured data for you.
 This is the structured data for our “veganshoes.com” example. Image courtesy of Google.
This is the structured data for our “veganshoes.com” example. Image courtesy of Google.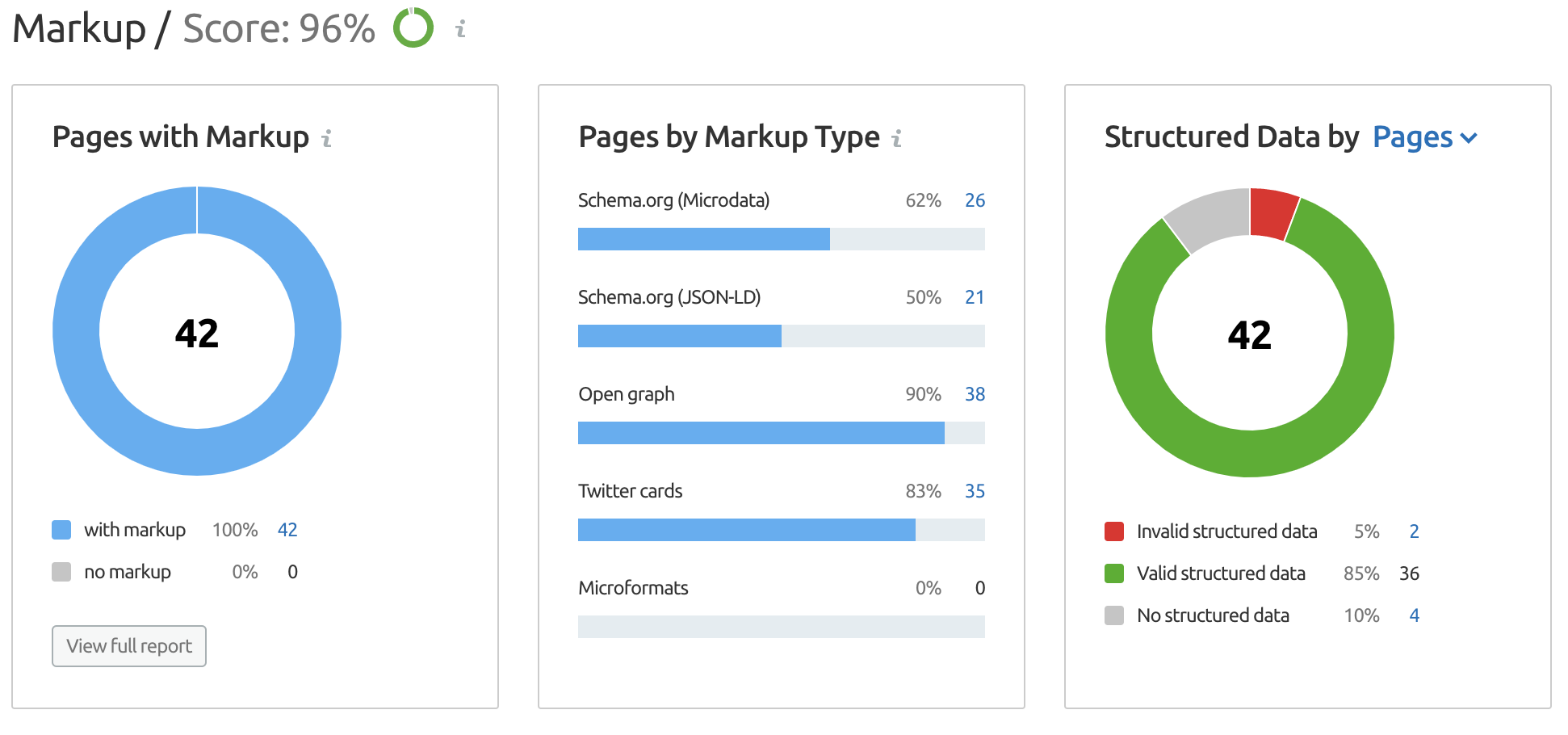
Another way to check on specific markup issues is to navigate to the Crawled Pages report on the main Site Audit page.
Filter for specific issues (Markup in the below example) and hover over the types listed underneath to see what type of markup the page has).
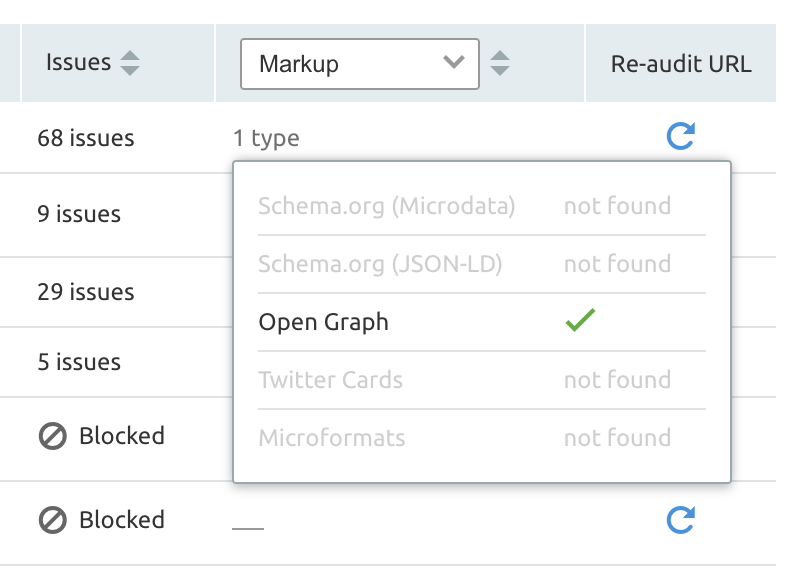
If there are any issues, Semrush will let you know which pages are causing the problem and how to fix them.
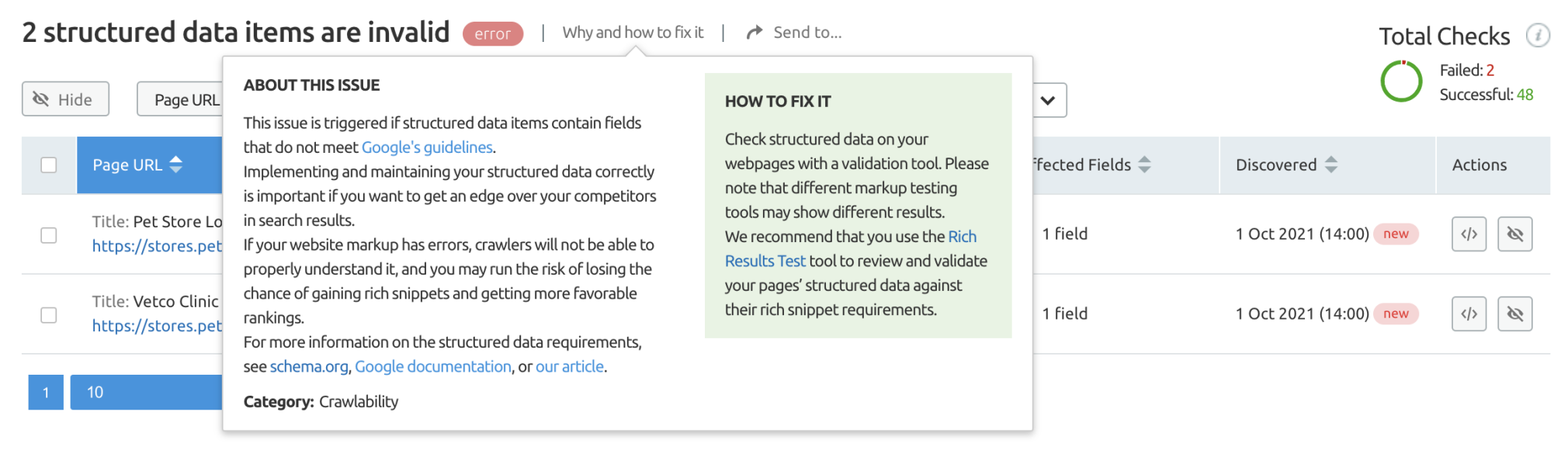
Page Speed
When the internet was in its early days, website pages were much easier for search engines to render. Programming was simplistic, and site elements were very bare bones.
Now, through the power of JavaScript and CSS, so many more things are possible for web developers. As web content becomes more rich and dynamic, page speed becomes a more critical factor in user experience (and in how well your content ranks in the SERPs).
Typically, the more JavaScript you have on your site (especially complex elements), the harder it is for that page to load. Because page speed is a ranking factor, you’ll want to make sure you pay close attention to how long it takes for content to load once a user requests it.
Core Web Vitals
One way to monitor how fast content is loading on your website is through our Site Audit tool’s Core Web Vitals metric.
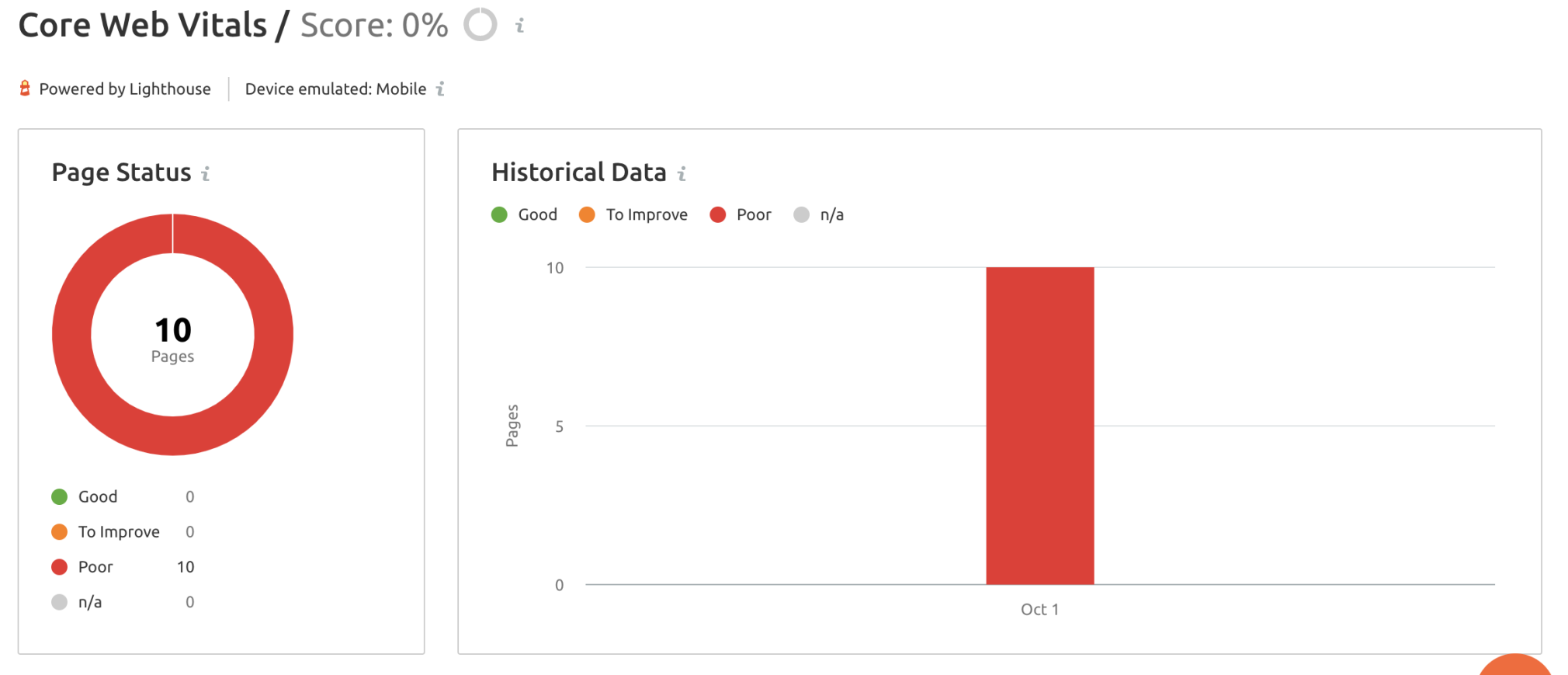
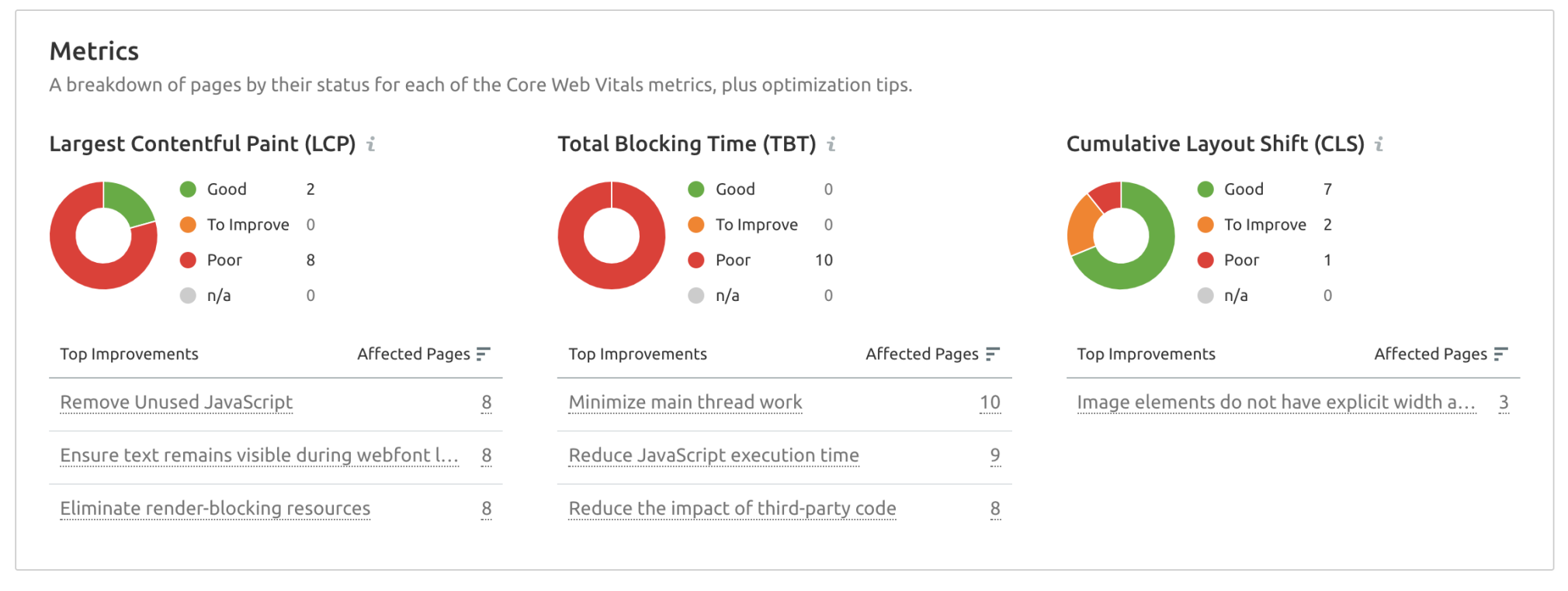
The Core Web Vitals are broken down into three main categories:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This defines the time it takes for the main portion of content on a web page to appear/load for users. First Input Delay (FID): FID measures a page’s response time when a user begins interacting with that page for the first time. This includes: clicking links, tapping buttons, and other custom JavaScript actions. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This is a measurement of the number of unexpected shifts in the page layout that impact the main content of a page.Google also provides these measurements through their Google Search Console Core Web Vitals Reports.
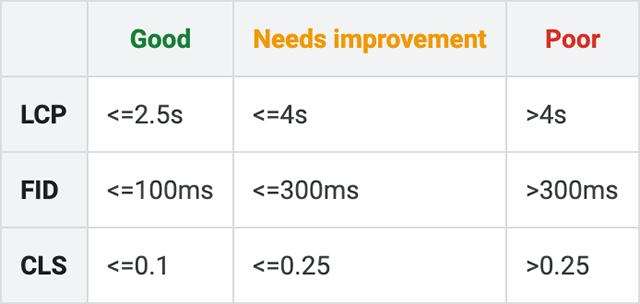 This is an example of a Google Core Web Vitals report. Image courtesy of Google.
This is an example of a Google Core Web Vitals report. Image courtesy of Google.Ideal Status Metrics for Core Web Vitals:
LCP: Under 2.5 seconds FID: Under 100 milliseconds CLS: Score of .1 or underUser-Friendly Sites
User-friendly sites are websites that optimize for the user experience first. This doesn’t mean you neglect or disregard what search engines require; it just means that you understand that people come first (Something even Google agrees with!).
There are several ways to have a user-friendly site, and we’ll talk about a few next.
Mobile-First Indexing
As the name suggests, Mobile-first indexing is when search engines (and therefore web developers) prioritize indexing mobile versions of sites for indexing.
This means that you should also consider putting a heavy emphasis on the experience and structure of your mobile site.
You can check if your site is on mobile-first indexing by going to the Google Search Console and reviewing the recent log of crawls to a recently added page to your site.
If you see “Googlebot smartphone” has crawled your page first, you know you’re all set. You might have already received a pop-up that your site has been switched over.
Accelerated Mobile Pages
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) is a type of open-source, HTML framework that Google has created in order to help web builders make web content friendly to mobile users.
This type of code allows you to prioritize mobile user experience first, which is something you should consider if you haven't already Mobile internet browsing has boomed in the last decade, with over 50 percent of web traffic coming from a mobile device.
So, you must build the kind of web content that is easily accessible from a mobile device or tablet. And, you might already have these types of pages on your website.
You can check by going to our Site Audit tool and navigating to the “Statistics” tab. From there, you can see how many of your web pages are AMP links.
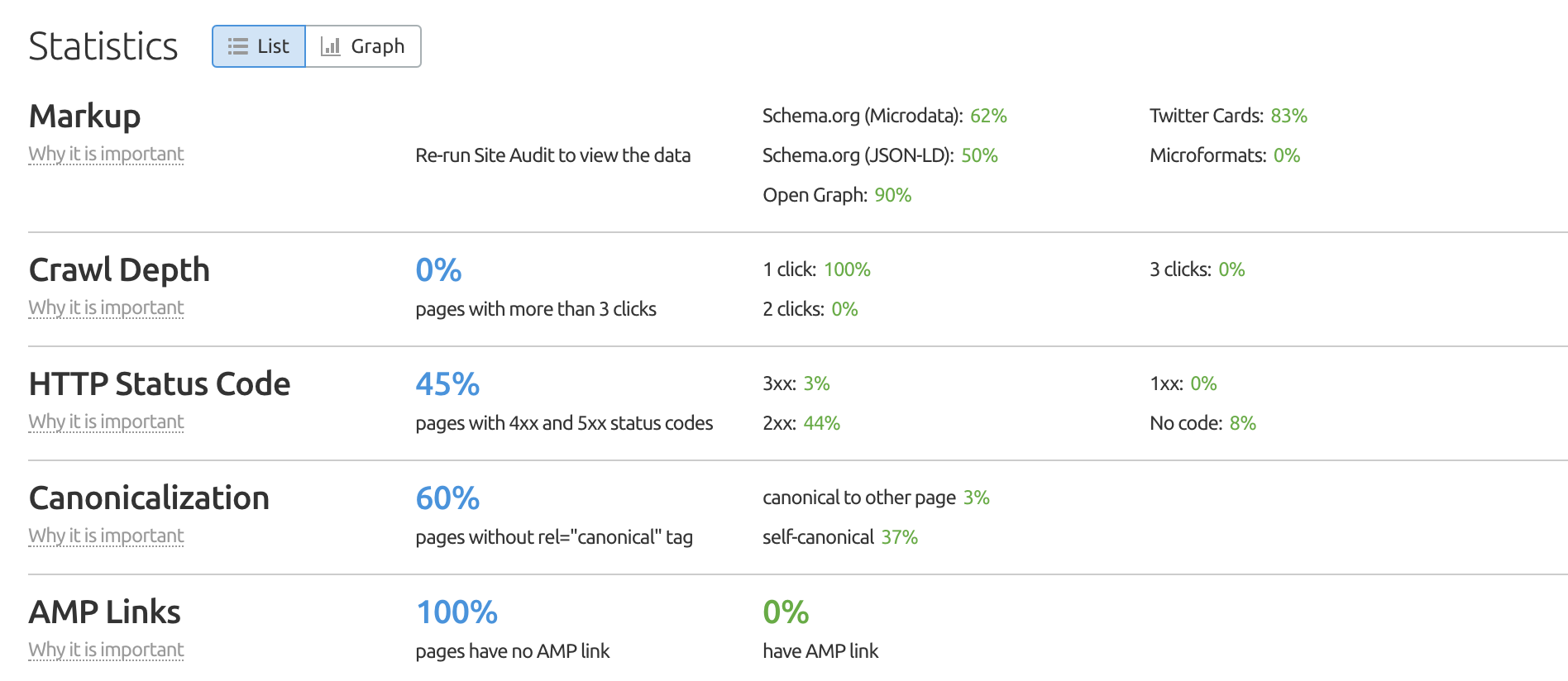 As you can see from this screenshot, this sample site has zero AMP links.
As you can see from this screenshot, this sample site has zero AMP links.Google is almost certainly giving preferential ranking to those who utilize this framework to build their web content. Google recognizes that most users will be coming from a mobile device, and therefore you’ll want to prioritize their type of experience.
Some other benefits of building web content with this open-source HTML framework known as AMP include:
AMP load almost instantaneously Much easier to build than other types of frameworks Loads of major platforms support AMP Developers can still implement CSS in AMP (though the code won’t be as complex) The groundwork components of AMP are already there — you just have to build on themThin/Duplicate Content
Two dangers web content developers can encounter are thin or duplicate content.
Thin content refers to blogs, articles, or web pages that don’t give Googlebot crawlers much to work with. Maybe there is no internal linking on the page to help direct crawlers to other parts of your site. It's also possible that the page's content doesn't correctly target users' search intent.
An example of thin content would be a service page that doesn’t link to any other page on your site and doesn’t actually talk about the services you offer. Instead, it references your employee names and extension numbers.
Duplicate content refers to blogs, articles, or web pages with identical copy somewhere else on your site. Don’t let the name fool you, though; near-identical content (like swapping out just the brand name for a product description) can also get swept up under the designation “duplicate content.”
An example of duplicate content might be that you have two pages devoted to dry dog food that don’t deviate from one another in language or page appearance.

Tips:
If you catch another website copying your content without credit, reach out to the webmaster to ask them to either accredit your work or remove it Use canonical tags (more on these in a second) on brand new content to identify that it is the original source of the informationCanonical Tags
You may have heard of canonical tags or have even seen canonical tags referred to as rel=”canonical.” If you aren’t familiar with the term, canonical tags are markers that indicate to search engines that the URL you specified is the original and true copy of a page.
Canonical tags appear in the <head></head> section of a page’s HTML code. They either refer back to a page’s URL (self-referencing), or they might even consolidate signals by referencing another page’s URL.
Tips:
Don’t canonicalize (or point) to a URL that has a 301-redirect (i.e., a page set to redirect to another page) Make sure the content you are canonicalizing to is relevant Use a tool like PageImprove to make make on-page changes to canonical tags and other elements directly from your browserHreflang
Let’s say you’ve built your site that’s ranking well in Google’s SERPs. You’re proud of the work you’ve done, and you would like for people who speak and read other languages to access your site and content. How do you go about that? With the Hreflang attribute/tag.
Hreflang is an HTML tag that notifies search engines of the language you are using on a specific page. This allows you to illustrate the relationship between web pages written in different languages.

This is especially important if you plan to target specific audiences by location. For example, let’s say you own a German business opening a service branch in France. You want to make sure that someone visiting your site from France can read all about your newest location.
The Hreflang tag “hreflang=fr” will tell Google that, should someone visit your site with an IP address that is likely originating from France, they should receive the French version of the page.
Hreflang improves not only the user experience but also accessibility. This is helpful for users, traffic, and business in general.
The Site Audit also includes an International SEO report that lets you know if your site has any hreflang issues.

Learn More About Technical SEO
We’ve highlighted a few individual checks and reports found in the Site Audit tool, but Site Audit checks for over 140 issues.
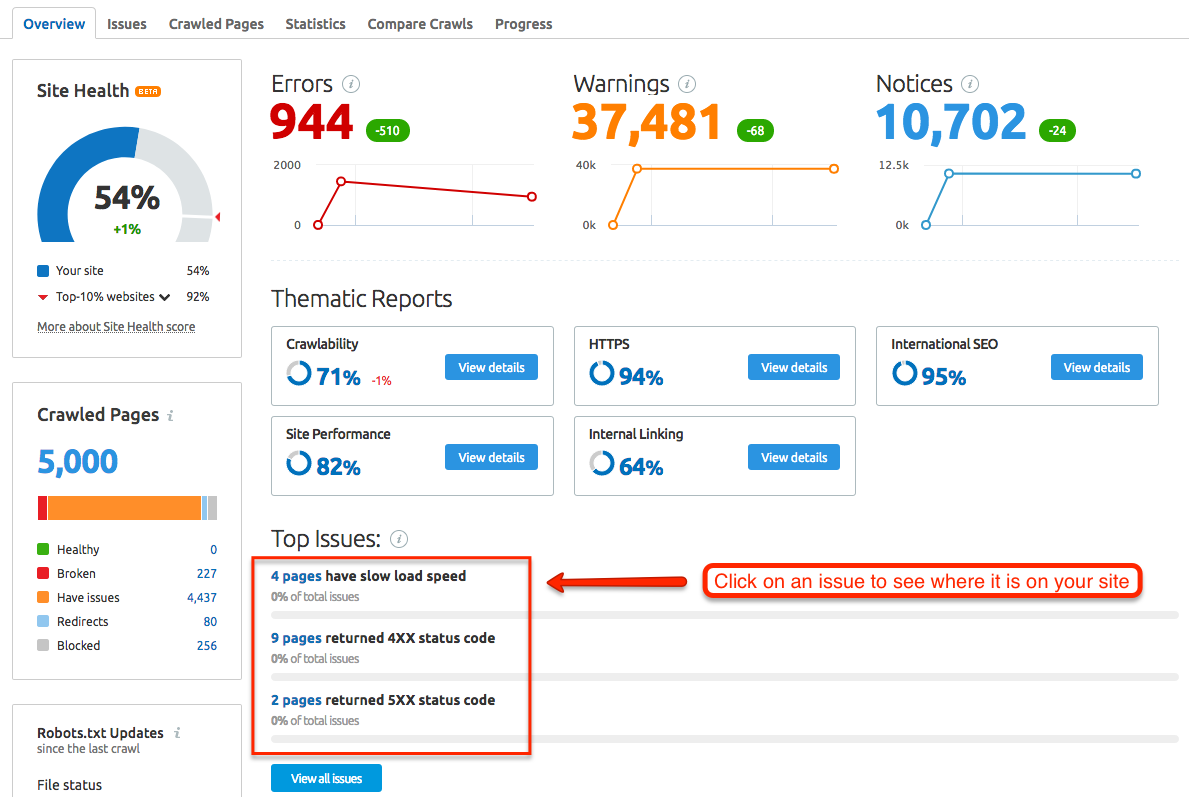
If you’re just getting started with tech SEO, you can audit 100 pages on a site once per month with a free account. This is a great way to familiarize yourself with potential technical SEO issues.
Final Thoughts
Technical SEO isn’t something you can master in a day or two—it requires lots of dedicated research and some trial and error.
However, there is good news; you don’t have to go it alone. Our Semrush Academy offers free courses and certifications in many different SEO elements, including technical SEO.
You can start chipping away at the technical side of SEO today, risk-free.
Innovative SEO services
SEO is a patience game; no secret there. We`ll work with you to develop a Search strategy focused on producing increased traffic rankings in as early as 3-months.
A proven Allinclusive. SEO services for measuring, executing, and optimizing for Search Engine success. We say what we do and do what we say.
Our company as Semrush Agency Partner has designed a search engine optimization service that is both ethical and result-driven. We use the latest tools, strategies, and trends to help you move up in the search engines for the right keywords to get noticed by the right audience.
Today, you can schedule a Discovery call with us about your company needs.
Source:





